Answers
The reasonable ground-state electron configuration would be \(1S^2,2S^2,2P^6\)
Electron configurationAccording to the rules of electron configurations, lower energy level orbitals are filled before higher energy level orbitals.
Thus, the order of filling orbitals according to their energy levels would be: 1S, 2S, 2P, 3S, 3P. etc.
Also, there is a need to be conversant with the number of electrons each orbital can take. S can only take 2, and P can take a maximum of 6 electrons.
Thus, the only reasonable electron configuration would be \(1S^2,2S^2,2P^6\)
More on electron configurations can be found here: https://brainly.com/question/14283892
#SPJ1
Related Questions
Concentration data is commonly monitored during a reaction to determine the order with respect to a reactant. Consider the types of observations listed, and determine which order is likely for that reactant. Assume all other factors are held constant. The reaction rate increases in direct proportion to the concentration of the reactant in solution.
1. An increase in the concentration of the reactant in solution causes the reaction rate to increase exponentially.
a. first order.
b. second order.
c. zero order.
2. The reaction rate is constant regardless of the amount of reactant in solution.
a. first order.
b. second order.
c. zero order.
3. The reaction rate increases in direct proportion to the concentration of the reactant in solution.
a. first order.
b. second order.
c. zero order.
Answers
Answer:
1) first order
2) zero order
3) second order
Explanation:
For a first order reaction, the concentration of the reactants varies exponentially with the rate of reaction. The curve of a first order reaction shows an exponential relationship between the rate of reaction and the change in the concentration of reactants.
For a zero order reaction, the rate of reaction is independent of the concentration of the reactants. So, regardless of the amount of reactant in solution, the rate of reaction is constant.
For a second reaction, the reaction rate increases in direct proportion to the concentration of the reactant in solution.
The measure of the length of events and the duration of intervals between events
Answers
The measure of the length of events and the duration of intervals between events is time.
What is time?The duration of events or the gaps between them can be measured, compared, or even ordered using time. The lengthy period of time that the Earth's geologic history takes up is known as geologic time. Starting at the beginning of the Archean Eon formal geologic time runs until the present. Geology is defined as the "Science of the Earth."
Geology is the fundamental Earth science that examines how the earth created, its structure and composition, and the various forces acting on it. It is sometimes known as geoscience or earth science.
Learn more about time at;
https://brainly.com/question/479532
#SPJ1
What practices from the article can members of the public or governmental agencies adopt as they look to improve water quality? Back up your answer with evidence from the article above.
Answers
The evidence from the article highlights these practices as effective means of improving water quality. By implementing these measures, both individuals and governmental agencies can contribute to the preservation and protection of water resources.
According to the article, there are several practices that members of the public and governmental agencies can adopt to improve water quality:
Implementing proper wastewater management: This involves treating wastewater before it is released back into the environment. The article emphasizes the importance of implementing advanced treatment technologies to remove pollutants effectively.Promoting sustainable agriculture: The article highlights the significance of adopting practices that minimize the use of fertilizers and pesticides, such as precision agriculture techniques. These practices can reduce the runoff of agricultural chemicals into water bodies.Establishing buffer zones: Creating vegetated buffer zones along rivers, lakes, and streams can help filter and absorb pollutants, preventing them from entering the water bodies. The article suggests that buffer zones should be implemented to reduce sediment, nutrient, and pesticide runoff from adjacent fields.Encouraging responsible industrial practices: The article emphasizes the need for industries to adopt eco-friendly practices, including proper disposal of industrial waste and the use of environmentally friendly production techniques.
Raising awareness and education: Public education campaigns can play a crucial role in improving water quality. The article suggests that educating the public about the impact of their actions on water bodies and providing information on sustainable practices can lead to positive changes.
for such more questions on practices
https://brainly.com/question/30310637
#SPJ8
HELP ASAP!! 5 MINS MAX- The diagram below shows the branching tree diagram for humans. The text box below it shows the set of derived shared characteristics for the branching tree.
A slanting, horizontal line is shown. On the extreme left, there is a label that says Common Ancestor. Along the slanting, horizontal line there are five dots labeled from left to right as 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. There is one vertical line between each of the consecutive five dots. The lines are labeled from left to right as Perch, Frog, Pigeon, Rats, and Human. A text box below the branching tree diagram is labeled Derived Shared Characteristics. In the box it says from left to right, Terrestrial during all stages, Jaws, Walking on two legs, Mammary glands and hair, and Four limbs.
Look at the possible derived shared characteristics, shown in the text box. Think about where these should be placed along the branching tree diagram. Where in the branching tree would you most likely write jaws? Explain your answer.
Answers
Jaws would most likely be written between dot 1 and dot 2 on the branching tree diagram. This is because the derived shared characteristic of jaws would have evolved after the common ancestor and before the perch, frog, pigeon, and other species evolved. Since jaws are not present in the common ancestor, but are present in species such as perch and frog, it is most likely that jaws evolved after the common ancestor and before the perch and frog split from the branching tree.
The formula for ammonia is NH3. How many moles are in 0.75 g of ammonia?
Answers
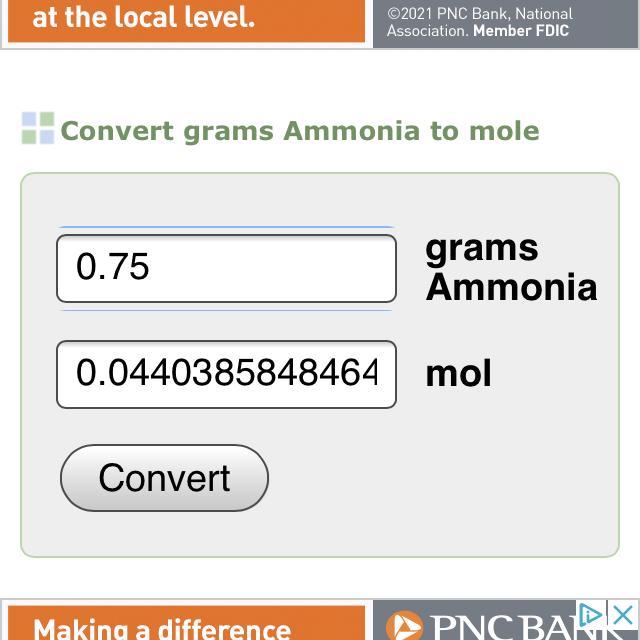
The number of moles that are present in 0.75 g of ammonia is 0.04 moles.
What is the relation between mass & moles?Relation between the mass and moles of any substance will be represented as:
n = W/M, where
W = given mass = 0.75gM = molar mass = 17g/molOn putting all these values, we can calculate the moles of ammonia as:
n = 0.75g / 17g/mol = 0.04 mole
Hence required moles of ammonia is 0.04 moles.
To know more about moles, visit the below link:
https://brainly.com/question/1034638
#SPJ2
Ibuprofen can be found in 800 mg doses in over-the-counter analgesics, such as Advil and Motrin. How many grams of iburofen
does such a tablet contain?
800 mg =
g
Answers
The grams of iburofen does such a tablet contain 800 mg = 0.8g Ibuprofen
1 g = 10^-3g = .001g
Ibuprofen has 800 mg doses in over-the-counter analgesic
800g = 800 × .001
= 0.8g
Ibuprofen is Nondteriodal Anti-inflammatory Drug (NSAID)Ibuprofen's Mechanism of Action is Decreases inflammation, pain, and fever through inhibition of cyclooxygenase activity and prostaglandin synthesisnonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication (NSAID) used for pain relief and to reduce fever by stops inflammation and by blocking formation of cyclo-oxygenase (COX-2) a chemical mediator of inflammatory chemicals. i.e prostaglandinsIt comes under the Class analgesic (reduce pain) and antipyretic (FIRE - reduce fever)e side effects of ibuprofen NSAID are peripheral edema, fluid retention with edema, tinnitus, purpura, petechiae, anorexia, diarrhea, rash, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, dizziness, lightheadedness, anxiety, confusionTo know more about analgesic visit :
https://brainly.com/question/2189504
#SPJ9
Please help, its due today! I'll also make you brainiest (put them in an order that's simple, look at the picture and you'll see what I mean) Thank you and God bless! <33
On beaches there are often areas of grassy dunes where people are prohibited from walking. How do these protected areas preserve ecosystem services? Use the graphic organizer to categorize the following as either examples of land reclamation of protecting biodiversity.

Answers
Answer:
Preventing erosion – Land Reclamation
Protecting nesting areas – Protecting Biodiversity
Preventing littering – Land Reclamation
Preventing habitat disruption – Protecting Biodiversity
Protecting native species – Protecting Biodiversity
Preventing contamination of soil – Land Reclamation
Explanation:
I really hope I'm right! I tried my hardest, please give me brainliest :)
have a good day!
‼️‼️‼️need help asap‼️‼️‼️

Answers
24. To calculate the molarity of a solution, we must first find out how many moles of \(BaI_2\) are in the solution.
Molar mass of BaI2 = (1 x atomic mass of Ba) + (2 x atomic mass of I)
= (1 x 137.33 g/mol) + (2 x 126.90 g/mol)
= 137.33 g/mol + 253.80 g/mol
= 391.13 g/mol
Number of moles of BaI2 = mass of BaI2 / molar mass of BaI2
= 413 g / 391.13 g/mol
= 1.056 mol
the molarity of the solution using the formula:
Molarity (M) = moles of solute / volume of solution (in liters)
Volume of solution = 750 ml = 750 ml / 1000 ml/L = 0.750 L
Molarity = 1.056 mol / 0.750 L
= 1.408 M
Therefore, the molarity of the solution is 1.408 M.
25. a. \(P_20_7\) - Ionic compound (Phosphorus(V) oxide)
b. \(SnBr_2\) - Ionic compound (Tin(II) bromide)
c. \(Fe(OH)_2\)- Ionic compound (Iron(II) hydroxide)
d. \(Cl_30_8\) - Not a valid chemical formula
26.
A. (NH4)2CO3 is soluble in water (NH4) in an ionic substance called 2CO3 containing the ions carbonate and ammonium.
B. Fe(OH)2 is insoluble in water. Iron(II) hydroxide is only sparingly soluble.
C. CaOH is not soluble in water. Only very little calcium hydroxide is soluble.
D. PbCl2 is insoluble in water. The chloride of lead(II) is sparingly soluble.
27. FeS + 2KCl = FeCl2 + K2S
FeS is an insoluble precipitate.
2KCl dissolves in aqueous solution.
ZnCl2 + SrSO4 = ZnSO4 + SrCl2
SrSO4 is an insoluble precipitate.
ZnCl2 dissolves in aqueous solution.
28. In salt water, the solute is the salt (sodium chloride, or NaCl), and the solvent is water. The element which dissolves in the solvent to form a solution is called solute.
29. Charles's law states that, if the pressure and volume of a gas remain constant, the volume of a gas falls as the temperature increases. As a result, the capacity of the balloon will decrease as it ascends to altitudes where the temperature is -15 °C.
30. The average kinetic energy of the particles of a substance increases with increase in its temperature. This is because temperature is a gauge for the specific kinetic energy of the constituent particles of a substance. On the other hand, the average kinetic energy falls as the temperature increases.
31. When the volume of a gas decreases, its pressure increases. Boyle's law, which states that at a given temperature, the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume, describes this relationship. On the other hand, pressure falls when volume increases.
32. The pressure of a gas increases along with its temperature. Gay–Lussac's law, which states that the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature, given the volume and volume of the gas is constant, describes this relationship.
33. The volume of a syringe is reduced as a marshmallow is pressed and the plunger is depressed. As a result the pressure inside the syringe increases. This is because Boyle's law states that the volume and pressure of a gas are inversely proportional. The decrease in volume causes the air inside the syringe to contract, exerting more pressure on the marshmallow, which is then crushed.
Learn more about Charles's law, here:
https://brainly.com/question/12835309
#SPJ1
PLEASE HELP!!
The bond energy of O-H is 464 kJ/mol. What is the total bond energy of 2OH?
Answers
The total bond energy of 2OH bond is 928 kJ/mol
Bond energyBond energy is the energy needed to break or form bonds. They are measured in kilojoule per mole (kJ/mol).
Total bond energy of 2OH
Since we are given that the bond energy of O-H is 464 kJ/mol and we require the total bond energy of 2OH. In 2OH, the are two O-H bonds.
So, the bond energy of the two O-H bonds will be twice that of the single O-H bond.
So bond energy of 2OH = 2 × bond energy of O-H = 2 × 464 kJ/mol
= 928 kJ/mol
So, the total bond energy of 2OH bond is 928 kJ/mol
Learn more about bond energy here:
https://brainly.com/question/26288260
protons
neutrons
atomic symbol
atomic number
chemical element
Atoms are tiny pieces of matter that make up all the substances around you. All atoms
contain one or more positively charged particles called
, which are
found in an atom's nucleus. In many atoms, the nucleus also contains
which have no electrical charge. There are also small, negatively
charged particles called electrons found outside the nucleus. Together, these three types
of particles make up the structure of atoms.
The number of protons in an atom is the atom's
When two atoms
have the same atomic number, they are are classified as the same
All known chemical elements are listed in the periodic table, where they are arranged by
atomic number. The periodic table contains information about each element, often
including a short version of the element's full name called its
Answers
The total volume required to reach the endpoint of a titration required more than the 50 mL total volume of the buret. An initial volume of 49.17±0.04 mL was delivered, the buret was refilled, and an additional 1.56±0.04 mL was delivered before the endpoint was reached. The titration of a blank solution without the analyte required 0.60±0.04 mL . Calculate the endpoint volume corrected for the blank and its absolute uncertainty. Note: Significant figures are graded for this problem. To avoid rounding errors, do not round your answers until the very end of your calculations. volume: mL ± mL
Answers
Answer:
The answer is "\(\bold{50.42 \pm 0.08}\)".
Explanation:
Overall delivered volume \(= [(49.06 \pm 0.05) + (1.77 \pm 0.05)]\ mL\)
Its blank solution without any of the required analysis \(= (0.41 \pm 0.04)\ mL\)
Compute the volume of the endpoint as follows:
Formula:
\(\text{End point volume = Total Volume delivered - volume required}\)
\(= (49.06 \pm 0.05) + (1.77 \pm 0.05) - (0.41 \pm 0.04) \\\\= (49.06 + 1.77 - 0.41) \pm \ \ (absolute \ \ uncertainty)\)
therefore,
absolute uncertainty \(=\sqrt{(0.05)^2 + (0.05)^2 + (0.04)^2}\)
\(=\sqrt{0.0025 +0.0025 +0.0016} \\ \\=\sqrt{0.0066}\\\\=0.08124\\\)
The Endpoint volume \(= (49.06+1.77-0.41)\pm (0.08124)\)
\(= 50.42 \pm 0.08\)
Therefore, the volume of the endpoint adjusted for the blank is:
\(\bold { = 50.42 \pm 0.08}\)
describe what xeriscaping is and what is involved in a successful xeriscaping project
Answers
Xeriscaping is a landscaping approach that focuses on conserving water by using drought-tolerant plants and efficient irrigation techniques. The goal is to create a visually appealing and sustainable garden while minimizing water usage.
Successful xeriscaping projects involve several key elements. Firstly, careful plant selection is crucial, opting for species that can thrive in arid conditions without excessive watering. Mulching is used to reduce evaporation and retain soil moisture.
Proper soil preparation, such as improving drainage and adding organic matter, promotes healthier plant growth. Efficient irrigation systems, like drip irrigation or soaker hoses, deliver water directly to plant roots, minimizing wastage.
Additionally, controlling erosion through the use of retaining walls or terracing is important. Lastly, regular maintenance, including appropriate pruning and weed control, ensures the longevity and vitality of the xeriscape garden. Overall, a successful xeriscaping project harmonizes sustainable practices with a beautiful outdoor environment.
For more such questions on Xeriscaping
https://brainly.com/question/12960529
#SPJ11
Using VSEPR model, how is the molecular arrangement about the central atom (molecular geometry) for XeF4?
Answers
Answer:
Square planar.
Explanation:
Hello,
In this case, it can be demonstrated that the central atom Xenon in XeF₄ has a sp³d² hybridization which means that its geometry is likely to be octahedral. Nevertheless Applying by applying the valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model to in order to minimize the repulsion among lone pairs, bond pairs and lone pair-bond pairs, we we realize repulsion is actually minimized when lone pairs are anti to one another and the fluorine atoms are in equatorial position, for that reason, the corrected and properly exhibited geometry or molecular arrangement of the compound turns out square planar. You can verify it on the attached picture.
Regards.

The compound butanol has the following structural formula.
A string of 4 C atoms are bonded above, left, and below to H. The right-hand end is bonded to O, which in turn is bonded to H.
Which of these is a structural isomer of butanol?
A string of 4 C atoms are bonded above, below, left and right to H.
A string of 4 C atoms is bonded above, below, left, and right to H, except the second C, which is bonded below to O, which is bonded below to H.
A string of 4 C atoms is bonded above, below, left, and right to H, but the chain is interrupted between the first and second C, which are bonded to an O between them.
A string of 4 C atoms is bonded above, below, and left to H, except the last C has no H below and is double-bonded to an O to the right.
Answers
The structural formula of butanol is C4H9OH. It consists of a chain of four carbon atoms, with a hydroxyl (-OH) group attached to one of the carbon atoms. Butanol has several structural isomers, which have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas.
A structural isomer is a compound that has the same molecular formula as another compound but has a different arrangement of its atoms. A string of 4 C atoms are bonded above, below, left, and right to H, except the second C, which is bonded below to O, which is bonded below to H is a structural isomer of butanol.
This is called butan-2-ol. The structural formula of butan-2-ol is CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3. In this isomer, the hydroxyl group is attached to the second carbon atom in the chain, whereas in butanol, the hydroxyl group is attached to the first carbon atom in the chain.
For more question on atoms
https://brainly.com/question/6258301
#SPJ8
Nitrogen and hydrogen combine at a high temperature, in the presence of a catalyst, to produce ammonia.
N2(g)+3H2(g)⟶2NH3(g)
There are four molecules of nitrogen and nine molecules of hydrogen present in the diagram.
When the reaction is complete, how many molecules of NH3 are produced?
What is the limiting reactant?
How many molecules of each reactant are remain after the reaction is complete?
Answers
After the reaction is complete, no nitrogen and no hydrogen molecules remain, and 8.00 x 1014 molecules of NH3 are produced.
In the equation, nitrogen and hydrogen react at a high temperature, in the presence of a catalyst, to produce ammonia, according to the balanced chemical equation:N2(g)+3H2(g)⟶2NH3(g)The coefficients of each molecule suggest that one molecule of nitrogen reacts with three molecules of hydrogen to create two molecules of ammonia.
So, to determine how many molecules of ammonia are produced when four nitrogen and nine hydrogen molecules are present, we must first determine which of the two reactants is the limiting reactant.
To find the limiting reactant, the number of moles of each reactant present in the equation must be determined.
Calculations:
Nitrogen (N2) molecules = 4Hence, the number of moles of N2 = 4/6.02 x 1023 mol-1 = 6.64 x 10-24 mol
Hydrogen (H2) molecules = 9Hence, the number of moles of H2 = 9/6.02 x 1023 mol-1 = 1.50 x 10-23 mol
Now we have to calculate the number of moles of NH3 produced when the number of moles of nitrogen and hydrogen are known, i.e., mole ratio of N2 and H2 is 1:3.
The mole ratio of N2 to NH3 is 1:2; thus, for every 1 mole of N2 consumed, 2 moles of NH3 are produced.
The mole ratio of H2 to NH3 is 3:2; thus, for every 3 moles of H2 consumed, 2 moles of NH3 are produced.
From these mole ratios, it can be observed that the limiting reactant is nitrogen.
Calculation for NH3 production:
Nitrogen (N2) moles = 6.64 x 10-24 moles
The mole ratio of N2 to NH3 is 1:2; therefore, moles of NH3 produced is 2 × 6.64 × 10−24 = 1.33 × 10−23 moles.
Now, to determine how many molecules of NH3 are produced, we need to convert moles to molecules.
1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 molecules
Thus, 1.33 x 10-23 moles of NH3 = 8.00 x 1014 molecules of NH3 produced.
To find the amount of each reactant remaining after the reaction is complete, we must first determine how many moles of nitrogen are consumed, then how many moles of hydrogen are consumed, and then subtract these from the initial number of moles of each reactant.
The moles of nitrogen consumed = 4 moles × 1 mole/1 mole N2 × 2 mole NH3/1 mole N2 = 8 moles NH3
The moles of hydrogen consumed = 9 moles × 2 mole NH3/3 mole H2 × 2 mole NH3/1 mole N2 = 4 moles NH3
Thus, the moles of nitrogen remaining = 6.64 × 10−24 mol – 8 × 2/3 × 6.02 × 10^23 mol-1 = 5.06 × 10−24 mol
The moles of hydrogen remaining = 1.50 × 10−23 mol – 4 × 2/3 × 6.02 × 10^23 mol-1 = 8.77 × 10−24 mol
Finally, the number of molecules of each reactant remaining can be calculated as follows:
Number of N2 molecules remaining = 5.06 × 10−24 mol × 6.02 × 10^23 molecules/mol = 3.05 × 10−1 molecules ≈ 0 molecules
Number of H2 molecules remaining = 8.77 × 10−24 mol × 6.02 × 10^23 molecules/mol = 5.28 × 10−1 molecules ≈ 0 molecules.
For more such questions on molecules
https://brainly.com/question/24191825
#SPJ8
Prior to science lab, Maria had been drinking a can of soda. When she walked into the lab she set it down on the hot plate at her station. She heard a liquid beginning to boil, and realized that the previous students had forgotten to turn off the hotplate and the boiling noise was from the remaining soda in the can. Without thinking, she picked up the can with her bare hands, and put it upside down into the sink which was half full of liquid. Immediately the can crushed as though it was going to be recycled. What do you think is happening to the soda and air in the can? Support you claim in Question 4, by explaining why you think it is happening. Formulate your hypothesis for the problem. Critique Maria’s laboratory safety procedures.
Answers
Answer:
See explanation
Explanation:
When the temperature was increased, the pressure of the gas in the can was increased.
When Maria removed the can and placed it in cold liquid, the decrease in temperature led to a corresponding decrease in pressure of the gas inside the can hence the can was crushed.
Hypothesis: The pressure of the gas in the can is directly proportional to temperature.
Maria was careless about the experiment. She ought to have first checked whether the hot plate was off before placing the soda can. Secondly,she should not have immediately plunged the soda can into liquid because it will shrink due to decrease in pressure. She should not also have removed the soda can with bare hands to avoid getting burns and blisters.
The primary responsibility for investigating allegations of research misconduct belongs to:A. Office of Research Integrity (ORI)
B. Researcher(s)
C. Research institution(s)
D. B and C.
E. A, B and C.
Answers
The primary responsibility for investigating allegations of research misconduct belongs to Office of Research Integrity (ORI). Option A
What is research misconduct?We say that a researcher is guilty of research misconduct if the researcher has been found to be found to be engaged in an action that seems to have undermined the principles of ethics. This implies that the research have not been able to follow the standard operation protocol as he or she is carrying out the research.
For instance, in the area of the social sciences, it could be a research misconduct of the identity of the subjects that have taken part in the experiment is made public to the society and this is done without the consent of the subject. This is a violation of the privacy of the subject.
Learn more about research misconduct:https://brainly.com/question/28275840
#SPJ1
Convert 1.25 x 1024 atoms of carbon to moles of carbon.
Answers
Answer:
2.076
Explanation:
1 mole is 6.02 * 10^23
To convert from atoms (or molecules or compounds or ions etc.) to mols, you divide the number of atoms (or molecules or etc.) by 6.02 * 10^23
So it is (1.25 * 10^24)/(6.02 * 10^23)
=2.076
Answer:
\(\boxed {\boxed {\sf 2.08 \ mol \ C}}\)
Explanation:
We are asked to convert a number of carbon atoms to moles.
We will use Avogadro's Number for this, which is 6.022 × 10²³. This is the number of particles (atoms, molecules, formula units, etc.) in 1 mole of a substance. For this problem, the particles are atoms of carbon. There are 6.022 ×10²³ atoms of carbon in 1 mole of carbon.
We will also use dimensional analysis to solve this problem. To do this, we use ratios. Set up a ratio using the underlined information.
\(\frac {6.022 \times 10^{23} \ atoms \ C}{1 \ mol \ C}\)
We are converting 1.25 ×10²⁴ atoms of carbon to moles, so we multiply the ratio by that value.
\(1.25 \times 10^{24} \ atoms \ C* \frac {6.022 \times 10^{23} \ atoms \ C}{1 \ mol \ C}\)
Flip the ratio. It remains equivalent, but it allows us to cancel the units atoms of carbon.
\(1.25 \times 10^{24} \ atoms \ C* \frac{1 \ mol \ C} {6.022 \times 10^{23} \ atoms \ C}\)
\(1.25 \times 10^{24} * \frac{1 \ mol \ C} {6.022 \times 10^{23} }\)
\(\frac{1.25 \times 10^{24} } {6.022 \times 10^{23} } \ mol \ C\)
\(2.075722351 \ mol \ C\)
The original measurement of atoms has three significant figures, so our answer must have the same. For the number we calculated, that is the hundredths place. The 5 in the thousandths place tells us to round the 7 up to an 8.
\(2.08 \ mol \ C\)
1.25 ×10²⁴ atoms of carbon is equal to approximately 2.08 moles of carbon.
Describe the difference between an exothermic and endothermic process in terms of a chemical compound or reaction.
Answers
exo releases energy endo absorbs
Select all of the following that are combustion reactions.

Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
1,2,4,
The equations that show combustion are equations A, B and D.
What is combustion?When we talk about combustion, the idea is that the substance would be burnt in oxygen. In other words, the combustion can be taken to be an oxidation reaction. It is an oxidation reaction in the sense that the oxidation number of the substance that is reacting with the oxygen would become increased.
When we look at the equations that we have, it is quite easy to pick out among the balanced reaction equations that are shown here the ones that has to do with the burning of the substance in oxygen and a consequent rise in the oxidation number.
Learn more about combustion:https://brainly.com/question/15117038
#SPJ1
What is the pOH of 0.5 M KOH?
Answers
Answer:
pOH = 0.3
Explanation:
As KOH is a strong base, the molar concentration of OH⁻ is equal to the molar concentration of the solution. That means that in this case:
[OH⁻] = 0.5 MWith that information in mind we can calculate the pOH by using the following formula:
pOH = -log[OH⁻]pOH = -log(0.5)pOH = 0.3An arrow is fired at a target on a high wall. How does the energy change between the moment the arrow is fired and
Che moment it hits the target?
O The potential energy and kinetic energy remain the same.
O The potential energy decreases as kinetic energy increases.
O The kinetic energy decreases as potential energy increases.
O The kinetic energy remains at zero, but potential energy increases.
Answers
Answer:
C brainliest
Explanation:
An arrow is fired at a target on a high wall. The kinetic energy will decrease as potential energy increase.
Kinetic energy is one of the energies that is related to the motion of the particle and potential energy is one of the energies that is related to the position and height of the particle.
As the arrow in the question will go high to the wall, speed of arrow will keep on decreasing and kinetic energy keeps on decreasing and as height increases potential energy also increases.
We know that As per law of conservation of energy, as kinetic energy decreases potential energy will increase in the same amount.
Therefore, An arrow is fired at a target on a high wall. The kinetic energy will decrease as potential energy increase.
To learn more about law of conservation of energy click:
https://brainly.com/question/29775341
#SPJ7
3. HNO3 + NaHCO3 → NaNO3 + H2O + CO2
4. AgNO3 +CaCl2 → AgCl + Ca(NO3)2
5. 3 H2(g) + N2(g) → 2 NH3(g)
6. 2 H202 → 2 H2O + O2
Write word equation and type of reaction
Answers
Answer:
hydrogen nitrate + sodium hydrochlorate- sodium nitrate+ water + co2 (acid base reaction)
silver nitrate + calcium chloride - silver chloride+ calcium nitrate ( double displacement reaction)
hydrogen + nitrogen - ammonia gas ( simple contact reaction)
hydrogen peroxide - water + oxygen ( single displacement reaction)
Hope it helps :)
Differences between voltage, current and resistance?
Answers
Answer:
Voltage is the measure of electric potential energy per unit charge, current is the flow of electric charge through a circuit, and resistance is the property of a material that opposes the flow of electric current.
Ohm's Law relates these three concepts by stating that current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance.
Hope this helps!
Control of microbial growth in an operating room may involve which of the following?
Answers
Answer:
Usually involves the removal of
vegetative or non-endospore forming pathogens.
Explanation:
Usually involves the removal of
vegetative or non-endospore forming pathogens.
What is the oxidation number for Chlorine
Answers
Answer:Chlorine:
It is an element that belongs to the p-block and non-metal.
It shows a variable oxidation state.
The oxidation number of chlorine can be - 1, 0, + 1, + 3, + 4, + 5, or + 7 which depends on the substance containing the chlorine.
Explanation:
Cl has a -1 oxidation number, except when bonded to a F or an O.
In the formula CO2 what do the symbols C and O refer to
Answers
Answer:
CO2 (Carbon Dioxyde), the C refers to the Carbon atom (which is only 1) and the O(2) refers to the Oxygen atoms (which are two).
What is the change in temperature (AT) when a 25 g block of aluminum absorbs 10,000 J of heat?
Answers
The change in temperature (ΔT) when a 25 g block of aluminum absorbs 10,000 J of heat is approximately 44.32°C.
To calculate the change in temperature (T) that occurs when an aluminium block absorbs a certain quantity of heat, we must utilise the specific heat capacity of aluminium (c) and the equation:
Q = mcΔT
Where Q is the heat absorbed or released, m is the substance's mass, c is the substance's specific heat capacity, and T is the temperature change.
The specific heat capacity of aluminium is approximately 0.897 J/g°C.
Given that the aluminium block weighs 25 g and absorbs 10,000 J of heat, we can plug the following values into the equation:
(25 g) * (0.897 J/g°C) * T = 10,000 J
We can now solve for T:
T = 10,000 joules / [(25 g) * (0.897 J/g°C)]
ΔT ≈ 44.32°C
for more questions on temperature
https://brainly.com/question/4735135
#SPJ11
A casein isolation experiment yields 0.2g from 10g of milk What is the percentage of casein in the milk?
Answers
Answer:
2%
Explanation:
.2 g / 10 g * 100% = 2%
respectively. the gas is then warmed in a two-step process that increases the pressure by a factor of three and the volume by a factor of five. determine the amount of energy transferred to the gas by heat if the first step is carried out at constant volume and the second step at constant pressure. (use any variable or symbol stated above as necessary.) q
Answers
The amount of energy transferred to the gas by heat is:
\(Q = (5/2)nRT_{1} - (3/2)nRT_{2}\)
ΔU = Q - W
where ΔU is the change in the system's internal energy, Q is the heat it adds, and W is the work it performs.
In this problem, the first step is carried out at constant volume, so no work is done by the system (W = 0). Therefore, the heat added to the system in the first step is equal to the change in internal energy:
\(Q_{1}\) = Δ\(U_{1}\)
We can use the ideal gas law to relate the initial pressure, volume, and temperature of the gas to its initial internal energy:
\(U_{1} = (3/2)nRT_{1}\)
where n is the number of moles of gas, R is the gas constant, and T1 is the initial temperature.
Similarly, we can use the ideal gas law to relate the pressure, volume, and temperature of the gas after the first step to its internal energy:
\(U_{2} = (3/2)nRT_{2}\)
where T2 is the temperature of the gas after the first step.
Since the first step is carried out at constant volume, we have:
\(V2 = V1\)
Using the ideal gas law, we can relate the pressure, volume, and temperature of the gas after the second step to its internal energy:
\(U_{3} = (3/2)nRT_{3}\)
where T3 is the temperature of the gas after the second step.
Since the second step is carried out at constant pressure, we have:
\(V_{3} = 4V_{2} = 4V_{1}\)
and
\(P_{3} = 5P_{2} = 5P_{1}\)
Using the ideal gas law, we can relate the temperature of the gas after the second step to its initial pressure, volume, and temperature:
\(T_{3} = (5/3)(P_{1} V_{1} /T_{1} )(4V_{1} /5P_{1} ) = (4/3)T_{1}\)
The change in internal energy of the gas during the two-step process is:
\(U = U_{3} - U_{1} \\= (3/2)nRT_{3} - (3/2)nRT_{1} \\= (3/2)nR((4/3)T_{2} - T_{1} )\\= (1/2)nRT_{1}\)
Therefore, the heat added to the gas during the first step is:
\(Q_{1}\) = Δ\(U_{1} = (1/2)nRT_{1}\)
and the heat added to the gas during the second step is:
\(Q_{2}\) = Δ\(U_{2} = U_{3} - U_{2}\)
\(= (3/2)nRT_{3} - (3/2)nRT_{2} \\= (3/2)nR((4/3)T_{1} - T_{2} )\)
The total heat added to the gas during the two-step process is:
\(Q = Q_{1} + Q_{2} \\= (1/2)nRT_{1} + (3/2)nR((4/3)T_{1} - T_{2} )\\= (5/2)nRT_{1} - (3/2)nRTx_{2}\)
Therefore, the amount of energy transferred to the gas by heat is:
\(Q = (5/2)nRT_{1} - (3/2)nRT_{2}\)
for such more question on volume
https://brainly.com/question/19491767
#SPJ4
Question
A container is filled with an ideal diatomic gas to a pressure and volume of P1 and V1, respectively. The gas is then warmed in a two-step process that increases the pressure by a factor of five and the volume by a factor of four. Determine the amount of energy transferred to the gas by heat if the first step is carried out at constant volume and the second step at constant pressure. (Use any variable or symbol stated above as necessary.)
We can approach this problem using the first law of thermodynamics, which states that the change in internal energy of a system is equal to the heat added to the system minus the work done by the system: