Block B (of mass m) is initially at rest. Block A (of mass 3m) travels toward B with an initial speed v0 (vee nought) and collides in an inelastic collision. Given that all surfaces have negligible friction, determine the maximum height h reached by the
two blocks.

Answers
Answer:
The maximum height reached by the two blocks is approximately 0.1147959 × v₀²
Explanation:
The mass of block B = m
The mass of block A = 3·m
The initial velocity of block B, v₂ = 0 m/s
The initial velocity of block A, v₁ = v₀
The amount of friction between the blocks and the surface = Negligible friction
By the Law of conservation of linear momentum, we have;
Total initial momentum = Total final momentum
3·m·v₁ + m·v₂ = (3·m + m)·v₃ = 4·m·v₃
Plugging in the values for the velocities gives;
3·m × v₀ + m × 0 = (3·m + m)·v₃ = 4·m·v₃
∴ 3·m × v₀ = 4·m·v₃
\(\therefore v_3 = \dfrac{3}{4} \times v_0 = 0.75 \times v_0\)
The kinetic energy, K.E. of the combined blocks after the collision is given as follows;
K.E. = 1/2 × mass × v²
\(\therefore K.E. = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 4\cdot m \times \left (\dfrac{3}{4} \cdot v_0 \right )^2 = \dfrac{9}{8} \cdot m\cdot v_0^2\)
The potential energy, P.E., gained by the two blocks at maximum height = The kinetic energy, K.E., of the two blocks before moving vertically upwards
The potential energy, P.E. = m·g·h
Where;
m = The mass of the object at the given height
g = The acceleration due to gravity
h = The height at which the object of mass, 'm', is located
Therefore, for h = The maximum height reached by the two blocks, we have;
P.E. = K.E.
\(m \cdot g \cdot h = \dfrac{9}{8} \cdot m\cdot v_0^2\)
\(h = \dfrac{\dfrac{9}{8} \cdot m\cdot v_0^2}{m \cdot g } = \dfrac{9}{8} \cdot \dfrac{ v_0^2}{ g } = \dfrac{9}{8} \cdot \dfrac{ v_0^2}{ 9.8} = \dfrac{42}{392} \cdot v_0^2 \approx 0.1147959 \cdot v_0^2\)
The maximum height reached by the two blocks, h ≈ 0.1147959·v₀².
Related Questions
a reaction has a rate constant of 1.25×10−4 s−1 at 28 ∘c and 0.230 s−1 at 78 ∘c .A. Determine the activation barrier for the reaction. B. What is the value of the rate constant at 16∘C ?
Answers
A. The activation barrier for the reaction is the difference between the rate constants at the two temperatures, which is 1.02×10−3 s−1.
What is the temperatures?The temperature can vary greatly depending on the location. In general, temperatures can range from very hot to very cold. In tropical climates, temperatures can reach up to the mid-30s Celsius (mid-90s Fahrenheit). In colder climates, temperatures can dip down to below -30 Celsius (-22 Fahrenheit). Temperatures can also vary greatly depending on the season. In summer, temperatures can be much higher than in winter. In some areas, temperatures can also vary depending on altitude, with higher altitudes having cooler temperatures.
B. The value of the rate constant at 16∘C can be estimated using the Arrhenius equation, which is k = A e^(-Ea/RT), where A is the pre-exponential factor, Ea is the activation energy, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. Plugging in the values for the two known temperatures, we get A = 1.25×10−4 s−1 and Ea/R = (0.230-1.25×10−4)/(8.314*(78+273)) = 6806.4 K. We can then use the equation to compute the rate constant at 16∘C, which is 0.14×10−4 s−1.
To learn more about temperatures
https://brainly.com/question/30396993
#SPJ1
If the atomic mass of neon is 20 amu, how much neon would be needed to have an avogadro's number of neon atoms?
Answers
By Avogadro's number, the mass of Neon atom is 20 grams.
We need to know about Avogadro's number to solve this problem. Avogadro's number is the number that explains how many carbon atoms are in one mol. The Avogadro's number is
Na = 6,02 × 10²³ atoms / mol
From the question above, we know that
Mr = 20
N = 6,02 × 10²³ atoms
By using Avogadro's number, we can calculate how much Neon atoms
N = n . Na
6,02 × 10²³ = gr / Mr . 6,02 × 10²³
gr / 20 = 1
gr = 20 grams
Hence, the mass of Neon atom is 20 grams.
For more on Avogadro's number at: https://brainly.com/question/1581342
#SPJ4
state 1 pascal pressure
Answers
Answer:
1 pascal pressure is define as the one newton force is given which covers 1 square metre area
if the majority of the baseball’s kinetic energy comes from power generation in the legs and hips, approximately how much energy do the lower extremities produce in the pitch?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
140 J
The kinetic energy of the baseball can be calculated using the equation 1/2 mv2. Paragraph 2 tells us that the average velocity of the ball is 30 m/s and its mass is 150 g, which is equivalent to 0.15 kg.
KE = (½)(0.15 kg)(30 m/s)2
KE = (½)(0.15)(900)
KE = (0.15)(450) = 67.5 J
a particularly scary roller coaster contains a loop-the-loop in which the car and rider are completely upside down. if the radius of the loop is 13.2 m, with what minimum speed must the car traverse the loop so that the rider does not fall out while upside down at the top? assume the rider is not strapped to the car.
Answers
The minimum speed that the car must traverse the loop with is approximately 11.5 m/s. The formula for centripetal force is: F = m × a, where m is the mass of the object moving in a circle, and a is its acceleration.
This question relates to the concept of centripetal force, which is defined as the force acting on an object that travels in a circle, which acts towards the center of that circle. When a rider is at the top of the loop-the-loop, they are upside down, and the force of gravity acting on them is pulling them away from the coaster. Therefore, to prevent the rider from falling out of the coaster, the minimum centripetal force required must be equal to the force of gravity acting on the rider.
The formula for centripetal force is: F = m × a, where m is the mass of the object moving in a circle, and a is its acceleration, given by: v² / R, where v is the velocity of the object, and R is the radius of the circle.
Substituting the value of acceleration in the first formula: F = m × v² / RF
= m × g where g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s²).
We can solve for velocity using the above two equations:
v² / R = gv²
= R × gv
= √(R × g)
= √(13.2 × 9.81)v
≈ 11.5 m/s
Therefore, the minimum speed that the car must traverse the loop with is approximately 11.5 m/s.
To know more about minimum speed, refer
https://brainly.com/question/30506635
#SPJ11
How do the individual forces compare when the rider experiences a sensation being lighter than his normal weight ? What is the acceleration direction when this occurs ?
Answers
Answer:
When the elevator is accelerating downward, the person feels lighter due to the downward normal force being less than the person's weight.
Explanation:
A person riding in an elevator subjected to a series of unbalanced forces depending on the direction the elevator is travelling.
Two forces are acting on the person; the force of gravity and the upward normal force from the elevator.
When the elevator is going upwards with acceleration a, the person feels heavier than his normal weight, due to the upward normal force being greater than the person's weight. N = mg + ma
When the elevator is moving downwards with acceleration a, the person feels lighter due to the downward normal force being less than the person's weight. N = mg - ma
However, when the elevator is moving up or down at constant velocity ie. acceleration a = 0, the person experience a normal force equal to weight. N = mg
When the elevator is moving downwards with acceleration a = g, the person experiences weightlessness. N = (mg - mg) = 0
what's a formula of velocity?
Answers
\( \boxed{\boxed{ \rm \: Velocity = \dfrac{Displacement}{Time} }}\)
how is the internal energy of the particles in the brake pads affected by the increase in temperature?
Answers
Answer:
increasedExplanation:As the temperature is increased the more the energy store
why does deceleration lower force during a collision?
Answers
Two metal disks are welded together and are mounted on a frictionless axis through their common centers. One disk has a radius R1 = 2.60 cm and mass M1 = 0.810 kg and the other disk has a radius R2 = 5.00 cm and mass M2 = 1.58 kg . (Figure 1) A string of negligible mass is wrapped around the smaller disk, and a 1.50-kg block, is suspended from the free end of the string. The block is released from rest a distance of 2.10 m above the ground. What is the block's speed just before it hits the ground?
Answers
The Inertia is 22. 488 kg. m² and the speed just before it hits the ground is 6. 4 m/s
How to determine the inertia
Using the formula:
I = 1/2 M₁R₁² + 1/2 M₂R₂²
Where I = Inertia
I = 1/2 * 0.810* (2. 60)² + 1/2 * 1. 58 * (5)²
I = 1/2 * 5. 476 + 1/2 * 39. 5
I = 2. 738 + 19. 75
I = 22. 488 kg. m²
To determine the block's speed, use the formula
v = \(\sqrt{2gh}\)
v = \(\sqrt{2* 10 * 2. 10}\)
v = \(\sqrt{42}\)
v = 6. 4 m/s
Therefore, the Inertia is 22. 488 kg. m² and the speed just before it hits the ground is 6. 4 m/s
Learn more about law of inertia here:
https://brainly.com/question/10454047
#SPJ1
Newton's _______ law of motion states that "For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction." A. second B. fourth C. first D. third
Answers
Answer:
first
Explanation:
Newton's Newton's first law of motion states that for every action and there's an equal and opposite reaction
Answer:
D. Third
Explanation:
3. Which type of wires (copper, aluminum, or string) are ferromagnetic metals?
Answers
Copper isn't ferromagnetic,
Aluminum isn't ferromagnetic,
String has a ferromagnetic property
Answer:
i think its aluminum
Explanation:
3. Since Aspeon is not expected togrow, Emily believes that the following equations can be used in the valuation analysis: (1) S=[EBIT−kd(D)](1−ks)
(2) V=S+D
(3) P=(V−D0)/n0
(4) n1=n0−D/P
(5) VL=VU+TD
Answers
The equations mentioned by Emily in the valuation analysis for Aspeon are as follows:
1) Equation (1): This equation represents the value of equity (S) and calculates it based on the EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes), the tax shield provided by debt (D), and the required return on debt (kd) and equity (ks). It implies that the value of equity is equal to the adjusted EBIT after deducting the tax shield from debt.
2) Equation (2): This equation calculates the total enterprise value (V) by adding the value of equity (S) and debt (D). It represents the total worth of the company, considering both equity and debt.
3) Equation (3): This equation calculates the price per share (P) by dividing the total enterprise value (V) minus the initial debt (D0) by the number of shares (n0). It represents the price per share based on the valuation of the company.
4) Equation (4): This equation calculates the new number of shares (n1) by subtracting the dividend (D) from the initial number of shares (n0) divided by the price per share (P). It represents the adjusted number of shares after the payment of dividends.
5) Equation (5): This equation calculates the levered value (VL) by adding the unlevered value (VU) with the tax shield value (TD). It represents the value of the company after considering the tax advantages of debt.
These equations provide a framework for valuation analysis, considering factors such as earnings, taxes, debt, and equity. They help assess the value and financial implications of Aspeon's growth prospects.
To know more about EBIT ,
https://brainly.com/question/31852554?referrer=searchResults
#SPJ11
How can we drop eggs the fewest amount of times without breaking it?
Answers
Answer:
drop in water
Explanation:
follow me m mm m
As insulators, dielecctrics are expected to prevent the passage of current through them. Their main funtion is to temporarily store harges for future use, which is definitely an advantage or a good thing. Likewise, when was the last time you did a good thing for the people arund you? Think of an unexpected at of goodwill, generosity, or kindness
Answers
The Dielectrics are indeed very useful as insulators and their ability to store charges for future use is highly beneficial in many applications. However, as an AI language model, I do not have personal experiences or emotions like humans do. Therefore, I cannot provide you with a specific example of a recent act of kindness or generosity.
The Nevertheless, I can encourage you to think about the positive impact that such actions can have on the people around you. Acts of goodwill and kindness can range from small gestures like holding the door open for someone or giving a compliment, to larger actions like volunteering or donating to a charitable cause. Being kind and generous not only benefits those around us, but it can also have positive effects on our own well-being and mental health. Research has shown that acts of kindness can release feel-good hormones like oxytocin, which can reduce stress and improve mood. In conclusion, while dielectrics serve a practical purpose in insulating and storing charges, it is important to also remember the value of kindness and generosity in our daily lives. By making small gestures of goodwill towards others, we can all contribute to a more positive and compassionate society.
learn more about dielectrics here.
https://brainly.com/question/29357753
#SPJ11
this refers to the process of manufacturing that introduced powered machinery to the production of goods
Answers
Integrated Concepts Space debris left from old satellites and their launchers is becoming a hazard to other satellites. (a) Calculate the speed of a satellite in an orbit 900 km above Earth's surface. (b) Suppose a loose rivet is in an orbit of the same radius that intersects the satellite's orbit at an angle of 90° relative to Earth. What is the velocity of the rivet relative to the satellite just before striking it? (c) Given the rivet is 3.00 mm in size, how long will its collision with the satellite last? (d) If its mass is 0.500 g, what is the average force it exerts on the satellite? (e) How much energy in joules is generated by the collision? (The satellite's velocity does not change appreciably, because its mass is much greater than the rivet's.)
Answers
Velocity of the satellite that is orbiting earth is 83.45m/s, which makes the velocity of the rivet relative before striking also 83.45m/s and the time duration of collision is 4.53× 10⁻⁵ s. The avg force that is exerted by the rivet on the satellite is 9.27N and the energy that is generated by the collision is 1.63J.
a) Velocity of the satellite in an orbit 900 km above Earth's surface can be calculated as follows: Formula: `v = sqrt(GM/r)` Where,v = velocity, M = Mass of Earth, r = radius of the orbit (r = R + h)R = radius of the Earth = 6.37 × 10⁶ mh = height above Earth's surface = 900 km = 9 × 10⁵ mG = 6.67 × 10⁻¹¹ N m²/kg²By substituting the given values, we getv = sqrt((6.67 × 10⁻¹¹ × 5.97 × 10²⁴)/(6.37 × 10⁶ + 9 × 10⁵))= sqrt(6.965 × 10³) = 83.45 m/s.
Therefore, the velocity of the satellite in an orbit 900 km above Earth's surface is 83.45 m/s.
b) Velocity of the rivet relative to the satellite just before striking it can be calculated as follows: Velocity of the rivet, `v_rivet = v_satellite * sin(θ)`Where, v_satellite = 83.45 m/sθ = 90°By substituting the given values, we getv_rivet = 83.45 * sin 90°= 83.45 m/s.
Therefore, the velocity of the rivet relative to the satellite just before striking it is 83.45 m/s.
c) The time duration of collision, `Δt` can be calculated as follows:Δt = (2 * r_rivet)/v_rivet, Where,r_rivet = radius of the rivet = 3/2 × 10⁻³ m. By substituting the given values, we getΔt = (2 * 3/2 × 10⁻³)/83.45= 4.53 × 10⁻⁵ s.
Therefore, the time duration of collision is 4.53 × 10⁻⁵ s.
d) The average force exerted by the rivet on the satellite, `F` can be calculated as follows: F = m_rivet * Δv/ΔtWhere,m_rivet = mass of the rivet = 0.5 g = 0.5 × 10⁻³ kgΔv = change in velocity of the rivet = 83.45 m/sΔt = time duration of collision = 4.53 × 10⁻⁵ sBy substituting the given values, we get F = (0.5 × 10⁻³ * 83.45)/4.53 × 10⁻⁵= 9.27 N.
Therefore, the average force exerted by the rivet on the satellite is 9.27 N.
e) The energy generated by the collision, `E` can be calculated as follows: E = (1/2) * m_rivet * Δv²Where,m_rivet = mass of the rivet = 0.5 g = 0.5 × 10⁻³ kgΔv = change in velocity of the rivet = 83.45 m/s. By substituting the given values, we getE = (1/2) * 0.5 × 10⁻³ * 83.45²= 1.63 J.
Therefore, the energy generated by the collision is 1.63 J.
Learn more about satellites:
https://brainly.com/question/13017835
#SPJ11
how do initial velocity and final velocity differ
Answers
An astronaut travels to a distant star with a speed of 0.56 c relative to Earth. From the astronaut's point of view, the star is 7.6 ly from Earth. On the return trip, the astronaut travels with a speed of 0.88 c relative to Earth.
What is the distance covered on the return trip, as measured by the astronaut? Give your answer in light-years.
L=___lightyear
Answers
An astronaut travels to a distant star with a speed of 0.56 c relative to Earth and from the astronaut's point of view, the star is 7.6 ly from Earth. On the return trip, the astronaut travels with a speed of 0.88 c relative to Earth.
To explain, "c" represents the speed of light and is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second. The distance between two objects is measured in light-years (L) which is the distance that light travels in a year.
In this scenario, the astronaut is traveling at 0.56 times the speed of light, which is incredibly fast. From their point of view, the star is 7.6 light-years away from Earth. On the return trip, they travel even faster at 0.88 times the speed of light relative to Earth.
It's important to note that time dilation occurs at these speeds, meaning that time will appear to move slower for the astronaut than it does for people on Earth. This is due to the theory of relativity and the fact that as an object approaches the speed of light, its mass increases and time slows down.
To know more about speed of light refer to
https://brainly.com/question/29216893
#SPJ11
A plane electromagnetic wave of intensity 6.00W/m² , moving in the x direction, strikes a small perfectly reflecting pocket mirror, of area 40.0cm², held in the y z plane.(c) Explain the relationship between the answers to parts (a) and (b).
Answers
The intensity of the reflected wave is equal to the intensity of the incident wave. This relationship holds true when a plane electromagnetic wave strikes a perfectly reflecting pocket mirror.
When an electromagnetic wave strikes a perfectly reflecting surface, such as a pocket mirror, the reflected wave has the same intensity as the incident wave. In part (a), the intensity of the incident wave is given as 6.00 W/m². This represents the power per unit area carried by the wave.
In part (b), the mirror has an area of 40.0 cm². To determine the intensity of the reflected wave, we need to calculate the power reflected by the mirror and divide it by the mirror's area. Since the mirror is perfectly reflecting, it reflects all the incident power.
The power reflected by the mirror can be calculated by multiplying the incident power (intensity) by the mirror's area. Converting the mirror's area to square meters (40.0 cm² = 0.004 m²) and multiplying it by the incident intensity (6.00 W/m²), we find that the reflected power is 0.024 W.
Dividing the reflected power by the mirror's area (0.024 W / 0.004 m²), we obtain an intensity of 6.00 W/m² for the reflected wave. This result confirms that the intensity of the reflected wave is equal to the intensity of the incident wave.
Learn more about electromagnetic wave
brainly.com/question/29774932
#SPJ11
1. What is the new kinetic energy of the 1900kg ship on the right moving at 4 m/s?
2. If the 0.10kg baseball on the right has a kinetic energy of 5 J, what is its velocity?
3. if the mosquito on the right is moving at 10 m/s anx has the the kinetic energy of 0.25 J, what is its mass?

Answers
Explanation:
That`s is the answer, just check
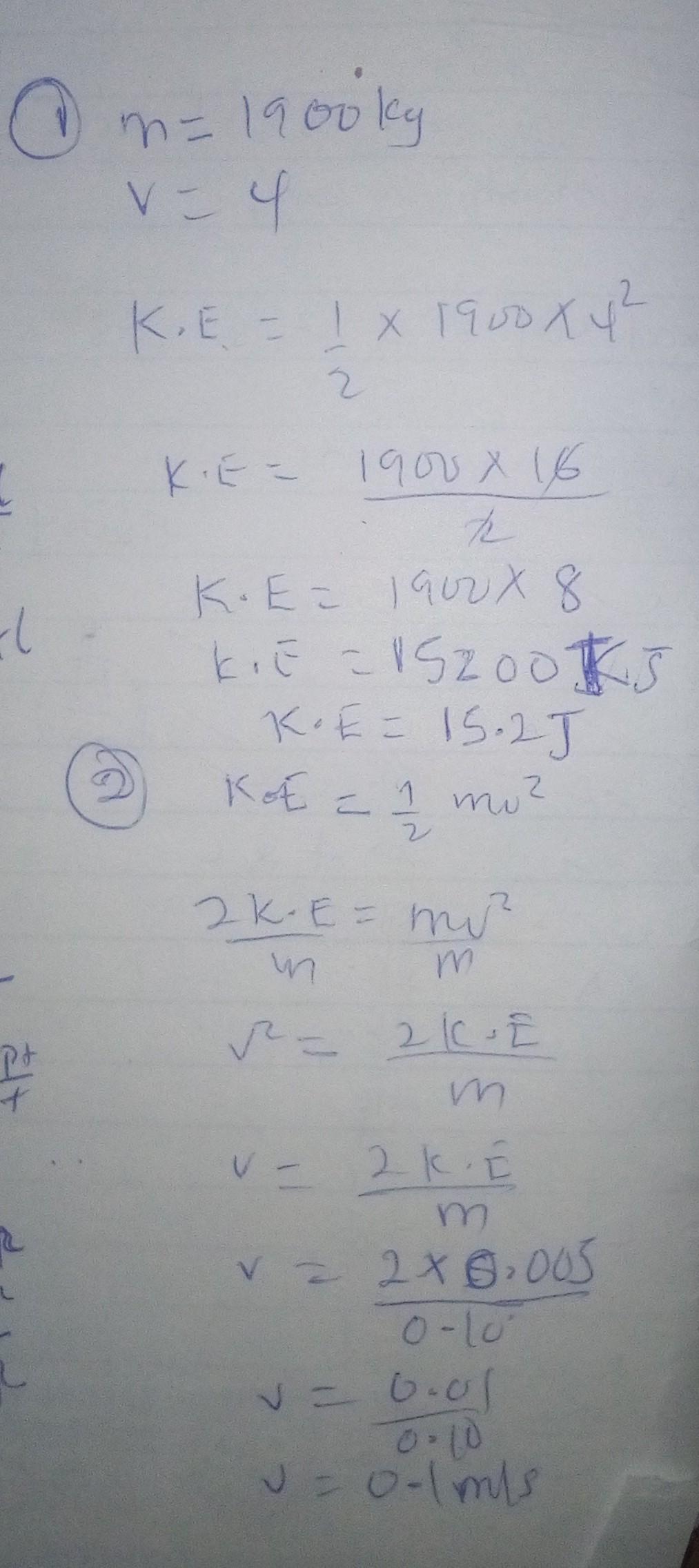

is newton third law accurate for electric forces?
Answers
An object with greater charge will exert a greater force on an object than an object with smaller charge would. However, if you consider two charges that exert a force on each other, regardless of the magnitude of charge, both charges will exert an equal force on each other because of Newton's third law.
name six kinds of simple machines.
Answers
Answer:
the wheel and axle, the lever, the inclined plane, the pulley, the screw, and the wedge
Explanation:
A bus start from rest and then moves with a constant acceleration of 2m/s square. calculate its time of traven if its final velocity is 20 m/s
Answers
Answer:
Its Answer is 10 s.
Explanation:
As acceleration is defined as time rate of change of velocity. So,
a = \(( vf - vi )\) ÷ t
2 = (20 - 0 ) ÷ t
2 = 20 ÷ t
t = 20 ÷ 2
t = 10 s
We have put initial velocity as zero because body is starting from rest.
Hope it helps.
Newton's Law of Cooling states that the rate of change of the temperature of an object, T, is proportional to the difference of T and the temperature of its surrounding environment. A pot of chili with temperature 21°C is placed into a -16°C freezer. After 2 hours, the temperature of the chili is 5°C. Part A: Assuming the temperature T of the chili follows Newton's Law of Cooling, write a differential equation for T. (10 points) Part B: What is the temperature of the chili after 4 hours? (20 points) Part C: At what time, t, will the chili's temperature be -12°C? (10 points)
Answers
Part A: Differential equation of temperature Assuming the temperature T of the chili follows Newton's Law of Cooling, we know that the rate of change of the temperature of an object, T, is proportional to the difference between T and the temperature of its surrounding environment, and can be represented by this equation:
dT/dt = k(T - Ts)
where k is the cooling coefficient and Ts is the temperature of the surrounding environment.
Part B: Temperature of the chili after 4 hours to find the temperature of the chili after 4 hours, we need to use the following equation:
T(t) = Ts + (T0 - Ts)e^(-kt)
where T0 is the initial temperature of the chili and t is the time in hours.
We know that T0 = 21°C, Ts = -16°C, and T(2) = 5°C.
Substituting these values into the equation, we get:
5 = -16 + (21 + 16)e^(-k * 2)37 = 37e^(-2k)e^2k = 1/2k = ln(1/2)/(-2)k ≈ 0.3466
Substituting k into the equation and solving for T(4), we get:
T(4) = -16 + (21 + 16)e^(-0.3466 * 4)T(4) ≈ -9.80°C
Therefore, the temperature of the chili after 4 hours is approximately -9.80°C.
Part C: The time at which the chili's temperature will be -12°C
We need to solve the equation T(t) = -12 for t:
T(t) = Ts + (T0 - Ts)e^(-kt)-12
= -16 + (21 + 16)e^(-0.3466t)4
= 37e^(-0.3466t)e^0.3466t
= 37/4t = ln(37/4)/0.3466t ≈ 7.14
Therefore, the chili's temperature will be -12°C after approximately 7.14 hours.
To know more about Newton's Law of Cooling visit:
https://brainly.com/question/30591664
#SPJ11
which of the following is a subsurface event takes place during the rock cycle
deposition
erosion
weathering
plate tectonics
Answers
Answer:
The answer is A. Cementing...
Explanation:
hope this helps
Answer:
plate tectonics
Explanation:
brainliest also 100% flvs
10 A ship is made of 4000 m' steel of density
7900 kgm^3
a. What volume of fresh water
1000 kg m) would the ship need to
displace in order for it to float?
b. Explain how the design of the ship enables
it to displace this much water.
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
mass of ship = volume x density
= 4000 x 7900 = 316 x 10⁵ kg
The ship must displace water equal to weight of ship that is 316 x 10⁵ kg .
If volume of displaced water be V .
V x 10³ is mass of displaced water
V x 10³ = 316 x 10⁵
V = 31600 m³.
b ) Now the volume of steel making ship is only 4000 m³ so if it is in the form of a lump , it will displace only water equal to its volume ie 4000 m³ . So in order that it may displace water equal to volume 31600 m³ , it must be given shape so that it is hollow .
the stars in elliptical galaxies generally move either 1) in irregular orbits in all directions or 2) together in a particular direction as they orbit. what is the general motion for the stars in an elliptical galaxy?
Answers
Stellar orbits in elliptical galaxies are random, as opposed to spiral galaxies, where all of the stars orbit the galaxy's core in the same way.
What direction do stars in elliptical galaxies migrate in?Stellar orbits in elliptical galaxies are random, as opposed to spiral galaxies, where all of the stars orbit the galaxy's core in the same way.The majority of elliptical galaxies' star motions are currently thought to be fundamentally random; the size of the anisotropy of the stellar motions, or how much random velocities vary in different directions, determines the form of these galaxies.Ellipsoidal galaxies are round or oval in shape, as their name suggests, and contain stars that are widely spaced out.To learn more about Elliptical galaxies refer to:
https://brainly.com/question/24985948
#SPJ4
what is the 2nd minimum thickness of film required? assume that the wavelength of the light in air is 470 nanometers.
Answers
The second-order minimum thickness of the film required is 1.41 μm.
The minimum thickness required for a thin film to reflect a given color is half the wavelength of the light in the film material. For a second-order minimum thickness, the formula is given by;
t2=2nλwhere t2 represents the second-order minimum thickness of the film, n is the refractive index of the film material, and λ is the wavelength of the light in air.
If the wavelength of the light in air is 470 nm, then the second-order minimum thickness of the film required is given by;t2=2nλ= 2 × 1.5 × 470 nm = 1410 nm = 1.41 μm.
The second-order minimum thickness of the film required is 1.41 μm.
To know more about wavelength visit:
brainly.com/question/31143857
#SPJ11
a driver is going at 120km h and sees a barrier 60.0 m ahead it takes 5secounds to apply the brakes and decelerates at 12m does the driver hot the barrier
Answers
Answer:
yes, if you're going at 120 km and you saw the wall that late then it wouldn't me possible to decrease 12 meters in 5 seconds and not hit the wall that's only 60 meters away
Explanation: