what percentage of 2-digit positive integers have a tens digit that is one greater than the ones digit?
Answers
10% of 2-digit positive integers have a tens digit that is one greater than the ones digit.
To solve this problem, we first need to determine how many 2-digit positive integers there are. Since the smallest 2-digit integer is 10 and the largest is 99, we have a total of 90 integers (99-10+1).
Next, we need to determine how many of these integers have a tens digit that is one greater than the ones digit. To do this, we can create a chart and list out all possible combinations:
10, 21, 32, 43, 54, 65, 76, 87, 98
There are a total of 9 such integers. Therefore, the percentage of 2-digit positive integers that have a tens digit that is one greater than the ones digit is:
9/90 * 100% = 10%
So, 10% of 2-digit positive integers have a tens digit that is one greater than the ones digit.
To answer your question, let's first identify the range of 2-digit positive integers and determine the number of combinations where the tens digit is one greater than the ones digit.
The range of 2-digit positive integers is from 10 to 99. Now, we need to find the pairs of digits where the tens digit is one greater than the ones digit. The possible pairs are:
(1,0), (2,1), (3,2), (4,3), (5,4), (6,5), (7,6), (8,7), and (9,8)
There are 9 pairs that meet the condition. Now we need to find the total number of 2-digit positive integers:
99 (the last 2-digit integer) - 10 (the first 2-digit integer) + 1 = 90
So, there are 90 two-digit positive integers in total.
Now, we can calculate the percentage of the 2-digit positive integers that have a tens digit one greater than the ones digit:
(9 / 90) * 100 = 10%
Therefore, 10% of 2-digit positive integers have a tens digit that is one greater than the ones digit.
Learn more about integers at: brainly.com/question/1768254
#SPJ11
Approximately 4.44% of 2-digit positive integers have a tens digit that is one greater than the ones digit.
Let's consider the possible pairs of tens digit and ones digit that satisfy the condition. There are 4 such pairs: \((1, 0)$, $(2, 1)$, $(3, 2)$\), and \((4, 3)$.\) For each tens digit, there is exactly one ones digit that satisfies the condition. So, out of the 90 possible two-digit positive integers (ranging from 10 to 99), only 4 of them have a tens digit that is one greater than the ones digit.
Therefore, the percentage of 2-digit positive integers that have a tens digit that is one greater than the ones digit is:
\($\frac{4}{90} \cdot 100% \approx 4.44%$\)
So, approximately 4.44% of 2-digit positive integers have a tens digit that is one greater than the ones digit.
Learn more about integers ,
https://brainly.com/question/15276410
#SPJ4
Related Questions
When Ashley left her house in the morning, her cell phone battery was partially charged. Let B represent the charge remaining in Ashley's battery, as a percentage, t hours since Ashley left her house. A graph of B is shown below. Write an equation for B then state the y-intercept of the graph and determine its interpretation in the context of the problem.
B = _____
The y-intercept of the function is ___ which represents
(A) the number of hours until Ashley's phone dies.
(B) the charge of the battery when Ashley left her house
(C) the percentage charge that Ashley's phone loses each hour
(D) the charge of the battery when Ashley woke up.
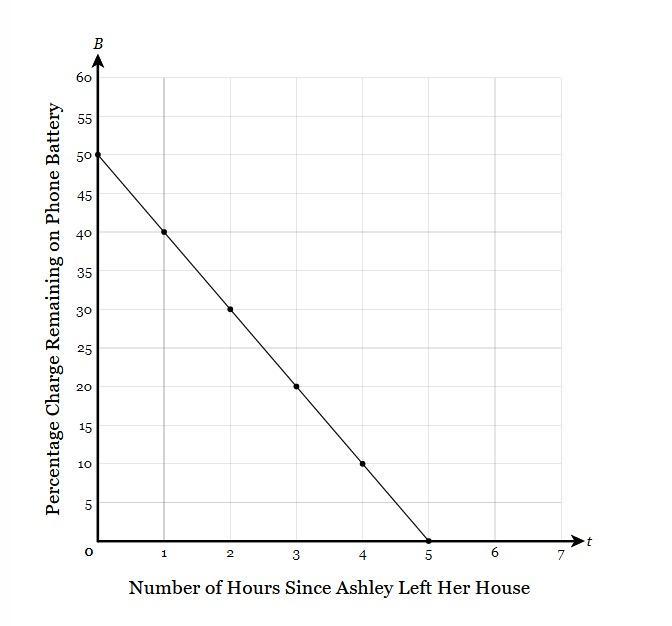
Answers
The y-intercept of the function is 50% which represents; (B) the charge of the battery when Ashley left her house
What is the y-intercept of the Linear Graph?The general format for the equation of a line in slope intercept form is;
y = mx + b
where;
m is slope
b is y-intercept
Now, the y-intercept is defined as the point where the graph line crosses the y-axis or the point at which x is zero.
The slope is defined as the ratio of change of the vertical axis with the horizontal axis.
From the given linear graph, we can see that;
The line intersects the y-axis at y = 50. Thus;
y-intercept = 50
Now, the y-axis represent the percentage charge remaining on the phone battery while the x-axis shows that number of hours since Ashley left her house. Thus;
When the number of hours is zero, the percentage charge remaining on the phone battery is 50%
Read more about y-intercept at; https://brainly.com/question/26249361
#SPJ1
Find an explicit solution for y ′ =ye^ −x2 ,y(0)=1
. It is alright to leave a definite integral in your answer.
Answers
The explicit solution for y = e^(x^2/2).
The explicit solution for the given differential equation is y = e^(x^2/2) * e^(C), where C is an integral constant. Substituting the initial condition, y(0) = 1, gives C = 0, thus the solution is y = e^(x^2/2).
Learn more about Explicit solution
brainly.com/question/24029948
#SPJ11
357.45 divided to 10 to the power of 4 is?
Answers
Answer:
1.63253e+6
Step-by-step explanation:
Answer:
0.035745
Step-by-step explanation:
\(10^{4}=10,000\\\)
357.45 ÷ 10,000 = Moving the decimal towards three, four times.
00357.45
0035.745 (One)
003.745 (Two)
00.3745 (Three)
0.03745 (Four)
357.45 ÷ 10,000 = 0.035745
What is the cube root of 64 over 343? The 64 over 343 is a fraction. What is it rounded to the nearest tenth?
Answers
Answer:
0.6
Step-by-step explanation:
Given problem:
\(\sqrt[3]{\frac{64}{343} }\)
if an expression is of this form, we simplify
\(\sqrt[3]{x}\) = \(x^{\frac{1}{3} }\)
\(\sqrt[3]{\frac{64}{343} }\) = \(\frac{64^{\frac{1}{3} } }{343\frac{1}{3} }\)
= \(\frac{4^{3x ^{\frac{1}{3} } } }{7 ^{3 ^x{\frac{1}{3} } } }\)
= \(\frac{4}{7}\)
= 0.57 to the nearest tenth
= 0.6
ignore the answer chosen but does anyone know the answer to this pls asap!!

Answers
Answer:
The diagonals bisect each other
Step-by-step explanation:
2s = 10 s+5 = 10 FJ = JH
t+12 = 18 3t = 18 EJ = JG
An analysis class has 13 seats. How many different ways can they be assigned to a group of 5 students?
Answers
Answer:
2.6
Step-by-step explanation:
13/5 is 2.6
I hope i am right but if not then i am so sorry
2.1 The sieve analysis results for an aggregate sample is displayed below. (a) Calculate the percentage passing for each sieve size
Answers
We determine the cumulative weight retained at each sieve and then calculate the cumulative percentage passing by dividing the cumulative weight passing by the total weight of the sample and multiplying by 100.
To calculate the percentage passing for each sieve size in a sieve analysis, we need to determine the cumulative percentage passing at each sieve size.
The sieve analysis provides information about the particle size distribution of an aggregate sample. It involves passing the sample through a series of sieves with different mesh sizes, and measuring the amount of material retained on each sieve.
To calculate the percentage passing, we first need to determine the cumulative weight retained at each sieve size. This is done by subtracting the weight retained on a particular sieve from the weight retained on the previous sieve.
Once we have the cumulative weight retained, we can calculate the cumulative percentage passing by dividing the cumulative weight passing by the total weight of the sample and multiplying by 100.
Here is an example:
Sieve Size (mm) | Weight Retained (g)
4.75 | 50
2.36 | 30
1.18 | 20
0.6 | 15
0.3 | 10
0.15 | 5
To calculate the cumulative percentage passing:
Calculate the cumulative weight retained:
Cumulative weight retained at sieve 4.75 mm = 50 g
Cumulative weight retained at sieve 2.36 mm = 50 g + 30 g = 80 g
Cumulative weight retained at sieve 1.18 mm = 80 g + 20 g = 100 g
Cumulative weight retained at sieve 0.6 mm = 100 g + 15 g = 115 g
Cumulative weight retained at sieve 0.3 mm = 115 g + 10 g = 125 g
Cumulative weight retained at sieve 0.15 mm = 125 g + 5 g = 130 g
Calculate the cumulative percentage passing:
Cumulative percentage passing at sieve 4.75 mm = (Total weight - Cumulative weight retained) / Total weight * 100 = (130 g - 50 g) / 130 g * 100 = 61.54%
Cumulative percentage passing at sieve 2.36 mm = (130 g - 80 g) / 130 g * 100 = 38.46%
Cumulative percentage passing at sieve 1.18 mm = (130 g - 100 g) / 130 g * 100 = 23.08%
Cumulative percentage passing at sieve 0.6 mm = (130 g - 115 g) / 130 g * 100 = 11.54%
Cumulative percentage passing at sieve 0.3 mm = (130 g - 125 g) / 130 g * 100 = 3.85%
Cumulative percentage passing at sieve 0.15 mm = (130 g - 130 g) / 130 g * 100 = 0%
Learn more about distribution here:
https://brainly.com/question/29664127
#SPJ11
Consider the initial value problem:
y" + 2y²y" - yy = sint
y(0) = y'(0) = 0, y" (0) = 1.
3.1) Write the higher order ODE as an initial value problem of a system of first-order ODES. 3.2) State (without proof) the formula for the fourth-order Runge-Kutta method in vector form. 3.3) Use the fourth-order Runge-Kutta method to approximate the solution y(1) with stepsize h = 0.5. Perform the calculations correctly to four decimals.
Answers
3.1) Initial conditions y(0) = 0, z(0) = 0, and w(0) = 1.
3.2) Where yn is the vector of approximate values at time tn, h is the step size, and f(tn, yn) is the vector-valued function that defines the differential equation.
3.3) The approximate solution to the initial value problem with step size h=0.5 is y(1) ≈ 0.1267 (rounded to four decimals).
3.1) To write the higher order ODE as an initial value problem of a system of first-order ODEs, we can introduce new variables z = y' and w = y". Then, we have:
y' = z
z' = yy - 2y²w + sint
w' = z
with initial conditions y(0) = 0, z(0) = 0, and w(0) = 1.
3.2) The formula for the fourth-order Runge-Kutta method in vector form is:
k1 = hf(tn, yn)
k2 = hf(tn + h/2, yn + k1/2)
k3 = hf(tn + h/2, yn + k2/2)
k4 = hf(tn + h, yn + k3)
yn+1 = yn + (k1 + 2k2 + 2k3 + k4)/6
where yn is the vector of approximate values at time tn, h is the step size, and f(tn, yn) is the vector-valued function that defines the differential equation.
3.3) Using the fourth-order Runge-Kutta method with step size h=0.5, we can approximate the solution y(1) by iteratively applying the above formula until we reach t=1. Starting with the initial conditions y(0) = 0, z(0) = 0, and w(0) = 1, we obtain the following results:
At t=0.5, we have y(0.5) = 0.0000, z(0.5) = 0.5000, and w(0.5) = 0.7502.
At t=1, we have y(1) = 0.1267, z(1) = 0.9353, and w(1) = 0.6007.
Therefore, the approximate solution to the initial value problem with step size h=0.5 is y(1) ≈ 0.1267 (rounded to four decimals).
Learn more about Initial conditions here:
https://brainly.com/question/32237720
#SPJ11
the point at which the medians intersect in a triangle
Answers
Hope this helps
You roll a number cube and then spin a spinner with two equal-sized sections.
What is the probability of rolling a number greater than 3 and spinning red?
A. 1/4
B. 1/6
C. 1/3
D. 1/2
Please explain how got the answer

Answers
Answer:What is the probability of spinning a 2 on the spinner?
Image result for You roll a number cube and then spin a spinner with two equal-sized sections. What is the probability of rolling a number greater than 3 and spinning red? A. 1/4 B. 1/6 C. 1/3 D. 1/2
There are 2 sections on the spinner that contain a '2'. The probability of spinning a 2 is 2 / 8 . The probability of spinning a 3 is also 2 / 8
Step-by-step explanation:
The probability of rolling a number greater than 3 and spinning red is 1/4.
We need to determine the favorable outcomes (the outcomes that satisfy both conditions) and the total possible outcomes.
The numbers greater than 3 and corresponding to the red section are: 4R, 5R, and 6R. So, there are 3 favorable outcomes.
Since we have a number cube with 6 sides and a spinner with 2 sections, the total possible outcomes are the product of the number of sides on the cube and the number of sections on the spinner, which is 6 × 2 = 12.
The probability is calculated by dividing the number of favorable outcomes by the total possible outcomes.
Probability = Favorable outcomes / Total possible outcomes
= 3 / 12
= 1 / 4
To learn more on probability click:
https://brainly.com/question/11234923
#SPJ2
Write a couple sentences to explain how you would find the area of the shaded region:

Answers
Answer:
I would find the area of the circle and then find the area of the shape in the middle and then minus that from the area of the whole circle
Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
1. Find the area of the circle. Area_c = pi * r^2
2.Find the area of the pentagon in terms of the radius Area_P =
3 sqrt(3) r^2 / 2
The answer you want is Area_shade = Area_c - area_P
Area = pi * r^2 - 3 sqrt(3)r^2/2
Area = r^2 (pi - 3 sqrt(3)/2)
If she worked 13 hours during the week and 14 hours on the weekend she earns 250.90 if she works 15 hours during the week and eight hours on the weekend she earns 204 .70 how much more does Charlotte earn per hour on the weekends then she earns during the week
Answers
Answer:
x=8.1 /hour during the week
y=10.4 /hour in the weekend
Step-by-step explanation:
x=earnings during the week
y= earnings in the wekend
13x+14y=250.90 |*-4
15x+8y=204.70 |*7
-52x-56y=-1003.6
105x+56y=1432.9
---------------------------
53x=429.3
x=8.1 /hour during the week
15*8.1+8y=204.7
121.5+8y=204.7
-121.5 -121.5
8y=83.2
:8 :8
y=10.4 /hour in the weekend
Someone help me please

Answers
Step-by-step explanation:
Step 1: Convert degrees into radians
\(\frac{degrees}{1}*\frac{\pi }{180}\)
\(\frac{52}{1}*\frac{\pi}{180}\)
\(\frac{52\pi}{180}\)
\(\frac{13\pi}{45}\)
Step 2: Find the arc length
\(S = r\theta\)
\(S=(3)(\frac{13\pi}{45})\)
\(S = \frac{39\pi}{45}\)
\(S=\frac{13\pi}{15}\)
Answer: Option B
Find the gradient of the straight line joining A(2,-5) and B(-7,-3).
1. -9/2
2. -2/9
3. -9
4. 1/9
Answers
Answer:
Step-by-step explanation: I do know bro is, sorry
brian, tim and kenny got paid a total of $240 for mowing neighborhood lawns . They split the money in the ratio of 5:9:10 . how much money did each boy make . PLEAEEEE SHOW THE work i’m really struggling rn
Answers
Answer:
$50 for Brian
$90 for Tim
$100 for Kenny
Step-by-step explanation:
Let 5x = amt for Brian
9x = amt for tim
10x = amt for ken
5x + 9x + 10x = 240
24x = 240
x = 10
5x = 5(10) = $50 for Brian
9x = 9(10) = $90 for Tim
10x = 10(10) = $100 for Kenny
Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
5x + 9x + 10x = $240
x = $10
Brian got 5x = $50
Tim got 9x = $90
Kenny got 10x = $100
I WILL MARK BRAINLIEST.
Find the product of 3.2 x 1012 and 4.25 x 109. Write the final answer in scientific notation.
1.36 x 1021
13.6 x 1021
1.36 x 1022
13.6 x 1022
Answers
The product in scientific notation is 1.36 x 10^22
How to find the product of 3.2 x 1012 and 4.25 x 109?The product expression is given as:
3.2 x 1012 and 4.25 x 109
Express the product, properly
3.2 x 10^12 x 4.25 x 10^9
Regroup the factors
3.2 x 4.25 x 10^12 x 10^9
Evaluate the product
13.6 x 10^21
Rewrite as:
1.36 x 10^22
Hence, the product in scientific notation is 1.36 x 10^22
Read more about scientific notation at
https://brainly.com/question/5756316
#SPJ1
Answer:
c 1.36 x 1012
explanation:
Suppose that X and Y are random variables and that X and Y are nonnegative for all points in a sample space S. Let Z be the random variable defined by Z(s) = max(X(s), Y (s)) for all elements s â S. Show that E(Z) ⤠E(X) + E(Y).
Answers
For the Random variables, X and Y where both are nonnegative for all points in a sample space S. The expected value of Z ( random variable) is, E(Z) = E(X) + E(Y).
We have X and Y are random variables and that X and Y are non-negative for all points in a sample space S. Let us consider X be another random variable defined as Z(s) = max( X(s), Y(s))
for all elements s belongs to S. We have to show that E( Z) = E(X) + E(Y)
Now, for simple way of representation let
Max ( X(s),Y(s)) = Max(X,Y)
We know that Max(X,Y) = [(X+Y) + |X-Y|]
So, Z = Max(X,Y) = [(X+Y) + |X-Y|]
Taking expectations E(Z) = E(Max(X,Y)
= E{[(X+Y) + |X-Y|]}
\(E(Z)= \frac{1}{2} [E(X+Y) + E|X-Y|] = [E(X) + E(Y) + E|X-Y|] \\ \) (Since E(X + Y) = E(X)+ E(Y))
\(E(Z) = \frac{1}{2}[E(X)+ E(Y) + E|X| + E|-Y|]\\ \)
\(= \frac{1}{2} [E(X) + E(Y) + E(X) + E(Y)]\) (Since X and Y are non negative so E|X| = E(X) and E(-Y)=E(Y) )
=> E(Z) = E(X)+ E(Y)
Hence, required results occurred.
For more information about expected value, visit :
https://brainly.com/question/24140707
#SPJ4
- 8x – 3=17 - given -8x=20
Answers
Answer:
-20
Step-by-step explanation:
I belive )
you could check using the internet step by step
For a standard normal distribution, find:P(1 < z < 2) = _______ % to one decimal place.
Answers
Write P(1 < Z < 2) as
P(1 < Z < 2) = P(0 < Z < 2) - P(0< Z < 1)
From the standard normal table,
P(0 < Z < 2) = 0.4772
and
P(0 < Z < 1) =0.3413
Then,
\(\begin{gathered} P\mleft(1
for educational purposes which is better vans or nike?
Answers
Which number best represents the location of point A on the number line shown?
A) -7.5
B) 7 3/10 (Fraction Answer)
C) 7 3/8 (Fraction Answer)
D) 7 3/7 (Fraction Answer)

Answers
B) \(7 \frac{3}{10} \)
This is the only fraction that converts into 7.3 (location of point a).
Let me convert it for you
\(7 \frac{3}{10} \\ \\ \frac{73}{10} \\ \\ 7.3\)
The location of point A is 7.3
The football team has a total 50 jerseys. There are 10 medium-sized jerseys. What percent of the jerseys are medium-sized jerseys?
Answers
Answer:
20 percent
Step-by-step explanation:
20% of 50 is 10
Answer:
20%
Step-by-step explanation:
10/50 = .2 or 0.2
and then u multiply that by 100.
.2 X 100 = 20%
Hope that Helps! :)
Triangle XYZ is translated by the rule (x + 1, y − 1) and then dilated by a scale factor of 4 centered at the origin. Which statement describes the properties of triangles XYZ and X''Y''Z'' after the transformations?
A. Y and ∠Y'' are congruent after the translation, but not after the dilation.
B. ∠Y and ∠Y'' are congruent after the dilation, but not after the translation.
C. segment YZ and segment Y double prime Z double prime are proportional after the translation, but not after the dilation.
D. segment YZ and segment Y double prime Z double prime are proportional after the dilation and congruent after the translation.
Answers
The statement that described the triangle properties is that the segment YZ and segment Y"Z" should be proportional when the dilation is done and it should be congruent when the translation should be done.
Given that,
There is the rule i.e. (x +1, y - 1) and it should be dilated by a scale factor of 4 centered at the origin.Based on the above information,
The figure should be proportional as the angle and the points should be the same. And, when the translation is done the image should be congruent to the pre-imageTherefore we can conclude that option d is correct.
Learn more: https://brainly.com/question/25063346
find the odds for rolling a 6-sided die and getting a 2. to find the odds against rolling a 6-sided die and getting a 2. to
Answers
The probability of an event not occurring refers to the probability of all other possible outcomes except for the event in question.
The odds for rolling a 6-sided die and getting a 2 are 1:5 or 1/5. This means that the probability of rolling a 2 is 1/6, and the probability of not rolling a 2 is 5/6. To find the odds against rolling a 6-sided die and getting a 2, we simply invert the odds for rolling a 2, which gives us the odds of rolling any number other than 2. The odds against rolling a 6-sided die and getting a 2 are therefore 5:1 or 5/1. This means that the probability of not rolling a 2 is 5/6, and the probability of rolling a 2 is 1/6. It's important to note that the odds against an event are not the same as the probability of that event not occurring. The odds against an event refer to the ratio of the number of unfavorable outcomes to the number of favorable outcomes, while the probability of an event not occurring refers to the probability of all other possible outcomes except for the event in question.
Learn more about probability here
https://brainly.com/question/13604758
#SPJ11
56 is less than the square of 10
Answers
From the given condition, we get X = X^2–56
=> X^2-X-56=0
Factorizing the above equation,
=> X^2–8X+7X-56=0
X(X-8)+7(X-8)=0
(X-8)(X+7)=0
X=8 or -7
Since it is said the number is positive. Our output number will be 7
Differentiate the function.
H(z)=ln[(d2-z2)/(d2+z2)]^1/2
Natural log of the square root of (d2-z2) divided by (d2+z2).
Answers
The derivative of H(z) is H'(z) = -2zd^2/[(d^2-z^2)(d^2+z^2)].
To differentiate the function H(z) = ln[(d^2-z^2)/(d^2+z^2)]^(1/2), we will use the chain rule and the power rule of differentiation.
First, we can simplify the expression inside the natural logarithm using the laws of exponents:
[(d^2-z^2)/(d^2+z^2)]^(1/2) = [(d^2-z^2)^(1/2)/(d^2+z^2)^(1/2)]
Now we can differentiate H(z) as follows:
H'(z) = d/dz [ln[(d^2-z^2)/(d^2+z^2)]^(1/2)]
= (1/2)[(d^2+z^2)^(1/2)/(d^2-z^2)^(1/2)] * d/dz [(d^2-z^2)/(d^2+z^2)]
Using the quotient rule, we can simplify the derivative:
d/dz [(d^2-z^2)/(d^2+z^2)] = [(2z)(d^2+z^2) - (d^2-z^2)(2z)]/(d^2+z^2)^2
= -4zd^2/(d^2+z^2)^2
Substituting this back into H'(z), we get:
H'(z) = (1/2)[(d^2+z^2)^(1/2)/(d^2-z^2)^(1/2)] * (-4zd^2/(d^2+z^2)^2)
= -2zd^2/[(d^2-z^2)(d^2+z^2)]
Therefore, the derivative of H(z) is:
H'(z) = -2zd^2/[(d^2-z^2)(d^2+z^2)]
Learn more about derivative here
https://brainly.com/question/31399608
#SPJ11
find the common ratio.
1\text{,}2\text{,}4\text{,}8\text{,}16\text{,}..1,2,4,8,16,...
48\text{,}12\text{,}4\text{, }2\text{,}..48,12,4, 2,...
Answers
The common ratios of the sequence are 4 and 1/4
How to calculate the common ratioFrom the question, we have the following parameters that can be used in our computation:
Sequence 1
1, 2, 4, 8, 16,...
The common ratio is the quotient of a term and the previous term
Using the first term and the second term, we have
Common ratio = Second term/First term
Substitute the known values in the above equation, so, we have the following representation
Common ratio = 2/1
Evaluate
Common ratio = 2
Sequence 2
Here, we have
48, 12, 4, 2,...
The common ratio is the quotient of a term and the previous term
Using the first term and the second term, we have
Common ratio = Second term/First term
Substitute the known values in the above equation, so, we have the following representation
Common ratio = 12/48
Evaluate
Common ratio = 1/4
Hence, the common ratio is 1/4
Read more about common ratio at
https://brainly.com/question/7153798
#SPJ1
HELP PLEASEEEE simplify (4^3)^5

Answers
Step-by-step explanation:
(4^3)^5 = 4^(3×5) = 4^15 (option C)
So
(4³)⁵4^{3(5)}4¹⁵Graph the linear function that passes through the point (1. -9) and has a slope of -3. (just give me points :)
What is the zero of the function?
Answers
The slope intercept form is y=-3x-6.
And the zero of the function is x=-2.
To find the graph, use the slope intercept equation and the points.
The roots or “Zeros” are the x values where the graph intersects the x-axis. To find the roots (zeros), replace y with 0 and solve for X.
Explain why it is necessary to check whether the population is approximately normal before constructing a confidence interval.
Answers
Checking for approximate normality in the population is essential for constructing a valid confidence interval, particularly when dealing with small sample sizes. This ensures the accuracy and reliability of the interval in estimating the true population parameter.
It's important to check whether the population is approximately normal before constructing a confidence interval because the accuracy and validity of the interval depend on the underlying distribution of the population. Here's a step-by-step explanation:
1. A confidence interval is a range of values within which the true population parameter (e.g., mean or proportion) is likely to fall, with a certain level of confidence (e.g., 95% or 99%).
2. The process of constructing a confidence interval relies on the Central Limit Theorem, which states that, for large sample sizes, the sampling distribution of the sample mean will be approximately normal, regardless of the population distribution.
3. However, for small sample sizes, the distribution of the population needs to be approximately normal in order to obtain an accurate confidence interval. This is because the normality assumption is crucial for the proper interpretation of the interval.
4. If the population is not approximately normal, the confidence interval may not provide a reliable estimate of the true population parameter, leading to incorrect conclusions and potentially invalid results.
Learn more about Central limit theorem here: brainly.com/question/18403552
#SPJ11