Calculate the volume of a gas with a pressure of 100 kPa, if its volume at 120 kPa is 1.50 L.
Answers
Answer:
120 kPa = 1.25 L
Explanation:
Because 120/1.50 is 80. And then if you divide 100 by 80, you get 1.25.
Related Questions
is there DNA in the stucture of prokryotic
Answers
Answer:
i hope this helped
They have no true nucleus as the DNA is not contained within a membrane or separated from the rest of the cell, but is coiled up in a region of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid. Prokaryotic organisms have varying cell shapes.
Explanation:
Answer:
Explanation:
The DNA in prokaryotes is contained in a central area of the cell called the nucleoid, which is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Many prokaryotes also carry small, circular DNA molecules called plasmids, which are distinct from the chromosomal DNA and can provide genetic advantages in specific environments.
which of the following is an example of a longitudinal wave

Answers
Answer:
Examples of longitudinal waves include: sound waves. ultrasound waves. seismic P-waves.
Explanation:
Which of the following can act as a Lewis base? Cr3+, SO3, CH3NH2, BeCl2 A. Cr3+, BeCl2 B. SO3 only C. CH3NH2, BeCl2 D. SO3, CH3NH2 E. CH3NH2 only
Answers
The term "Lewis base" refers to a molecule or ion that can donate a pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond with a metal or metalloid center. In the given options, CH3NH2 (methylamine) is a Lewis base because it has a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom that can act as a donor. BeCl2 (beryllium chloride) can also act as a Lewis base because it has two empty orbitals that can accept a pair of electrons from a Lewis acid.
Therefore, options C and E are correct, and the answer is either C) CH3NH2, BeCl2 or E) CH3NH2 only, depending on whether BeCl2 is considered a Lewis base or not. Cr3+ and SO3 are not Lewis bases because they do not have any lone pair of electrons to donate.
A Lewis base is a molecule or ion that can donate an electron pair to form a coordinate covalent bond with a Lewis acid. Among the given options, we need to find which ones can act as a Lewis base.
Cr3+ is a cation and does not have an electron pair to donate, so it cannot act as a Lewis base.
SO3 is a molecule with all its oxygen atoms double-bonded to the sulfur atom, so it does not have any lone pair to donate, and thus, cannot act as a Lewis base.
CH3NH2 (methylamine) has a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom, making it a good candidate to donate an electron pair and act as a Lewis base.
BeCl2 is an electron-deficient molecule and would rather accept a lone pair of electrons, acting as a Lewis acid, not a base.
Considering these explanations, the correct answer is:
E. CH3NH2 only
Learn more about :
Lewis base : brainly.com/question/29665378
#SPJ11
Determine the moles of chlorine needed to react with 38.9 of iron (III) chloride.
2 Fe+3 CI, - 2 Feci
Answers
Answer: 0.360 moles
Explanation:
To calculate the moles :
\(\text{Moles of solute}=\frac{\text{given mass}}{\text{Molar Mass}}\)
\(\text{Moles of} FeCl_3=\frac{38.9g}{162.2g/mol}=0.240moles\)
The balanced chemical reaction is:
\(2Fe+3Cl_2\rightarrow 2FeCl_3\)
According to stoichiometry :
2 moles of require = 3 moles of
Thus 0.240 moles of \(FeCl_3\) will require=\(\frac{3}{2}\times 0.240=0.360moles\) of \(Cl_2\)
Thus 0.360 moles of chlorine needed to react to produce 38.9 of iron (III) chloride.
Why is wind a different type of resource than coal?
O Wind is natural.
O Wind is plentiful.
O Wind is limited.
O Wind is powerful.
Answers
Answer:
Wind is plentiful.
Unlike coal, there is wind everywhere on Earth. This means wind is plentiful unlike coal because coal is not everywhere outdoors like wind. Hope it helps!
There is a limited amount of coal on this earth, but there is an unlimited amount of wind seeing that it’s always being created.
PLS HELP URGENT
Electron dot diagrams
Use your periodic table to write the electron dot diagrams for the following atoms.
1. Calcium (Ca)
2. Polonium (Po)
3. Moscovium (Mc)
4. Boron (B)
5. Fluorine (F)

Answers

Of the following, which are not polyprotic acids?
hi
hno3
hcl
h2so4
Answers
Answer:
HI
H2SO4
Explanation:
H2SO4-diprotic acid
At a high concentration do you have more or less particles per unit volume
Answers
Answer:
More particles per unit volume
Explanation:
Concentration means the amount of solute in a solution. Now, the amount of solute also means the number of particles of solute present in a solution.
Hence, when we use the term "high concentration", we imply that the amount of solute present or the number of particles present in a solution is high.
Thus, at high concentration, there are more solute particles than solvent particles in a solution.
The binding of aspartic acid to the c1 carbon during catalysis is an example of:.
Answers
The binding of aspartic acid to the c1 carbon during catalysis is an example of a covalent bond formation or a nucleophilic substitution mechanism. During the reaction, aspartic acid, which is an amino acid, undergoes nucleophilic substitution and forms a covalent bond with the substrate.
This reaction is part of the mechanism by which aspartic acid proteases cleave peptide bonds. Aspartic acid proteases are a type of enzyme that uses aspartic acid as its active site residue. The binding of aspartic acid to the c1 carbon during catalysis is an example of a covalent bond formation or a nucleophilic substitution mechanism. During the reaction, aspartic acid, which is an amino acid, undergoes nucleophilic substitution and forms a covalent bond with the substrate. This reaction is part of the mechanism by which aspartic acid proteases cleave peptide bonds.
Aspartic acid proteases are classified into two types: retroviral and cellular. Retroviral proteases are involved in the maturation of viral particles, while cellular proteases are involved in the degradation of proteins. The best-known example of aspartic acid proteases is HIV-1 protease, which plays a vital role in the life cycle of the human immunodeficiency virus. Because of its importance, HIV-1 protease is a target for antiretroviral drugs.
In conclusion, the binding of aspartic acid to the c1 carbon during catalysis is an example of a covalent bond formation or a nucleophilic substitution mechanism. This reaction is part of the mechanism by which aspartic acid proteases cleave peptide bonds. Aspartic acid proteases are a type of enzyme that uses aspartic acid as its active site residue.
To know more about aspartic acid visit:
brainly.com/question/31329443
#SPJ11
classify each of the following changes as either a physical or a chemical change
1: The addition of the water to quicklime (i.e., the slaking of lime)
2: The melting of candle wax
3: The change in colour of zinc oxide from white to yellow and vice versa during heating and after cooling, respectively
4: The dissolution of common salt
5: The hardening of cement by the absorption of carbon (Iv) oxide
Answers
The changes are classified as follows:
1: Chemical change - The addition of the water to quicklime
2: Physical change - The melting of candle wax
3: Physical change - The change in colour of zinc oxide from white to yellow and vice versa during heating and after cooling, respectively
4: Physical change- The dissolution of common salt
5: Chemical change - The hardening of cement by the absorption of carbon (Iv) oxide
1: The addition of water to quicklime (slaking of lime) is a chemical change. It involves a chemical reaction between calcium oxide (quicklime) and water to form calcium hydroxide (slaked lime). This reaction is exothermic and produces heat.
2: The melting of candle wax is a physical change. It involves a phase transition from a solid state to a liquid state due to the application of heat. The chemical composition of the wax remains unchanged during this process.
3: The change in color of zinc oxide from white to yellow and vice versa during heating and cooling is a physical change. It is a reversible process caused by the alteration of the crystal structure of zinc oxide. The change in color is due to the absorption or release of energy during the heating and cooling processes, respectively.
4: The dissolution of common salt (sodium chloride) is a physical change. It involves the separation of ionic bonds between sodium and chloride ions in the solid salt and their subsequent dispersal in water. The chemical composition of the salt remains the same; it simply forms a homogeneous mixture with water.
5: The hardening of cement by the absorption of carbon dioxide (CO2) is a chemical change. It involves a chemical reaction known as carbonation, where carbon dioxide reacts with the calcium hydroxide in cement to form calcium carbonate. This reaction leads to the formation of new chemical compounds and a change in the structure and properties of the cement, resulting in its hardening or curing process.
For more such questions on quicklime visit:
https://brainly.com/question/15315072
#SPJ8
why sahlis method most frequently employed as routines test
Answers
The fundamental idea behind Sahli's acid haematin technique is that hemoglobin is changed into acid haematin by the action of HCl, which results in a brown color.
The International Committee for Standardization in Haematology recommends the direct cyanmethaemoglobin method2 as the method that is most frequently used to estimate hemoglobin quantitatively. It is comparatively easy and inexpensive, because it involves the creation of cyanmethaemoglobin, a stable compound3. Blood's hemoglobin content can be found out using Sahli's method. The haemoglobin content of blood samples is determined using Sahli's haemoglobinometer by converting hemoglobin to hematin acid, which is then diluted to produce hematin acid that matches the comparator's color.
Learn more about hemoglobin here:
https://brainly.com/question/15011428
#SPJ4
A swimmer pushes against a wall with his feet, as shown below.
The wall pushes back against the swimmer's feet with the same force. Which of Newton's laws does this best demonstrate?
A.
Newton's law of universal gravitation
B.
Newton's second law of motion
C.
Newton's third law of motion
D.
Newton's first law of motion
Answers
Answer:
C. newton's third law of motion
Explanation:
as newton's third law of motion states that every action has a reaction that is equal in size, opposite in direction, and acts simultaneously.
What is the texture of hydrogen?
Answers
Answer: The texture is one of the most important physical characteristics of the solid or liquid materials.
Texture is actually the physical feel of the surface layer of a material when we physically touch it.
So,by it's definition we came to know that the texture is only possible for the substances which have physical surfaces.
And the gaseous materials don't have any physical surface to feel it's texture.
That's why gaseous materials including hydrogen gas don't have any kind of texture.
Explanation:
What is the acceleration of the object’s motion? 0.5 m/s2 -0.5 m/s2 2 m/s2 -2 m/s2

Answers
Answer: -2m/s2
Explanation:
Using the following equation ; acceleration = Change in velocity / time
i.e a = v - u / t
where 'a' = acceleration
v = final velocity
u = initial velocity
t = time
Therefore; from the graph we have acceleration to be, 0 - 6m/s / 3s = -2m/s2
A new computer costs $1200 and depreciates 30% in value every year. what is the value of the computer in 4 years?
Answers
The value of the computer in 4 years is $537.60.
What is the final value of the computer after 4 years?To determine the value of the computer in 4 years, we need to calculate its depreciation each year. The computer depreciates by 30% of its value annually, which means it retains 70% of its value each year.
In the first year, the computer's value is $1200. After depreciating 30%, the value becomes 70% of $1200, which is $840. In the second year, the computer's value is 70% of $840, which is $588. In the third year, the value is 70% of $588, which is $411.60. Finally, in the fourth year, the value is 70% of $411.60, which amounts to $288.12.
Therefore, after 4 years, the value of the computer is approximately $288.12.
Learn more about Value
brainly.com/question/13799105
#SPJ11
what is the equivalent volume occupied by three millimeters of water?
3 kg
3 cg
3 cubic cm
3 cm
also I apologize I am very stupid
Answers
Answer:
three cubic centimeters
Explanation:
Fill in the coefficients that will balance the following reaction: (Note: Use 1 as coefficient where appropriate.) Hg(C)3)2 + AgCl -> HgCl4 +Ag2CO3
Answers
i just answered this question and it was actually 1,4,1,2
What is the mass concentration of 2mole HCL solution?(h=1,Cl=35.5)
Answers
Answer:
So the answer to the question “What is the mass concentration of hydrogen chloride in 2.0-molar hydrochloric acid?” is 73 grams per liter.
Alpha particles were deflected by the positively charged
Answers
Answer:
See explanation
Explanation:
In Rutherford's experiment, a gold foil was bombarded with positively charged alpha particles. A zinc sulphide screen was used to observe the movement of the alpha particles during the experiment.
A few particles passed through without deflection while some particles were deflected through large angles. This observation led Rutherford to the conclusion that the atom was made up of a dense positively charged nucleus where most of its mass was concentrated.
in the lab, john has two solutions that contain alcohol and is mixing them with each other. he uses milliliters less of solution a than solution b. solution a is alcohol and solution b is alcohol. how many milliliters of solution b does he use, if the resulting mixture has milliliters of pure alcohol?
Answers
To determine the number of milliliters of solution B used by John, we need to consider that the resulting mixture has a certain volume of pure alcohol. Additionally, it is mentioned that solution A contains alcohol and that John uses fewer milliliters of solution A than solution B. By comparing the volumes of pure alcohol in each solution and considering their respective concentrations, we can calculate the amount of solution B used by John.
Let's assume that John uses x milliliters of solution B. Since he uses fewer milliliters of solution A, the volume of solution A used would be x - y, where y represents the milliliters less of solution A used.
To determine the amount of pure alcohol in each solution, we need to consider their concentrations. Let's denote the concentration of solution A as A and the concentration of solution B as B. Given that the resulting mixture contains z milliliters of pure alcohol, we can set up the equation:
(A * (x - y)) + (B * x) = z
Simplifying the equation, we can solve for x:
Ax - Ay + Bx = z
(A + B) * x - Ay = z
x = (z + Ay) / (A + B)
By substituting the given values of y, A, B, and z into the equation, we can determine the number of milliliters of solution B used by John.
To know more about Pure alcohol :
brainly.com/question/14113912
#SPJ11
The noble gas electron configuration of S2- isGroup of answer choices[Ar]4s2[Ne]3s2 3p4[Ne]3s2 3p6[Ar][Ne]
Answers
Answer
[Ne] 3s² 3p⁶
Explanation:
Neutral sulfur has an atomic number of 16.
Neutral sulfur has 16 electrons and 16 protons.
However, S²⁻ implies neutral sulfur has gain two more electrons.
So, S²⁻ is negatively charged (anion) and has 18 electrons.
Electronic Configuration
Neutal sulfur (S) → 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁴ → [Ne] 3s² 3p⁴.
Charged sulfur (S²⁻) → 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ → [Ne] 3s² 3p⁶.
Therefore, the electron configuration of S²⁻ is [Ne] 3s² 3p⁶.
Oxalic acid C2H204) is a dibasic acid with a pK 1.4 and pK2-4.3 (a) Write out the two ionization reactions for this b) Plot the fractions of each species of oxalic acid as a function of pH.
Answers
a). The two ionization reactions for oxalic acid are: C₂H₂O₄(aq) ⇌ H+(aq) + HC₂O₄\(^-^(^a^q^)\) and HC₂O₄\(^-^(^a^q^)\) ⇌ H+(aq) + C2O₄²-(aq).
b).The fractions of each species of oxalic acid change with pH.
(a) What are the ionization reactions for oxalic acid?The ionization reactions of oxalic acid (C2H2O4) can be written as follows:
C₂H₂O₄ ⇌ H+ + HC₂O₄- (First ionization)HC₂O₄- ⇌ H+ + C2O₄²- (Second ionization)In the first ionization reaction, one hydrogen ion (H+) and one hydrogen oxalate ion (HC₂O₄-) are formed from oxalic acid. In the second ionization reaction, one hydrogen ion (H+) and one oxalate ion (C2O₄²-) are formed from the hydrogen oxalate ion.
(b) How do the fractions of oxalic acid species vary with pH?(b) The fractions of each species of oxalic acid (C₂H₂O₄), hydrogen oxalate ion (HC₂O₄-), and oxalate ion (C2O₄²-) can be plotted as a function of pH. At low pH values, most of the oxalic acid exists in the undissociated form.
As the pH increases, the concentration of hydrogen ions increases, causing the first ionization reaction to occur and leading to the formation of hydrogen oxalate ions. At higher pH values, the second ionization reaction takes place, resulting in the formation of oxalate ions.
The plot would show that as the pH increases, the fraction of oxalic acid decreases, while the fractions of hydrogen oxalate ion and oxalate ion increase. This reflects the shift from the acidic form of oxalic acid to its conjugate base forms as the pH becomes more basic.
Overall, the ionization reactions and the corresponding plot of species fractions provide insights into the behavior of oxalic acid in different pH conditions, illustrating its acidic nature and the transition to its conjugate base forms as the pH increases.
Learn more about ionization reactions
brainly.com/question/31834398
#SPJ11
What is the frequency of an X-ray that has a wavelength of 1.5 x 10 -9 m? The speed of electromagnetic radiation is 3.0 x 10 8 m/s. [v = λƒ]
Answers
Answer:
2.0x10¹⁷ Hz is the frequency of the X-ray
Explanation:
We can find the frequency of a wave of energy from the wavelenght and its speed using the formula:
v = λƒ
Where v is speed (For electromagnetic radiation = 3.0x10⁸m/s)
λ is the wavelength in meters = 1.5x10⁻⁹m
And f is the frequency in s⁻¹ = Hz
Replacing:
3.0x10⁸m/s = 1.5x10⁻⁹m*ƒ
3.0x10⁸m/s / 1.5x10⁻⁹m = f
f =
2.0x10¹⁷ Hz is the frequency of the X-ray
A liquid is allowed to evaporate and leaves no residue. can you determine whether it was an element, a compound, or a mixture?
Answers
A liquid is allowed to evaporate and leaves no residue. It can not be determined whether it was an element, a compound, or a mixture.
A water vapor molecule stays roughly 10 days in the atmosphere after it has evaporated. Water vapor starts to cool back down as it ascends higher in the atmosphere. The water vapor condenses when it becomes cold enough, turning it back into liquid water. Eventually, individual water droplets will condense to create clouds and precipitation.
It is not possible to determined whether it would be an element, a compound and mixture because the size of the particle will be too less.
A method for separating homogenous mixtures with one or even more dissolved salts is called evaporation. The procedure separates the liquid from the solid components. Usually, the procedure entails heating the combination until there is no more liquid is present.
Therefore, it can not be possible to determined whether it was an element, a compound, or a mixture by evaporation.
To know more about liquid
https://brainly.com/question/25579356
#SPJ4
PLS PLS PLS HELP PLS I REALLY NEED IT AND I WILL MARK YOU BRAINLYEST:((
PLSSSS

Answers
Answer:
D and A
Explanation:
D is a Mitochondria (the powerhouse of the cell)
A is a Choroplast (the part that takes in the sun)
air pollutants are a concern because they can lead to a variety of negative environmental and human health consequences. one group of such pollutants is nitrogen oxides. identify one way nitrogen oxides (nox) are commonly introduced into the atmosphere. explain how nitrogen oxides released into the atmosphere can lead to the formation of a secondary pollutant that can lead to acid deposition. describe one method for reducing nitrogen oxide emissions into the atmosphere from anthropogenic sources. nitrogen dioxide is a nitrogen oxide that can lead to the formation of ozone (o3) and photochemical smog in the troposphere. the three figures below show three scenarios involving o3 formation and destruction in the troposphere
Answers
Use of low-nitrogen fuels is one way to reduce NOx emissions. Altering combustion needs is another way to reduce NOx production. NOx can be eliminated using flue gas treatment methods like selective catalytic reduction technologies.
What is nitrogen oxide?Two gases with molecules consisting of nitrogen and oxygen atoms are nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). These nitrogen oxides play a part in the development of smog and acid rain, adding to the issue of air pollution. Nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide, the nitrogen oxides that are most important for air pollution, are referred to collectively as NOx in atmospheric chemistry. These gases also have an impact on tropospheric ozone and contribute to the development of smog and acid rain.
Where is nitrogen oxide found?In the course of burning fuel, nitrogen compounds contribute to the production of nitrogen oxides, but the main source is the direct reaction between air oxygen and nitrogen in flames. Natural sources of nitrogen oxides include lightning and, to a lesser extent, microbiological activity in soil.
Briefing :These six contaminants include sulfur oxides, ground-level ozone, lead, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and particle pollution (also known as particulate matter).
To know more about Nitrogen Oxide visit:
https://brainly.com/question/28884437
#SPJ4
30 points please help!!!!!!!!
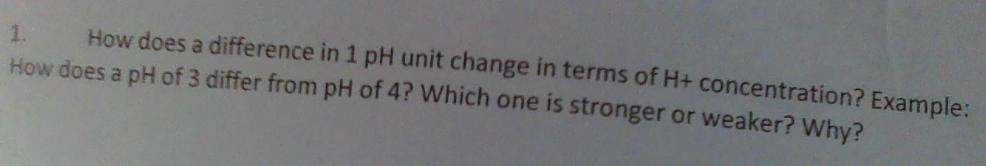
Answers
pH 3 = 10 times of pH 4 in terms of H⁺ concentration
Further explanationpH is the degree of acidity of a solution that depends on the concentration of H⁺ ion. The greater the value the more acidic the solution and the smaller the pH.
pH = - log [H⁺]
So that the two quantities between pH and [H⁺] are inversely proportional because they are associated with negative values.
A solution whose value is different by n has a difference in the concentration of H⁺ ion of 10ⁿ.
So pH 3 and pH 4 have a difference in the concentration of H⁺ ion of 10¹ = 10
pH 3 = -log[10⁻³]
pH 4 = - log[10⁻⁴]
pH 3 = 10 times of pH 4 in terms of H⁺ concentration
And pH 3 is stronger in acid than pH 4
How many grams of NaOH are there in 700.0 mL of a 0.18 M NaOH solution? *
a. 3.5 g
b. 2.19 x 10^-3 g
c. 149
d. 1149
e. 5.049
Answers
Answer:
E. 5.049
Explanation:
Multiply the concentration by volume (in liters) first to get moles of NaOH. Then multiply by the molar mass of NaOH to convert to grams.
0.18 M • 0.7000 L = 0.126 mol NaOH
0.126 mol • 39.997 g/mol = 5.040 g --> The closest answer seems to be e. 5.049 g
What happens to the carbon dioxide that the alveoli receive from the blood?
Answers
Answer:
it is then exhaled
Explanation:
Carbon dioxide passes from the blood into the alveoli and is then exhaled.
Does cool air push warm air upward?
Answers
Answer:
Cooler, denser air flows in underneath the warmer, less dense air, and pushes the warmer air upward. When this air cools, it becomes more dense than the warmer air beneath it. The cooled air sinks and moves under the warmer air.
Answer
Hot air is less dense than cold air, which is why hot air rises and cold air sinks, according to the United States Department of Energy. Hot and cold air currents power the weather systems on earth. The sun plays a major role in heating the planet, which also creates hot and cold air energy systems. Warm air currents typically bring rain, because they form over oceans. That’s why hurricanes and tropical storms form at sea and eventually move toward land.