Write a complete, balanced chemical equation where tin metal reacts with aqueous hydrochloric acid to produce tin(II) chloride and hydrogen gas. Include states.
From the equation, which element is oxidized, and which element is reduced?
Answers
Answer:
Zn(s)+2HCl(aq)→ZnCl2(aq)+H2(g)
Explanation:
The net reaction is Z n ( s ) + 2 H + ( a q ) → Z n 2 + ( a q ) + H 2 ( g ) The C l − ions are spectators - they don't change.
Related Questions
What formula is used for solving problems involving Boyle’s law?P1T1=P2T2P1T1=P2T2P1=V2P1=V2V1T1=V2T2V1T1=V2T2P1V1=P2V2

Answers
Step 1 - Brief revision of Boyle's Law
Boyle's law is a law concerning the behavior of gases. It states that the pressure and the volume are inversely proportional given that the temperature is kept constant.
That is, if we increase the pressure, the volume will decrease. This principle is behind the proper functioning of our lungs, for example. This can also be described mathematically as:
\(P_1V_1=P_2V_2\)Step 2 - Choosing the right alternative
As we have seen in step 1, we can use the following formula to work with Boyle's Law:
\(P_1V_1=P_2V_2\)Therefore, the correct alternative is item d.
Consider the chemical equation for the combustion of sugar. _C6H12O6(s) + _O2(g) Right arrow. _CO2(g) + _H2O(l) Which sequence of coefficients should be placed in the blanks to balance this equation?
Answers
Answer:
1C₆H₁₂O₆(s) + 6O₂(g) → 6CO₂(g) + 6H₂O(l)
Explanation:
In general equation combustions where all carbon produce CO₂ and all hydrogen H₂O we must begin the balance with these two species:
_C₆H₁₂O₆(s) + _O₂(g) → _CO₂(g) + _H₂O(l)
If sugar is 1, CO₂ and H₂O must be:
1C₆H₁₂O₆(s) + _O₂(g) → 6CO₂(g) + 6H₂O(l)
Thus, C and H are balanced. In the right side we have 12 oxygen from CO₂ + 6 oxygen from H₂O = 18 oxygen
In the left there are 6, thus, O₂ must provide 12 oxygens, thus:
1C₆H₁₂O₆(s) + 6O₂(g) → 6CO₂(g) + 6H₂O(l)And this is the balanced reaction
what are the best units for a scientist to measure the distance between cities?
Answers
Kilometers (km) and miles (mi) are the preferred units for measuring the distance between cities in scientific contexts.
The distance between cities is an essential measurement for scientists, and it is typically expressed in kilometers (km) or miles (mi).
Kilometers (km) are widely adopted by scientists as the primary unit of distance measurement globally.
It is the standard unit in the metric system, which is widely used in scientific research and international communication.
One kilometer is equal to 1000 meters, providing a convenient scale for measuring long distances.
For example, a distance of 100 km between two cities indicates that they are separated by 100,000 meters.
In the United States and the United Kingdom, miles (mi) are commonly used to measure distances.
Although not as prevalent in scientific literature as kilometers, miles are still utilized, especially when dealing with transportation-related data or working within these regions.
One mile is equivalent to approximately 1.6 kilometers. For instance, if the distance between two cities is 50 miles, it means that the two cities are approximately 80.5 kilometers apart.
kilometers (km) and miles (mi) are the preferred units for measuring the distance between cities in scientific contexts.
Kilometers are the global standard, while miles are commonly used in specific regions.
Both units provide scientists with effective measurements for studying and analyzing geographical distances.
To know more about Standard units here: https://brainly.com/question/32814357
#SPJ11
a neutral atom is bombarded with sufficient energy that an electron is liberated. the result is called
Answers
Answer:
A cation.
Explanation:
When an electron is liberated, that means it is removed from the atom.
When an electron is lost, the atom is ionized, and becomes a cation.
It becomes a cation because it loses one negative charge, and therefore become positively charged.
As a gas condenses to a liquid does the potential energy increase or decrease?
Answers
As a gas condenses to a liquid, the potential energy decreases.
When a substance transitions from the gaseous phase to the liquid phase, the intermolecular forces of attraction become stronger. These forces, such as London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole interactions, or hydrogen bonding, start to dominate as the gas molecules come closer together. In the gaseous state, the molecules have higher kinetic energy and are moving more freely, with greater distances between them. As the gas condenses and transitions into a liquid, the molecules become more closely packed and their motion becomes restricted. The intermolecular forces pull the molecules together, allowing them to form stable arrangements. As the gas molecules move closer and the intermolecular forces become stronger, the potential energy of the system decreases. The potential energy decreases because the molecules are moving from positions of higher potential energy (with weaker intermolecular forces) to positions of lower potential energy (with stronger intermolecular forces). Therefore, during the process of condensation, the potential energy of the system decreases as the gas transitions into a liquid.
for more questions on potential
https://brainly.com/question/19291483
#SPJ8
what would be the final volume when 2.20 M solution is made from 25.0 mL of a 12.0 M solution? plzz show work
Answers
Answer:
136.36 mL
Explanation:
Here we have to use the dilution formula
From C1V1= C2V2
Where;
C1= initial concentration of the solution= 12.0 M
C2= final concentration of the solution= 2.20 M
V1 = initial volume of the solution= 25.0 ml
V2= final volume of the solution= ?????
Then recall;
C1V1=C2V2
V2 = C1V1/C2
Substituting values from the parameters given;
V2= 12.0 × 25.0 / 2.20
V2= 136.36 mL
The half-life for Carbon-14 is 5614 years. An ancient piece of cloth is found to contain ¼ of its original Carbon-14. How old is the cloth? Describe or show in detail how you solved this.
Answers
Answer:
To determine the age of the ancient cloth, we can use the concept of radioactive decay and the half-life of Carbon-14.
Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope of carbon, which decays over time into nitrogen-14 through beta decay. The half-life of Carbon-14 is 5614 years, which means that after 5614 years, half of the original amount of Carbon-14 in a sample will have decayed.
In this case, the cloth contains only ¼ of its original Carbon-14. This means that three half-lives have passed since the cloth was first created, as each half-life reduces the amount of Carbon-14 by half.
To determine the age of the cloth, we can use the following formula:
N = N0(1/2)^t/T
where N is the current amount of Carbon-14 in the cloth, N0 is the original amount of Carbon-14 in the cloth, t is the time that has passed, and T is the half-life of Carbon-14.
We know that N = ¼ N0, and T = 5614 years. Plugging these values into the formula, we get:
¼ N0 = N0(1/2)^(3/T)
Solving for t, we get:
t = (3/T) * log(2)
Substituting in T = 5614 years, we get:
t = (3/5614) * log(2) ≈ 1,684 years
Therefore, the cloth is approximately 1,684 years old.
In summary, we can use the concept of radioactive decay and the half-life of Carbon-14 to determine the age of the ancient cloth. By knowing the current amount of Carbon-14 in the cloth, we can calculate the time that has passed since it was first created using a simple formula. In this case, the cloth is approximately 1,684 years old.
What is primarily released in radioactive decay?
Answers
Answer:
When radioactive atoms decay, they release energy in the form of ionizing radiation (alpha particles, beta particles and/or gamma rays). The energy is called ionizing radiation because it has enough energy to knock tightly bound electrons from an atom's orbit. This causes the atom to become a charged ion.
Explanation:
A student designs a gravity experiment. She will time how long it takes different objects to fall from her school’s roof to the ground. She will use three objects: a 2-foot-long board, a toy car, and a paper bag. What is wrong with her experiment’s design?
A. Gravity will not affect how long it takes for the objects to fall to the ground.
B. The school roof is not tall enough to test the effect of gravity on different objects.
C. The objects do not have the same size, shape, or mass, so any differences in drop times cannot be attributed to one variable.
D. The experiment does not test enough objects.
Answers
Answer:
C
Explanation:
How does the temperature change when a layer of glass is added?
Answers
Answer:
thermal shock
Explanation:
the temperatures inside the glass jar should have continued to increase over time. Internal stresses due to uneven heating. This is also known as “thermal shock”.
In general, the thicker the glass, the more prone it will be to breaking due to the immediate differences in temperature across the thickness of glass.
Borosilicate glass is more tolerant of this, as it has a higher elasticity than standard silicon glass.
You may also note that laboratory test tubes and flasks are made with thinner walls, and of borosilicate glass, when designated for heating.
what will be the result of the reaction
(CH3COO)2+redP +Cl2
Answers
Answer:
(CH3COO)2 + redP + Cl2 → ClCH2COOH + HCl
Explanation:
This is an example of halogenation of carboxylic acids at alpha carbon atom. In this reaction, red phosphorus and chlorine are treated with carboxylic acids having alpha hydrogen atom followed by hydrolysis to form alpha chloro carboxylic acid.
The following are halogens except
a. fluorine
b. iodine
c. chlorine
d. phenol
Answers
Answer:
i think this is [d. phenol]
The correct answer:
Phenol
\( \large{ \boxed{ \bf{ \color{green}{Option \: D}}}}\)
Phenol is a compound, While other are elments found under the 17th group, and popularly known as Halogens.
Explore more:-The name halogen comes from the Greek words "hals", meaning "salt", and "gen", meaning "to make."The halogens are a group of elements in the periodic table. They are located to the right of the other nonmetals and to the left of the noble gases.The halogens include the five elements fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine. They make up column 17 of the periodic table.They have seven valence electrons in their outer shell.They all exist as diatomic molecules (two atoms) when in their pure form.Simple compounds that contain halogens are called halides.━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
q1.8. imagine you performed a litterbag experiment using a 100-gram sample of leaves from a forest stand at coweeta. at the end of 2 years, the dry mass of your sample was 30 grams. based on these results, what is the decomposition rate, k for these leaves in this forest?
Answers
The decomposition rate (k) for the leaves in the Coweeta forest stand is 0.4502 per year.
The decomposition rate (k) can be calculated using the litterbag method formula: k = -ln(m₂/m₁)/t, where m₁ is the initial mass of the sample, m₂ is the mass of the sample after time t, and ln is the natural logarithm.
In this case, m₁ = 100 g, m₂ = 30 g, and t = 2 years.
Plugging these values into the formula, we get
k = -ln(30/100)/2 = 0.4502.
This means that the leaves in the Coweeta forest stand have a decomposes at rate of 0.4502.
To know more about decomposition, here
brainly.com/question/11325249
#SPJ4
Why is sodium an active metal
Answers
Answer:
Sodium is very reactive in nature. When exposed in air, it automatically forms Na2O. When it is put in water it reacts vigorously and starts burning on water. Due to the above reasons Sodium is called an active metal
Explanation: hope this helps pls mark as brainliest ty
Ming has two unknown substances. One is nonpolar, and the other is polar.
Which process would most likely help Ming identify which substance is polar and which is nonpolar?
Test the boiling points. The polar substance should have a lower boiling point because of its dipole-dipole forces.
Test for an odor. The nonpolar substance should have a higher volatility and stronger odor because of its London dispersion forces.
Test the boiling points. The nonpolar substance should have a higher boiling point because of its hydrogen bonds.
Test for an odor. The polar substance should have a higher volatility and weaker odor because of its dipole-dipole forces.
Answers
Answer:
Test for an odor. The nonpolar substance should have a higher volatility and stronger odor because of its London dispersion forces.
Explanation:
To help Ming identify the non-polar compound, assuming the non-polar compound will have an odor test for it and most importantly, the non-polar substance should have a higher volatility due to its London dispersion forces.
London dispersion forces are weak attractions found between non-polar molecules and noble gases. They account for the reason why compounds as such are volatileAnswer:
B
Explanation:
Silver tarnishes as silver metal reacts with hydrogen sulfide, h2s, in the air. in this reaction, dark silver sulfide, au2s, covers the surface of silver. when silver is polished, this coating of silver sulfide can be removed from the surface. this makes the silver shiny again. enter the coefficients that balance the tarnishing reaction equation. (type 1 for no coefficient.) 2 silver dishes. photo by mgeurts ag(s) h2s(g) → ag2s(s) h2(g)
Answers
To make the silver shiny again, we can do silver tarnishes. The balanced tarnishing reaction is 2Ag(s) + H2S(g) --> Ag2S(s) + H2(g). Hence, the correct coefficients for the reaction above are: 2, 1, 1, 1.
How to write a balanced chemical equation?A balanced reaction is when the coefficient of all atoms in the reactants (the left side) is the same as the products (the right side). Given this equation:
Ag(s) + H2S(g) --> Ag2S(s) + H2(g)
The balanced reaction is:
2Ag(s) + H2S(g) --> Ag2S(s) + H2(g)
Hence, the coefficients of the reaction above are: 2, 1, 1, and 1.
Learn more about balancing chemical equations here https://brainly.com/question/26227625
#SPJ4
PLEASE ANSWER ALL I WILL GIVE BRAINLIEST PLEASE!!

Answers
hey guys i need help with this story problem
A student measured a cylinder to have a length of 4.21 cm and a diameter of 1.29 cm. What is the volume of the cylinder? Include units (cm3) and round to the proper number of significant digits. V = π x r^2 x L
Answers
A student measured a cylinder to have a length of 4.21 cm and a diameter of 1.29 cm. The volume of the cylinder is \(V \approx 5.5 \mathrm{~cm}^3\).
\(V=\pi\left(\frac{d}{2}\right)^2 h=\pi \cdot\left(\frac{1.29}{2}\right)^2 \cdot 4.21 \approx 5.50239 \mathrm{~cm}^3\)
A cylinder's volume refers to the amount of interior room it has to hold a given quantity of material. To put it another way, a cylinder's volume is how much it can hold. You can store any one of the three forms of matter—solid, liquid, or gas—within the confines of a cylinder. You cannot hold any liquid, solid, or gas in a two-dimensional cylinder, hence this capacity can only be observed in a three-dimensional cylinder.
Two congruent and parallel identical bases make up a complete three-dimensional cylinder. The right circular cylinder is what is meant by this. Each line segment makes up the lateral curved surface, which is perpendicular to the bases, of a right circular cylinder, which has circular bases. The proper circular cylinders might have crossed your path on a regular basis. Can shapes, paper roll shapes, straight glass, and many other things.
Learn more about volume of the cylinder https://brainly.com/question/16134180
#SPJ9
OMG PLEASE HELP IM DOING SO WELL IN SCIENCE AND THIS IS GRADED AND MY PROFEESER WONT HELP
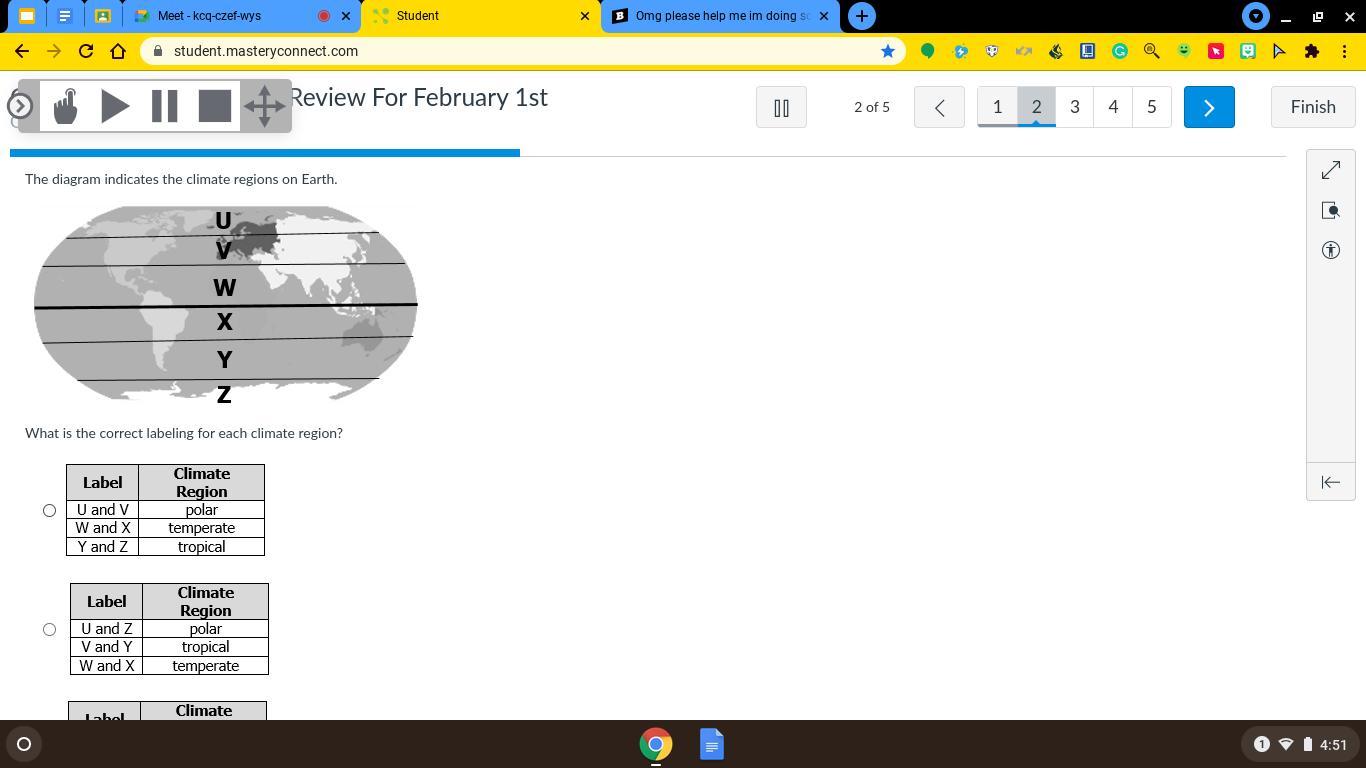

Answers
Answer:
bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
Explanation:
11) Which group of Elements have Similar chemical Properties? *
Li, Be, B
K, Ca, Rb
Ca, Sr, Ba
Answers
Explanation: They are in the same group (Alkaline Earth Metals)
What is the pH of a solution that has a hydronium ion concentration of 8.26 ´ 10–5 M?
Answers
pH = -log[H3O+] = -log(8.26 x 10^-5) = 4.083 (three decimal places because the concentration had three sig figs)
Can someone please help me with the last column!! ASAP

Answers
The ratio of the volume and temperature of the gas in the given table is as follows:
0.72/276 = 0.002620.78/294 = 0.002650.84/313 = 0.002680.87/330 = 0.002630.93/355 = 0.002620.98/371 = 0.00264What is the relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas?Charles's law, also known as the law of volumes, describes the relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas at a constant pressure. According to this law, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (measured in Kelvin) when the pressure is constant.
In other words, as the temperature of a gas increases, its volume will also increase proportionally, and vice versa. Mathematically, Charles's law can be expressed as:
V/T = k
where V is the volume of the gas, T is its temperature in Kelvin, and k is a constant of proportionality.
Learn more about the volume and temperature of a gas at: https://brainly.com/question/17100204
#SPJ1
Mr. Wang works in a recycling center. Recyclable materials arrive at the center mixed. Workers use magnets to separate steel cans from other items. Which two statements are true about the force between a steel can and a magnet?
Answers
Answer:
Option 3, The attraction between the can and the magnet is a pull.
Explanation:
The complete question is
Mr. Wang works in a recycling center. Recyclable materials arrive at the
center mixed together. Workers use magnets to separate steel cans from
other items. Which two statements are true about the force between a steel can and a magnet?
1 Gravity pushes the can toward the magnet.
2 The force between the can and the magnet is a noncontact force.
3 The attraction between the can and the magnet is a pull.
4 The attraction between the can and the magnet is a push
Solution
The force exerted by magnet on steel is the pull force. In magnets unlike poles attract each other (pull force) while the like poles repel (push force). Now, the steel or any ferrous object in the garbage when experience magnetic field develop magnetic field of their own in such a way that their north always faces the south of the external magnet or vice versa.
Hence, the force between a steel can and a magnet is pull force
N2O4 ⇌ 2NO2
for the following reaction at 373 K, Kc = 0.36. If initial concentration of N2O4 is 0.1 mol dm^-3, what is the equilibrium concentration of NO2? (Is there a way to solve this without using quadratics?)
Answers
Okay, let's solve this step-by-step without using quadratics:
1) The equilibrium constant Kc = 0.36 means the equilibrium lies to the left. So there will be more N2O4 than NO2 at equilibrium.
2) The initial concentration of N2O4 is 0.1 mol dm^-3. Let's call this [N2O4]initial.
3) At equilibrium, the concentrations of N2O4 and NO2 will be [N2O4]equil and [NO2]equil respectively.
4) We know the equilibrium constant expression for this reaction is:
Kc = ([NO2]equil)^2 / [N2O4]equil
5) Setting this equal to 0.36 and plugging in 0.1 for [N2O4]initial, we get:
0.36 = ([NO2]equil)^2 / (0.1 - [NO2]equil)
6) Simplifying, we get:
0.036 = [NO2]equil^2
7) Taking the square root of both sides, we get:
[NO2]equil = 0.06 mol dm^-3
So the equilibrium concentration of NO2 is 0.06 mol dm^-3.
Let me know if you have any other questions! I can also provide a more step-by-step explanation if needed.
if you have 20 grams of carbon-14 and it goes through 2 half lives, how much carbon-14 is left?
Answers
Answer: I belive it is 25%. Correct me if you know the answer or think I am wrong.
Explanation:
Looking at a potential energy diagram what is the name given to represent the amount of energy given off during an exothermal reaction?
Released energy
Stored energy
Activation energy
Free energy
Answers
Answer:
Released energy
Explanation:
Answer:
The answer is: Released energy
Hope this helped <33
Explanation:
3. Chemical A has a pH value of 9.0. How many times more acidic is chemical B, with a pH value of 8.2, than chemical A? Recall: pH = -log[H]
Answers
The ratio indicates that the hydrogen ion concentration of chemical A is 0.158 times lower than that of chemical B. Alternatively, the hydrogen ion concentration of chemical B is 6.31 times more acidic than that of chemical A.
The pH value of a substance is an essential indicator of its acidity or alkalinity. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14. The midpoint of the scale is 7.0, which is neutral. Solutions with pH values below 7.0 are acidic, while those with pH values above 7.0 are alkaline.
Acid solutions have a high concentration of hydrogen ions. The negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration (H+) is referred to as the pH. Similarly, solutions with a high hydroxide ion concentration have high pH values. The formula for pH is pH = -log[H].
1. Calculation of [H+] for Chemical A:Hence, we can rearrange the pH equation to calculate the hydrogen ion concentration as follows:[H] = 10^-pH= 10^-9= 1.0 × 10^-9 mol/L2. Calculation of [H+] for Chemical B:pH = -log[H]log[H] = -pHlog[H] = -8.2[H] = 10^-pH[H] = 6.31 × 10^-9 mol/L3.
Calculation of the ratio of [H+] for Chemical A and Chemical B:The ratio of [H+] for chemical A to that of chemical B can be found using the following formula:Ratio = [H+] of Chemical A / [H+] of Chemical B= (1.0 × 10^-9) / (6.31 × 10^-9)= 0.158The ratio indicates that the hydrogen ion concentration of chemical A is 0.158 times lower than that of chemical B. Alternatively, the hydrogen ion concentration of chemical B is 6.31 times more acidic than that of chemical A.
To learn more about hydrogen visit;
https://brainly.com/question/30623765
#SPJ11
what is the third quantum number of a 3 s 2 electron in phosphorus, 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 6 3 s 2 3 p 3 ?
Answers
The third quantum number (m_l) of a 3s² electron in phosphorus is 0.
The third quantum number, denoted as m_l, represents the magnetic quantum number and describes the orientation of an orbital within a subshell. It can have integer values ranging from -l to +l, where l is the azimuthal quantum number.
In the electron configuration of phosphorus, we see that the 3s subshell is being filled. The azimuthal quantum number (l) for the 3s subshell is 0. Since the electron is in the 3s² subshell, there are two electrons present in the 3s orbital.
For the two electrons in the 3s orbital, they will have opposite spins due to the Pauli exclusion principle. However, the magnetic quantum number (m_l) for both electrons in the 3s orbital will be the same, which is 0.
Therefore, the third quantum number (m_l) of a 3s² electron in phosphorus is 0. This means that both electrons in the 3s orbital have the same orientation within the subshell.
To learn more about quantum number, here
https://brainly.com/question/31955577
#SPJ4
Calculate 8D of water vapor in isotopic equilib- rium with fresh water whose 8D value is -65%0, assuming that a (liquid-vapor) = 1.090.
Answers
The value of 8D of water vapor in isotopic equilibrium with fresh water whose 8D value is -65%0 is -67.79125‰.
The expression for calculating 8D of water vapor in isotopic equilibrium with fresh water can be given by: 8D = α 8D (vapor) + (1 - α) 8D (liquid). Where,α is a fractionation factor and 8D (vapor) and 8D (liquid) are the deuterium enrichments in water vapor and liquid, respectively.
The value of α is given by:a (liquid-vapor) = 1.090So,α = (a (liquid-vapor) - 1) / (a (liquid-vapor) + 1)α = (1.090 - 1) / (1.090 + 1)α = 0.045So,8D = α 8D (vapor) + (1 - α) 8D (liquid)Given,8D (liquid) = -65‰ (‰ denotes permil, which is equal to parts per thousand)
Substitute the given values in the expression and simplify:8D = 0.045 × 8D (vapor) + (1 - 0.045) × (-65)8D = 0.045 × 8D (vapor) - 61.9258D + 2.79125 = 8D (vapor)
Therefore,8D (vapor) = 8D - 2.79125= -65 - 2.79125= -67.79125‰ (answer)Therefore, the value of 8D of water vapor in isotopic equilibrium with fresh water whose 8D value is -65%0 is -67.79125‰.
To learn more about vapor visit;
https://brainly.com/question/32499566
#SPJ11
There are 0.55 moles of carbon dioxide gas in a 15.0 L container. This container is at a temperature of 300 K. What is the pressure of the gas inside the container? Use 8.31 L*kPa/mol*K for the gas constant.
A.)760 mm Hg\
B.) 271 kPa
C.) 2 atm
D.) 91.4 kPa
Answers
Answer:
\(\large \boxed{\text{D.) 91 kPa}}\)
Explanation:
We can use the Ideal Gas Law — pV = nRT
Data:
V = 15.0 L
n = 0.55 mol
T = 300 K
Calculation:
\(\begin{array}{rcl}pV & =& nRT\\p \times \text{15.0 L} & = & \text{0.55 mol} \times \text{8.31 kPa$\cdot$ L$\cdot$K$^{-1}$mol$^{-1}\times$ 300 K}\\15.0p & = & \text{1370 kPa}\\p & = & \textbf{91 kPa}\end{array}\\\text{The pressure in the container is $\large \boxed{\textbf{91 kPa}}$}\)