Two or more tissues grouped together and performing specialized
functions defines a(n).
a. organelle
b. cell
c. organ
d. organ system
Answers
Answer:
\(c. \: organ\)
Answer:
C.
Explanation:
Related Questions
Josh is playing pool. During his shot, an orange billiard ball with a momentum of 165 g · m/s hits a green billiard ball at rest. After the collision, the orange billiard ball continues in the same direction with a momentum of 60 g · m/s. What is the momentum of the green ball right after the collision?
Answers
Answer:
105 g.m/s
Explanation:
The law of conservation of momemtum states that initial momemtum is equal to final momentum.
initial momentum of orange ball = 165 g.m/s
initial momentum of green ball = 0 g.m/s
final momentum of orange ball = 60 g.m/s
final momentum of green ball = x
165+0=60+x
⇒x = 165-60= 105 g.m/s
the momentum of the green ball right after the collision =105 g.m/s
The pressure of water flowing through a 6.5×10−2 −m -radius pipe at a speed of 2.0 m/s is 2.2 ×105 N/m2.
a.) What is the flow rate of the water?
b.) What is the pressure in the water after it goes up a 6.0 −m -high hill and flows in a 4.1×10−2 −m -radius pipe?
Answers
Q = π r₁² v₁ = π r₂² v₂v₂ = (r₁ / r₂)² v₁v₂ = (6.5 x 10^-2 / 4.1 x 10^-2)² x 2v₂ = 2.9 m/s, Substituting the value of v₂ in equation we get:P₂ = 1.37 x 10^5 N/m²
Radius of the pipe, r = 6.5 x 10^-2 mSpeed of water flow, v = 2.0 m/sPressure of water flow, P = 2.2 x 10^5 N/m²Formula used: Poiseuille's EquationThe flow rate of water through a pipe is given by Poiseuille's Equation which is expressed as:Q = πr⁴ΔP / 8ηlWhere Q is the flow rate of the fluid in the pipe,r is the radius of the pipe
ΔP is the pressure difference between the ends of the pipeη is the viscosity of the fluidl is the length of the pipeFrom the given values, the pressure difference ΔP = P = 2.2 x 10^5 N/m²The viscosity of water is 0.89 x 10^-3 N s/m²Length of the pipe can be assumed to be equal to 1mSubstituting the given values in the equation we get,Q = π (6.5 x 10^-2)⁴ (2.2 x 10^5) / (8 x 0.89 x 10^-3 x 1)Q = 5.1 x 10^-5 m³/s
To know more about equation visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/29657983
#SPJ11
If you drive a newer vehicle, it features vehicle impact and restraint systems designed to absorb energy and help protect you in a crash. The vehicle impact and restraint systems all work together. These systems help reduce injury and provide occupant impact protection.T/F
Answers
True. In newer vehicles, vehicle impact and restraint systems are designed to work together to absorb energy and protect occupants in a crash.
These systems help reduce injury and provide occupant impact protection.
Vehicle manufacturers invest significant effort into designing and implementing safety features that enhance occupant protection in the event of a collision.
These safety features include various structural components, such as crumple zones, reinforced frames, and impact-absorbing materials, which are strategically positioned throughout the vehicle's body.
Crumple zones, located at the front and rear of the vehicle, are engineered to deform and absorb energy during a crash. When a collision occurs, these areas are designed to crumple and collapse, effectively dissipating the energy of the impact.
By doing so, crumple zones help protect the vehicle's occupants by reducing the forces transferred to the passenger compartment.
Furthermore, vehicles are equipped with restraint systems, such as airbags and seat belts, which play a crucial role in occupant protection. Airbags are designed to rapidly inflate upon impact, providing an additional cushioning effect and reducing the risk of head and chest injuries.
Seat belts are instrumental in restraining occupants and preventing them from being thrown forward or out of the vehicle during a collision.
To learn more about compartment, refer below:
https://brainly.com/question/30833077
#SPJ11
your new designer chair has an s shaped tubular metal frame that behaves just like a spring. when your friend, who weighs 581 n, sits on the chair, it bends downward 3.00 cm. what is the spring constant for this chair?
Answers
The spring constant for this chair is the amount of force (in Newtons) that needs to be applied to the chair in order to cause it to bend by one meter. In this particular case, the chair bends 3.00 cm when a person who weighs 581 N sits on it.
Therefore, the spring constant of this chair can be calculated by dividing the weight of the person (581 N) by the distance the chair bends (0.03 m). This gives us a spring constant of 19,367 N/m.
In general, the spring constant for any system with a spring-like behavior is a measure of the stiffness of the system. A higher spring constant means that the system is more resistant to bending and will require more force to bend by a certain distance. This is why in this case, a higher weight requires a higher spring constant to bend the chair by the same amount.
Know more about stiffness here
https://brainly.com/question/13095331#
#SPJ11
This sport involves travelling down a
fast-flowing river in an inflatable boat.
What is called?
Answers
Answer: rafting
Explanation:
this sport is called rafting because they go down a river with fast paced water and a blow up boat because they do it for a thrill like a water ride.
A. It Implies That M Is Finitely Generated. B. It Implies That M Has Nonzero Elements Of Nonzero Order. C. When Every Non-Null Element Has Null . D. In The Case That The Ring R Is A Body. E. None Of The Above Alternatives Gives A
Which of the following alternatives give a true statement. Justify your answer.
A modulus M over a ring R has a finite basis:
a. It implies that M is finitely generated.
b. It implies that M has nonzero elements of nonzero order.
C. When every non-null element has null .
d. in the case that the ring R is a body.
e. None of the above alternatives gives a true statement.
Which of the following statements are true?
a. If a subset of a module generates that whole module, then the subset cannot be
empty.
b. Every submodule S of a module M verifies the inequality C. Two different subsets of M have to generate two different submodules of M.
d. If S generates a submodule N of the module M, then contains S.
e. Neither statement is true.
Answers
The correct answer is e. None of the above alternatives gives a true statement. None of the statements in options a, b, c, and d are true when it comes to a modulus M over a ring R having a finite basis.
When a modulus M can be formed entirely from a finite set of elements, the modulus M is said to be finitely generated. M's finite basis does not, however, automatically imply that M is finitely generated. A basis is a set of linearly independent elements, and it might not be enough to produce all of the components of the modulus.
According to the assertion in option b, M must include nonzero items of nonzero order if it has a finite basis. This is untrue, though. The smallest positive number k, such that the element raised to the power of k equals the identity element, is referred to as the order of an element.
According to option c, every non-null element in a modulus with a finite basis has a null. Nevertheless, this claim is likewise untrue. It is possible for a modulus with a finite basis to have non-null elements without a null element.
According to option d, a ring R is a body, or a field, and only then can a modulus have a finite basis. However, this assertion is also untrue. Even though the ring R is not a field, a modulus can nonetheless have a finite basis. None of the given alternatives provides a true statement about a modulus M over a ring R having a finite basis.
To know more about modulus here https://brainly.com/question/30402322
#SPJ4
what seems to control the assembly and disassembly of intermediate filaments?
Answers
The assembly and disassembly of IFs are regulated by a variety of factors, including phosphorylation, subunit availability, pH, and ionic strength.
Intermediate filaments (IFs) are components of the cytoskeleton that control a variety of biological processes. IFs are typically less dynamic than microtubules and actin filaments, and they appear to be more stable. The assembly and disassembly of intermediate filaments are regulated by phosphorylation-dephosphorylation mechanisms.
The assembly and disassembly of intermediate filaments are controlled by a variety of factors. One of the primary determinants of IF dynamics is phosphorylation. Phosphorylation of specific residues on the IF proteins affects both the ability of the protein to form filaments and its stability once it has formed a filament.
In some cases, the presence of free subunits can promote filament formation, while in others, the formation of complexes between subunits can inhibit filament assembly. Changes in pH or ionic strength can also affect the assembly and disassembly of IFs.Intermediate filaments (IFs) are cytoskeletal structures that are typically more stable than microtubules or actin filaments.
To know more about filaments visit :
https://brainly.com/question/31953314
#SPJ11
Fill The Blank? the tangential speed on the outer edge of a rotating carousel is _______.
Answers
The tangential speed on the outer edge of a rotating carousel is dependent on the carousel's rotational speed and the distance from the center of rotation to the outer edge.
It can be calculated using the formula: tangential speed = radius × angular speed
Where the radius is the distance from the center of rotation to the outer edge, and the angular speed is the rate of rotation measured in radians per second.
The carousel's rotational speed of a carousel refers to the rate at which it completes one full revolution, and it is usually measured in units of revolutions per minute (RPM) or radians per second (rad/s). The faster the carousel rotates, the higher the outer edge's tangential speed. The rotational speed of a carousel can be controlled by adjusting the power source that drives it, such as an electric motor.
To learn more about carousel's rotational speed, visit here
https://brainly.com/question/30608354
#SPJ4
what are theadvantages of high specific heat capicity of water?.
Answers
Answer:
There are several advantages to the high specific heat capacity of water. Some of the key advantages are:
1.Water can store a large amount of heat energy without undergoing significant temperature changes. This means that water can help to regulate the temperature of the Earth and other bodies of water, providing a stable environment for life to thrive.
2.The high specific heat capacity of water allows it to act as a buffer against temperature changes. For example, when the temperature outside is very hot, water bodies such as oceans and lakes can absorb some of the heat energy, preventing the temperature from getting too high. Similarly, when the temperature outside is very cold, water bodies can release some of their stored heat energy, helping to keep the temperature from dropping too low.
3.The high specific heat capacity of water also makes it a useful heat transfer medium. Water can be heated and then used to transfer heat to other objects, such as in a radiator or a steam engine. This allows water to be used in a variety of industrial and domestic applications.
The coldest clouds in the ISM are molecular clouds, so named because their temperatures are low enough and their densities high enough for atoms to join together into molecules. These clouds are capable of collapsing to form new stars, in a stellar nursery like the one in the left image. The Pleiades (right image) is an example of stars that formed recently within such a nursery.
Molecular clouds range in mass from a few times the mass of our Sun (solar masses) to 10 million solar masses. Individual stars range from 0.08 to about 150 solar masses.
What does all of this imply about how stars form from molecular clouds?
Answers
Stars form from molecular clouds through a process known as stellar formation.
These clouds, characterized by low temperatures and high densities, provide the ideal conditions for atoms to combine and form molecules. With a mass range spanning from a few solar masses to millions of solar masses, molecular clouds serve as the birthplaces of new stars. The Pleiades cluster serves as a notable example of stars that have recently formed within such a stellar nursery.
The formation of stars from molecular clouds involves several key steps. Firstly, gravitational forces acting on regions of higher density within the cloud cause them to collapse under their own gravity. As the cloud collapses, it begins to fragment into smaller, denser clumps called protostellar cores. These cores continue to collapse, and their central regions become increasingly dense and hot. At this stage, they are known as protostars.
To know more about molecular clouds here https://brainly.com/question/30631889
#SPJ4
While a camera has film where the image is formed, the eye forms the image on the:
a. pupil.
b. cornea.
c. retina.
d. optic nerve.
Answers
The eye forms the image on the retina. The correct option is c.
When light enters the eye, it passes through the cornea, the clear outer covering of the eye, and then through the pupil, which is the opening in the center of the iris. The iris is the colored part of the eye that helps to control the amount of light that enters. The lens then focuses the light onto the retina, which is a layer of light-sensitive cells located at the back of the eye.
These cells, called photoreceptors, convert the light into electrical signals that are sent to the brain via the optic nerve. The brain then processes these signals to create the visual image that we perceive. Therefore, the retina is where the actual image is formed in the eye, and the optic nerve carries this information to the brain for interpretation. Therefore, the correct option is c.retina.
To know more about photoreceptors refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/31935609#
#SPJ11
What is the difference between zone coverage and man coverage, and how can the offense team read those coverages?
Answers
Answer:
zone coverage is about sensing what the offense is attempting to accomplish against the defense. Each defensive player reacts when the ball is in the air, whereas in man-to-man coverage, he simply plays the receiver.
Explanation:
I am confused and need help with the question above??

Answers
No work is done if you push against the wall of a building.why?
Answers
Explanation:
Even though the man exerts force on the wall, the wall doesn't move . Work done= Force applied* displacement and since the displacement of the wall is zero., work done is also zero.
2.5 molmol of monatomic gas a initially has 4900 jj of thermal energy. it interacts with 2.9 molmol of monatomic gas b, which initially has 8000 jj of thermal energy.ou may want to review ( pages 559 - 561) .
Part A Which gas has the higher initial temperature? Which gas has the higher initial temperature? Gas A. Gas B.
Part B What is the final thermal energy of the gas A? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Ef =
Part C
What is the final thermal energy of the gas B?
Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Ef =
Answers
Part A: Gas B has the higher initial temperature.
Part B: If = 4900 J
Part C: If = 8000 J
Which gas has the higher initial temperature? What is the final thermal energy of gas A? What is the final thermal energy of gas B?Part A: To determine which gas has the higher initial temperature, we can compare the thermal energies of the two gases. Since the thermal energy is directly proportional to the temperature, the gas with the higher thermal energy will have the higher initial temperature. In this case, gas B has a higher initial thermal energy (8000 J) compared to gas A (4900 J). Therefore, gas B has the higher initial temperature.
Part B: To calculate the final thermal energy of gas A, we need to consider the conservation of energy during the interaction with gas B. Assuming an ideal gas behavior and no other energy transfer or work done, the total thermal energy before and after the interaction remains constant.
The initial thermal energy of gas A is given as 4900 J. Since there is no information provided about the energy exchange or transfer between the gases, we assume that the total thermal energy is conserved. Therefore, the final thermal energy of gas A would still be 4900 J.
Part C: Similarly, the final thermal energy of gas B can be calculated by assuming the conservation of energy. The initial thermal energy of gas B is given as 8000 J.
Since there is no information provided about the energy exchange or transfer between the gases, we assume that the total thermal energy is conserved. Therefore, the final thermal energy of gas B would still be 8000 J.
Learn more about higher initial
brainly.com/question/31956283
#SPJ11
when an electric current runs through a wire, a magnetic field is induced
Answers
Answer:
yes it is
Explanation:
Pls help this is due today.
Beyonce weighs 500 N and is sitting at one end of a see-saw which is 4 m long and balanced in the middle. Jordan is 2000 N. Where should she sit in order to balance the see-saw?
Answers
Answer:
11 moments docx has the answer
Explanation:
Calculate what the expected voltage is across the capacitor and resistor using the peak to peak voltage of 4v and frequency of 1000 Hz
Answers
To calculate the expected voltage across the capacitor and resistor, we need to use the peak-to-peak voltage of 4V and the frequency of 1000 Hz. The peak-to-peak voltage represents the difference between the maximum and minimum voltage levels in a waveform.
First, convert the peak-to-peak voltage to RMS voltage by dividing by the square root of 2:
Vrms = Vpp / √2 = 4V / √2 ≈ 2.83V
Next, we need to know the capacitance of the capacitor (C) and the resistance of the resistor (R) to determine the impedance of each component at 1000 Hz. Since these values are not provided, we will represent them as C and R.
Calculate the capacitive reactance (Xc) using the formula: Xc = 1 / (2π * f * C)
Calculate the impedance (Z) of the RC circuit using the formula: Z = √(R^2 + Xc^2)
Finally, use Ohm's Law to find the voltage across the capacitor (Vc) and resistor (Vr): Vc = Vrms * (Xc / Z)
Vr = Vrms * (R / Z)
In summary, to find the expected voltage across the capacitor and resistor, you need to convert the given peak-to-peak voltage to RMS voltage, calculate the capacitive reactance and impedance, and apply Ohm's Law. Since the values of C and R are not provided, the final answer is represented in terms of these variables.
For more information on Ohm's Law see:
https://brainly.com/question/1247379
#SPJ11
when an object reaches terminal velocity its acceleration is
Answers
When an object reaches terminal velocity its acceleration becomes zero.
Terminal velocity is also called constant velocity. When there is no acceleration in the moving object. We can take the example of sedimentation.
Sedimentation is the process of settling down the soil particles at the bottom of the water. When soil particles comes down in water there are three forces which act on the particles. Downward force is weight of the particle. Upward force buoyant force of the water, and drag force. When upward forces become equal to the downward force then particles begins to settle down with a constant velocity. which is called terminal velocity.
To know more about acceleration, here
https://brainly.com/question/12550364
#SPJ4
1. A car starts from rest and accelerates uniformly at 8m/s² until it attains a maximum velocity of 80m/s in 10s. It continues with this speed for further 100s until it is brought to rest for another 25s. Using a v-t graph, find the total distance travelled.
Answers
The total distance that have been travelled by the car is obtained as 9400 m.
What is the velocity time graph?The velocity time graph is used to obtain the various parameters that has to do with the movement of an object. It is a plot of the velocity of the object on the vertical axis and the time taken on the horizontal axis.
Now, we know that the total distance that is travelled is obtained from the v - t graph as 1/2(AB + OC) * AE. The velocity time graph have been shown in the image attached to this answer.
We then have;
Total distance travelled = 1/2(100 + 135) * 80
= 9400 m
Learn more about velocity time graph:https://brainly.com/question/28357012
#SPJ1
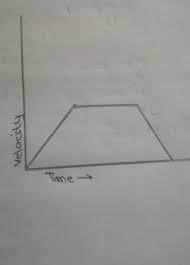
What information does a distance time graph provide
Answers
Hope this helps
Squall lines most often form ahead of a: a. cold front. b. warm front. c. cold-type occluded front. d. warm-type occluded front.
Answers
Squall lines most often form ahead of a cold front. A squall line is a narrow band of thunderstorms that form along or ahead of a cold front.
As the cold front moves into a warm, moist air mass, it causes the warm air to rise rapidly and triggers the development of thunderstorms. These storms can produce strong winds, heavy rain, and lightning, and can sometimes develop into severe thunderstorms that produce tornadoes. Squall lines are often associated with the development of severe weather, and it is important to monitor weather forecasts and take appropriate safety precautions when a squall line is expected.
While squall lines can form ahead of other types of fronts, they are most commonly associated with cold fronts. In contrast, warm fronts tend to produce more widespread, light to moderate precipitation and are less likely to produce severe weather.
To know more about Squall Lines visit:
https://brainly.com/question/29802991
#SPJ11
At which points in space does destructive interference occur for coherent electromagnetic waves (EM waves) with a single wavelength λ ? A. where their path length differences are 2λ B. where their path length differences are λ C. where their path length differences are even integer multiples of λ/2 D. where their path length differences are odd integer multiples of λ/2
Answers
Therefore, the correct option is D, where their path length differences are odd integer multiples of λ/2.
The correct answer to the given question is option D, where their path length differences are odd integer multiples of λ/2.In interference, two waves meet with each other, and the amplitude of the resultant wave depends on the phase difference between the two waves.
In the case of constructive interference, the phase difference between the two waves is a multiple of 2π, and in destructive interference, the phase difference is a multiple of π. For electromagnetic waves, destructive interference occurs when the path length difference between two waves is an odd integer multiple of half of the wavelength.
The expression for destructive interference can be written as follows:Δx = (2n + 1)λ/2Here, Δx represents the path length difference, n represents an integer, and λ represents the wavelength of the wave.Therefore, the correct option is D, where their path length differences are odd integer multiples of λ/2.
to know more about wavelength
https://brainly.com/question/1206358
#SPJ11
Examine the motion map. One animal is an antelope that is already running. The other is a cheetah that starts running after the antelope passes it. Does A or B represent the motion of the cheetah?
Answers
Answer:
A although am not seeing the cheetah
how is charged particles related to electric current, electric circuits, and resistance
Answers
Charged particles are fundamental to the behavior of electric currents, electric circuits, and resistance. An electric current is the flow of charged particles, typically electrons, through a conductor.
The flow of charged particles generates an electric field that induces a potential difference, or voltage, across the conductor.Electric circuits are constructed by connecting conductors and electrical components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, in a specific configuration. The arrangement of the components determines how the current flows through the circuit.
The flow of current through the circuit depends on the resistance offered by the components in the circuit and the potential difference across the circuit.Resistance is the property of a conductor that opposes the flow of current. The resistance of a conductor is proportional to the number of charged particles in the conductor, the length of the conductor, and the cross-sectional area of the conductor. The resistance can also be affected by the temperature of the conductor and its material properties.
In summary, charged particles are responsible for generating electric currents that flow through electrical circuits. The behavior of the currents is determined by the arrangement of the components in the circuit and the resistance offered by the conductors and components. Resistance is a fundamental property of a conductor that opposes the flow of charged particles and can be affected by various factors.
For more such questions on resistance visit:
https://brainly.com/question/7669692
#SPJ11
If 120 g of naoh were used to prepare 500 ml of solution, what would the concentration be?.
Answers
If 120 g of NaOH were used to prepare 500 ml of solution, the concentration would be 6 M
Molarity = ( Weight of solute * 1000 ) / ( GMV * V )
GMV = Gram molecular weight
V = Volume of solution
GMV of NaOH = 26 + 16 + 1
GMV of NaOH = 40
Molarity = ( 120 * 1000 ) / ( 40 * 500 )
Molarity = 120 / 20
Molarity = 6
Molarity or molar concentration is the concentration of chemical species mainly solute in a solution. It is the amount of substance per unit volume of solution.
Therefore, the concentration of NaOH is 6 M
To know more about Molarity
https://brainly.com/question/16727614
#SPJ4
How is the potential difference same in capacitors arranged in parallel combination?
Answers
Answer:
Potential difference across capacitors in parallelTwo or more capacitors are said to be connected in parallel if each one of them is connected across the same two points. In a parallel combination of capacitors potential difference across each capacitor is same but each capacitor will store different charge.
The car travels 28m in 7s. What is the speed of the car?
Answers
The Speed of the car is 4m/s.
What is the speed?
The speed of an object can be defined as the total distance traveled by it in a particular interval of time. This can be determined by dividing the total distance moved by the object by the time taken to move.
It is the ratio of distance in m and time taken by the object to travel in seconds.
Hence: Distance D=28m
Time T=7s
Speed S=D/T
S=28m/7S
S=4m/S
Therefore car's speed is 4m/S
Learn more on speed from
brainly.com/question/28626511
#SPJ1
The speed of the car is 4m/s
What is speed?Speed is the rate of change of distance with time.
It is a scalar quantity and it's S.I unit is given as m/s. Distance is the space or gap between two point. Speed can generally be defined as the distance travelled per a given time
From the definition, speed = distance/time
distance is 28m and time is 4s, therefore
Speed = 28/4= 7m/s.
Therefore the speed of the car is 7m/s
learn more about speed from
https://brainly.com/question/13943409
#SPJ1
A typical protostar may be several thousand times more luminous than the sun. what is the source of this energy?
Answers
The source of this energy is from the release of gravitational energy as the protostar continues to shrink.
How are stars born and what is a protostar?Nebulae have as possible differences in gas and dust. Some factors, such as turbulence, can cause one of them to contract. This contraction of the set of materials causes the elaboration and execution of this phase of materials, generating what is usually called, in this protostar.
A protostar is formed by the contraction of a giant molecular cloud in the interstellar medium. Stars form within relatively dense concentrations of interstellar gas and dust known as molecular clouds.
See more about protostar at brainly.com/question/14317247
#SPJ4
Which object would have a greater buoyant force: 350 g of copper (ρ= 8,890 kg/m3) or 350 g of ice (ρ= 917 kg/m3) if both are submerged in water?
Answers
three plus four NERD