The heat loss from a boiler is to be held at a maximum of 900Btu/h ft2 of wall area. What thickness of asbestos (k= 0.10 Btu/h ft ℉) is required if the inner and outer surfaces of the insulation are to be 1600 and 500℉, respectively? Now if a 3-in.-thick layer of kaolin brick (k= 0.07 Btu/h ft ℉) is added to the outside of the asbestos, what heat flux will be result if the outside surface of the kaolin is 250℉? What will be the temperature at the interface between the asbestos and kaolin for this condition?
Answers
Answer:
a. 0.122 ft b. -70 Btu/h ft² c. 633.33 °F
Explanation:
a. Since the rate of heat loss dQ/dt = kAΔT/d where k = thermal conductivity, A = area, ΔT = temperature gradient and d = thickness of insulation.
Now [dQ/dt]/A = kΔT/d
Given that [dQ/dt]/A = rate of heat loss per unit area = -900Btu/h ft², k = 0.10 Btu/h ft ℉(for asbestos), ΔT = T₂ - T₁ = 500 °F - 1600 °F = -1100 °F. We need to find the thickness of asbestos, d. So,
d = kΔT/[dQ/dt]/A
d = 0.10 Btu/h ft ℉ × -1100 °F/-900Btu/h ft²
d = 0.122 ft
b. If the 3 in thick Kaolin is added to the outside of the asbestos, and the outside temperature of the asbestos is 250℉, the heat loss due to the Kaolin is thus
[dQ/dt]/A = k'ΔT'/d'
k' = 0.07 Btu/h ft ℉(for Kaolin), ΔT' = T₂ - T₁ = 250 °F - 500 °F = -250 °F and d' = 3 in = 3/12 ft = 0.25 ft
[dQ/dt]/A = 0.07 Btu/h ft ℉ × -250 °F/0.25 ft
[dQ/dt]/A = -70 Btu/h ft²
c. To find the temperature at the interface, the total heat flux equals the individual heat loss from the asbestos and kaolin. So
[dQ/dt]/A = k(T₂ - T₁)/d + k'(T₃ - T₂)/d' where [dQ/dt]/A = -900Btu/h ft², k = 0.10 Btu/h ft ℉(for asbestos), k' = 0.07 Btu/h ft ℉(for Kaolin), T₁ = 1600 °F, T₂ = unknown and T₃ = 250℉.
Substituting these values into the equation, we have
-900Btu/h ft² = 0.10 Btu/h ft ℉(T₂ - 1600 °F)/0.122 ft + 0.07 Btu/h ft ℉(250℉ - T₂)/0.25 ft
-900Btu/h ft² = 0.82 Btu/h ft ℉(T₂ - 1600 °F) + 0.28Btu/h ft ℉(250℉ - T₂)
-900 °F = 0.82(T₂ - 1600 °F) + 0.28(250℉ - T₂)
-900 °F = 0.82T₂ - 1312°F + 70 °F - 0.28T₂
collecting like terms, we have
-900 °F + 1312°F - 70 °F = 0.82T₂ - 0.28T₂
342 °F = 0.54T₂
Dividing both sides by 0.54, we have
T₂ = 342 °F/0.54
T₂ = 633.33 °F
The thickness of asbestos required is 0.122 ft.
The heat flux will be -70 Btu/h ft²
And the temperature of the interface is 633.33 °F.
(i) the rate of heat loss :
dQ/dt = kAΔT/d
where k = thermal conductivity, A = area, ΔT = temperature gradient, and
d = thickness of insulation.
[dQ/dt]/A = kΔT/d
Given that [dQ/dt]/A = rate of heat loss per unit area = -900Btu/h ft²,
k = 0.10 Btu/h ft ℉,
ΔT = 500 °F - 1600 °F = -1100 °F
We have to find the thickness of asbestos that is d.
d = kΔT/[dQ/dt]/A
d = 0.10 Btu/h ft ℉ × -1100 °F/-900Btu/h ft²
d = 0.122 ft is the thickness required.
(ii) a 3-in thick Kaolin is added to the outside of the asbestos
outside temperature of the asbestos is 250℉,
the heat loss due to the Kaolin is:
[dQ/dt]/A = k'ΔT'/d'
k' = 0.07 Btu/h ft ℉(for Kaolin), ΔT' = T₂ - T₁ = 250 °F - 500 °F = -250 °F and d' = 3 in = 3/12 ft = 0.25 ft
[dQ/dt]/A = 0.07 Btu/h ft ℉ × -250 °F/0.25 ft
[dQ/dt]/A = -70 Btu/h ft²
(iii) temperature at the interface
the total heat flux :
[dQ/dt]/A = k(T₂ - T₁)/d + k'(T₃ - T₂)/d'
where [dQ/dt]/A = -900 Btu/h ft²,
k = 0.10 Btu/h ft ℉ (for asbestos),
k' = 0.07 Btu/h ft ℉ (for Kaolin),
T₁ = 1600 °F and T₃ = 250℉.
-900 = 0.10(T₂ - 1600 °F)/0.122 + 0.07(250℉ - T₂)/0.25
-900 = 0.82(T₂ - 1600 °F) + 0.28(250℉ - T₂)
-900 °F = 0.82(T₂ - 1600 °F) + 0.28(250℉ - T₂)
-900 °F = 0.82T₂ - 1312°F + 70 °F - 0.28T₂
-900 °F + 1312°F - 70 °F = 0.82T₂ - 0.28T₂
342 °F = 0.54T₂
Dividing both sides by 0.54, we have
T₂ = 342 °F/0.54
T₂ = 633.33 °F
Learn more:
https://brainly.com/question/3102316
Related Questions
How does the newton law work
Answers
Answer:
The first law is that if no force acts on an object, its motion will not change. In the second law, the force acting on an object is equal to its mass and acceleration. The third law is that when two objects interact, they act on each other with equal magnitude and opposite forces.
What type of circuit is shown

Answers
Answer:
electric circuit............
which grade
. Consider a one-dimensional wavefunction given by ψ(x)=Axe −αx
, with A,α as constants, and 0≤ x<[infinity]. a. Show that this wavefunction satisfies the 1-D time independent Schrödinger equation having a potential term V(x)=− x
q 2
, where q is a constant and α= ℏ 2
mq 2
. b. Calculate the energy eigenvalue, E, in terms of ℏ,m,q. c. Find the value of A that normalizes the wavefunction. Hint: the following definite integral will be helpful: ∫ 0
[infinity]
x n
e −ax
dx= a n+1
n!
where n is an integer and a is a constant.
Answers
The wavefunction ψ(x) = Axe^(-αx) satisfies the one-dimensional time independent Schrödinger equation with the potential term V(x) = -xq^2, where q = √(αℏ^2/m).
To show that the wavefunction ψ(x) = Axe^(-αx) satisfies the one-dimensional time independent Schrödinger equation, we need to verify if it satisfies the equation:
(-ℏ^2/2m) * (d^2ψ/dx^2) + V(x)ψ = Eψ
where V(x) = -xq^2. Let's substitute the wavefunction and potential term into the equation and simplify:
(-ℏ^2/2m) * (d^2(Axe^(-αx))/dx^2) + (-xq^2)(Axe^(-αx)) = E(Axe^(-αx))
Differentiating ψ(x) twice, we get:
(-ℏ^2/2m) * [(Ae^(-αx))(α^2x - 2α + 2α^2x^2 - 2αx)] + (-xq^2)(Axe^(-αx)) = E(Axe^(-αx))
Simplifying further, we have:
(Ae^(-αx)) * [(-ℏ^2/2m)(α^2x - 2α + 2α^2x^2 - 2αx) - xq^2] = E(Axe^(-αx))
Expanding and rearranging terms, we obtain:
(Ae^(-αx)) * [-ℏ^2α^2x + ℏ^2(2α - α^2x - 2α^2x^2) - 2mαx^2 - mα^2x^3 + xq^2] = E(Axe^(-αx))
Comparing the coefficients of similar powers of x on both sides, we can equate the terms and obtain a relationship between q and α:
-ℏ^2α^2 = Eq^2 ... (1)
By substituting α = ℏ^2/(2mq^2) into equation (1), we can verify that the relationship holds. Therefore, the wavefunction satisfies the one-dimensional time independent Schrödinger equation with the given potential term.
Learn more about Schrödinger equation
brainly.com/question/31642338
#SPJ11
Bumpers, collapsible frames, airbags and seat belts all come into play when an an accident occurs. True or false
Answers
Bumpers, collapsible frames, airbags, and seat belts are safety features in vehicles designed to protect occupants in the event of an accident.
Bumpers help absorb impact and minimize damage to the vehicle, collapsible frames absorb and distribute energy, airbags rapidly inflate to provide a cushioning effect, and seat belts restrain occupants and prevent them from being thrown forward. All of these safety features work together to enhance occupant safety during accidents.
Learn more about Bumpers, collapsible here:
https://brainly.com/question/28525009
#SPJ11
I just got asked a question about quantum entanglement. Can someone please give me a basic understandable of what it is
Answers
a property of a set of subatomic particles whereby a quantum characteristic (such as spin or momentum) of one particle is directly and immediately correlated with the equivalent characteristic of the others regardless of separation in space
In quantum entanglement, subatomic particles maintain a relationship—for instance, vibrating when the other vibrates—even when separated and even if they are at great distances from each other.
Hope it helps you.
Moving along the elevtromagnetic spectrum from low frequency to high frequency, what , if anything, happens to the wavelength?
wavelength get longer
wavelength remains constant
the wavelengths get shorter
wavelength eventually disappear altogether
Answers
Explanation:
the wavelengths get shorter
Explain why the radiative zone of the sun is hotter than the corona of the sun
Answers
Answer: Because The spectra provided evidence to explain why the sun's atmosphere is so much hotter than its surface. ... Clear evidence now suggests that the heating mechanism depends on regular, but intermittent explosive bursts of heat, rather than on continuous gradual heating.
Explanation:
Question 2 10 pts A company has designed and built a new air compressor section for our advanced Gas turbine engine used in electrical power generation. They state that their compressor operates adiabatically, and has a pressure ratio of 30. The inlet temperature is 35 deg C and the intet pressure is 100 kPa. The mass flow rate is steady and is 50 kg/s The stated power to run the compressor is 24713 kW Co = 1.005 kJ/kg K k-1.4 What is the isentropic temperature at the compressor exit? 815.2 K 752K 800 K 93 deg C
Answers
In the given scenario, a new air compressor section for an advanced gas turbine engine is designed and built. The compressor is claimed to operate adiabatically with a pressure ratio of 30.Therefore, the correct answer is 815.2 K, which corresponds to the isentropic temperature at the compressor exit.
To calculate the isentropic temperature at the compressor exit, we can use the isentropic process equation for an ideal gas:
T2s / T1 = (P2 / P1)^((k-1)/k),
where T2s is the isentropic temperature at the compressor exit, T1 is the inlet temperature, P2 is the outlet pressure (which can be determined using the pressure ratio), P1 is the inlet pressure, and k is the specific heat ratio.
Given the pressure ratio of 30, the inlet temperature of 35 °C (308 K), and the inlet pressure of 100 kPa, we can calculate the isentropic temperature using the equation. Considering the specific heat ratio for air as 1.4, we find that the isentropic temperature at the compressor exit is approximately 815.2 K.
Learn more about isentropic temperature here:
https://brainly.com/question/30896816
#SPJ11
The probability distribution for a
random variable x is given in the table.
-10
-5
0
5
10
15
20
Probability
.20
.15
.05
.1
.25
.1
.15
Find the probability that x < 20

Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
6
Probability for X<20 for given probability distribution is 0.85.
Probability is concern with possibility. It is a branch of statistics which deals with the occurrence of a random event. Sum of probabilities for a particular event is one. Probability has been introduced in statistics to predict how likely events are to happen. Probability means an extent to which something is likely to happen. To find the probability of a particular event to occur, firstly we must know the total number of possible outcomes. The distribution of probability for an event is called as probability distribution.
for example when a coin is tossed, it gives two possible outcomes Head and Tail. There is 50% of chance of getting Head or tail.
The Total probability is the sum of all the probabilities and it is always one.
In this problem Probability that x < 20,
P(x<20) = P(x<-10)+P(x<-5)+P(x<0)+P(x<5)+P(x<10)+P(x<15)
P(x<20) = 0.20+0.15+0.05+0.1+0.25+0.1 = 0.85
To know more about Probability :
https://brainly.com/question/30034780
#SPJ7.
I need help it is due today

Answers
Answer:
Option 3. The tennis ball began from rest and rolls at a rate of 14.7 m/s safer 1.5 seconds.
Explanation:
To know the the correct answer to the question, it is important that we know the definition of acceleration.
Acceleration can simply be defined as the rate of change of velocity with time. Mathematically, it is expressed as:
a = (v – u) /t
Where
a => acceleration
v => final velocity
u => Initial velocity
t => time
With the above information in mind, let us consider the options given in the question above to know which conform to the difinition of acceleration.
For Option 1,
We were told that the tennis ball has the following:
Distance = 4 m
Time = 1.5 s
This talks about the speed and not the acceleration.
Speed = distance / time
For Option 2,
We were only told about the average speed and nothing else.
For Option 3,
We were told that the tennis ball have the following:
Initial velocity (u) = 0 m/s
Final velocity (v) = 14.7 m/s
Time = 1.5 s
This talks about the acceleration.
a = (v – u) /t
For Option 4,
We were only told that the tennis rolls to the right at an average speed. This talks about the average velocity. We need more information like time to justify the acceleration.
From the above illustrations, option 3 gives the correct answer to the question.
Una caja de 5.0kg de masa se acelera desde el reposo a través del piso mediante una fuerza a una tasa de 2.0 /s2 durante 7.0s encuentre el trabajo realizado sobre la caja
Answers
Responder:
490 juliosExplicación:
Se dice que el trabajo se realiza cuando una fuerza aplicada a un objeto hace que el objeto se mueva a través de una distancia. El trabajo realizado por un cuerpo se expresa mediante la fórmula;
Workdone = Fuerza * Distancia
Como Fuerza = masa * aceleración,
Workdone = masa * aceleración * distancia
Masa dada = 5.0kg, aceleración = 2.0m / s² d =?
Para obtener d, usaremos una de las leyes del movimiento,
d = ut + 1 / 2at²
u = 0 (ya que el cuerpo acelera desde el reposo) yt = 7.0s
d = 0 + 1/2 (2) (7) ²
d = 49m
Workdone = 5 * 2 * 49
Workdone = 490 Julios
What does mass of an object depend on
Answers
Answer:
the inertia of an object
Hay Que!
Explain world’s most famous formula which describes the relationship between mass and energy. Also give 1 suitable application.
Answers
Answer:
E = mc² relation between mass and energy
it is only applicable in space. example One of the most extraordinary things about Einstein's energy-mass equivalence equation is its simplicity.A 100 watt light bulb uses 100 joules of energy every second, i.e. one watt is one joule per second.Explanation:
hope it will help you :)
what are two reasons communication is important in scientific research
Answers
Answer:
It allows them to write better and more comprehensible research papers. As well as being able to communicate the relevance and impact of their ideas and discoveries.
Explanation:
Help pls ;) and thank you
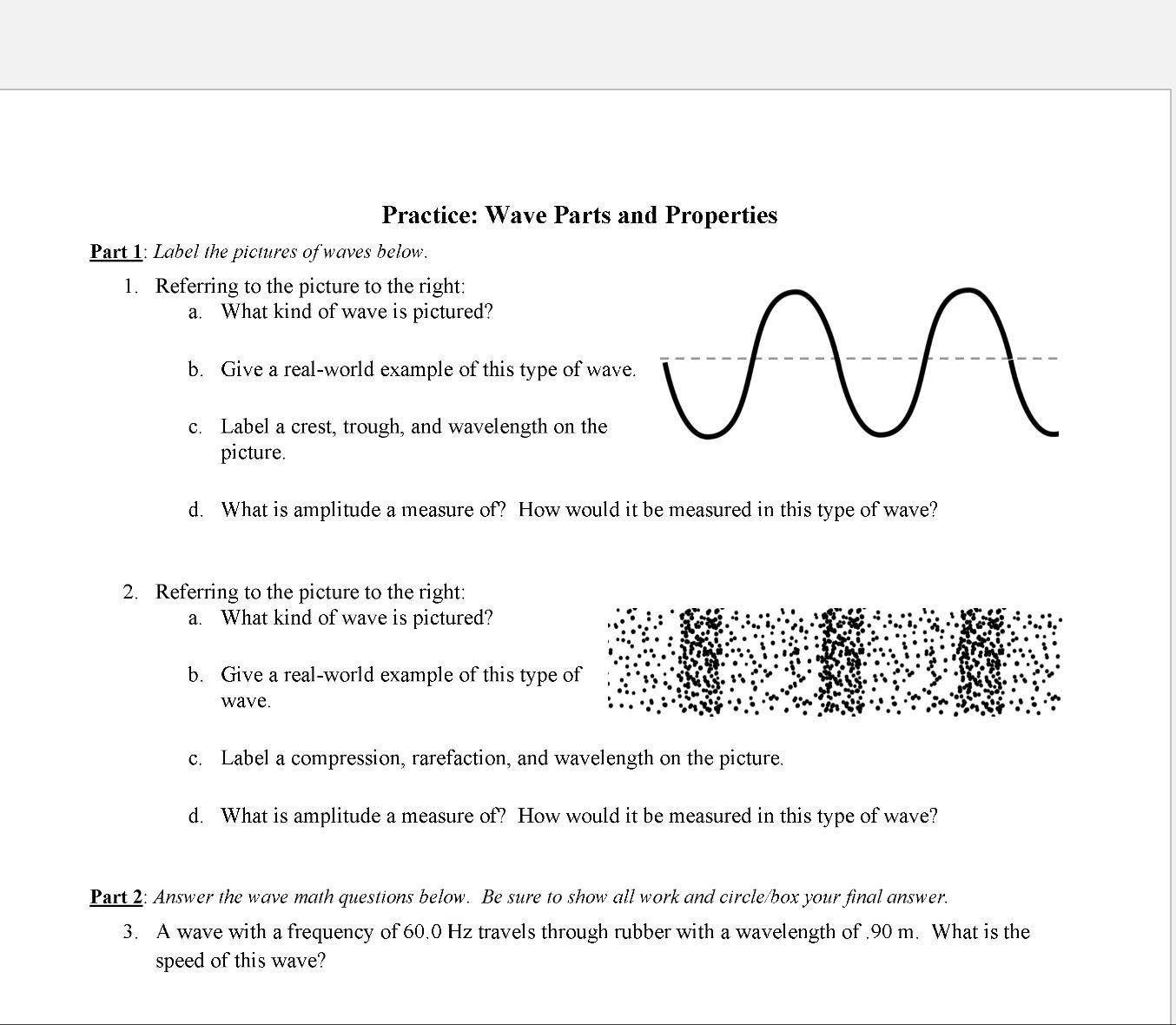
Answers
Answer:
1a) Transverse wave.
1b) Ripples on the surface of water.
1c) See first attachment.
1d) See below for explanation.
2a) Longitudinal wave.
2b) Sound waves.
2c) See second attachment.
2d) See below for explanation.
Part 2) 54 m/s
Explanation:
Part 1Question 1a) The wave in the picture is a transverse wave.
In transverse waves, the oscillations are at right angles to the direction of wave travel.
b) A real world example of a transverse wave is ripples on the surface of water.
c) See first attachment.
The crest is the highest point.The trough is the lowest point. The wavelength is one full wave cycle measured from crest to crest, or trough to trough.d) The amplitude is the maximum displacement of a point of a wave from its resting position. It is measured by calculating the difference in height between a crest and the resting position (mid-line).
Question 2a) The wave in the picture is a longitudinal wave.
In longitudinal waves, the oscillations are parallel to the direction of wave travel.
b) A real world example of a longitudinal wave is sound waves.
c) See second attachment.
Compression: The region where the particles are compressed together.Rarefaction: The region where the particles are spread apart.Wavelength: One full wave cycle measured from one compression to the next compression, or from one rarefaction to the next rarefaction.d) The amplitude is the maximum displacement of a point of a wave from its resting position. It is measured by calculating the distance between the particles in the areas where it is compressed.
Part 2Wave Speed
\(\large\boxed{v=f \lambda}\)
where:
v = Wave speed measured in meters per second (m/s).f = Frequency measured in Hertz (Hz).λ = Wavelength measured in meters (m).Given values:
Frequency = 60.0 HzWavelength = 0.90 mSubstitute the given values into the formula and solve for speed:
\(\implies v=60.0 \times 0.90\)
\(\implies v=54\;\sf m/s\)
Therefore, the speed of the wave is 54 m/s.


You weigh 710 N. What would you weigh if the Earth were three times as massive as it is and its radius were five times its present value? Answer in units of N
Answers
Answer:
85.2 N
Explanation:
You want to know your weight if the Earth were 3 times as massive and had 5 times the present radius. Your weight is 710 N.
WeightYour weight is proportional to the mass of the Earth and the square of the radius between your mass and the center of the Earth. The revised dimensions of the earth would multiply your weight by ...
W = k(M/r²) = 710 N
W' = k((3M)/(5r)²) = k(M/r²)(3/25) = (710 N)(3/25) = 82.5 N
Your weight would be 82.5 N.

in longitudinal waves in a spring, the parts where the coils are close together are called
Answers
Answer:
compression
Explanation:
compression
What is downward force that acts on an airplane in flight
Answers
Answer:
重力
Explanation:
这是正确的答案还是不是
how do you determine if something is physical or chemical
Answers
We can determine whether a change is physical or chemical by analyzing the what type of change is occurred. The change in color or formation of new product is a chemical change.
What is a chemical change ?A chemical change is a type of change which include the breaking or making of chemical bonds and the formation of new products which has properties different from the initial substances.
Phase changes, change in size, shape, dissolving, conductivity etc. are physical changes. They do not involve any change in chemical bonds or the formation of new product.
The change in color indicates the formation of a new product. All the chemical reactions like the corrosion of metals reaction of metals with acids or water etc . are all chemical changes.
Find more on physical changes:
https://brainly.com/question/21509240
#SPJ1
One molecule of calcium oxide, Cao, and one molecule of carbon dioxide, CO2, combine in a chemical reaction to form one
substance. Given that matter is neither created nor destroyed, which chemical formula is the product of this reaction? (1 point)
Ca2CO3
CaCO2
Ca203
0 CaCO3
Answers
Here, we are required to determine which chemical formula is the product of the reaction between CaO and C02 given that matter is neither created nor destroyed.
The chemical formula of the product of this reaction is ; CaCO3.
The law of conservation of mass is the basis for the balancing of equations of chemical reactions.
The law states that matter( which is the building block of mass) can neither be created nor destroyed.
Therefore, in a reaction where one molecule of calcium oxide, CaO, and one molecule of carbon dioxide, CO2, combine in a chemical reaction to form one substance;
The chemical formula of the product of this reaction is ; CaCO3.
Read more:
https://brainly.com/question/17882354
can someone help ???

Answers
Answer:
All of these
Explanation:
a space vehicle is traveling at 2600 km/h relative to earth when the exhausted rocket motor is disengaged and sent backward. the relative speed between the motor and the command module is then 73 km/h. the mass of the motor is four times the mass of the module. what is the speed of the command module relative to earth just after the separation?
Answers
The speed of the command module relative to earth just after the separation is 2585.4 km/h
Since we don't know the masses of the motor and the module, So considering the mass of the module M, and the mass of the motor to be 4M and v be the velocity of the motor
So, The total mass of the vehicle is 5M( in kg), before separation,the momentum of the vehicle is:
2600 * 5M = 13000 M kg-km/h.
since the velocity of the module will be v + 73. After the separation, the momentum of the motor is 4Mv, and the momentum of the module is
M(v + 73) = Mv + 73M.
therefore, The total momentum is 4MV + Mv + 73M = 5Mv + 73M.
which will be the same as the initial momentum.
So, it gives us the equation :
13000 M = 5Mv + 73M
Dividing both sides by M:
=>13000 = 5v + 73
=>12927 = 5v
=>2585.4= v
But v is the velocity of the motor, so we have to add 93 to get the velocity of the module, which is 2658.4
To know more about velocity refer to the link https://brainly.com/question/18084516?referrer=searchResults.
#SPJ4
The field between two charged parallel plates is kept constant. If the two plates are brought closer together, the potential difference between the two plates.
Answers
Since the electric field between the plates is constant, If the two plates are brought closer together, the potential difference between the two plates decreases
The relation between potential difference and the electric field is given by ΔV = E.d
Since the electric field is maintained constant, the potential difference is directly inversely proportional to the distance between the plates.
The potential difference between the plates will therefore likewise decrease if the distance between the plates is reduced, we will state in this case.
The energy required to move a unit charge, or one coulomb, from one point to the other in a circuit is measured as the potential difference between the two points. Potential difference is measured in volts or joules per coulomb.
Refer to more about the potential difference here
brainly.com/question/12198573
#SPJ4
Calculate the KE in joules of a 1500 kg car moving at 29 m/s?
Answers
Answer:
x J = (1500 kg)(29 m/s)(y m/s)
Explanation:
x J = (1500 kg)(29 m/s)(y m/s)
To know that a 1500 kg car is moving at 29 m/s is not enough.
The value of x depends on y. You’re missing a number of meters and a quantity of ‘per seconds’ somewhere in your problem statement and you need to find them in order to solve the problem
Stand next to a partner so that you are side-by-side. Each of you should hold your left arm out to the side and then point with your finger. Describe whether you and your partner are pointing in the same direction.
Answers
Answer:
They would be pointing in the same direction
Explanation:
If they were facing each other then it may seem like they are pointing in different directions they would still point the same way.
A radio station's channel, such as 100.7 FM or 92.3 FM, is actually its frequency in megahertz (MHz),where 1 MHz =106 Hz and 1 Hz = 1 s−1. Calculate the broadcast wavelength of the radio station 95.90 FM
Answers
The radio station's broadcast wavelength. 299792458/95700000=3.133m . λ=\(\frac{3.10^{8}m/s }{95.90.10^{6}Hz }\) =3.38m
In the actual world, what is frequency?Frequency of a wave is defined as the total amount of waves generated in a second. Frequency is the measurement of the quantity of vibrations per second. As an example, consider the following: If five full waves are created in a second, their frequency is 5 hertz (Hz), or 5 cycles every second.
Which two frequencies are there?The two primary frequency distribution types utilized in data analysis are cumulative and relative frequency distributions. Both depend on incidence, which in descriptive and inferential statistics refers to how frequently a particular event happens within a particular data set.
To know more about Frequency visit:
https://brainly.com/question/5102661
#SPJ4
Which planetary body has the fastest orbit, and which has the slowest orbit? Do you notice a general pattern here? Briefly explain a relationship between orbital velocity and orbital radius.
Answers
The planetary body with the fastest orbit is Mercury, and the one with the slowest orbit is Neptune.
There is a general pattern between orbital velocity and orbital radius known as Kepler's second law of planetary motion. According to this law, a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times as it orbits the Sun. This implies that planets closer to the Sun have smaller orbital radii and must travel faster to cover the same area in the same amount of time.
The relationship between orbital velocity and orbital radius can be expressed as v ∝ 1/r, where v represents the orbital velocity and r denotes the orbital radius. This relationship shows that as the orbital radius increases, the orbital velocity decreases. In other words, planets farther from the Sun have slower orbital velocities compared to those closer to the Sun.
This pattern is consistent with observations in our solar system. The inner planets, such as Mercury, have smaller orbital radii and faster orbital velocities, while the outer planets, like Neptune, have larger orbital radii and slower orbital velocities.
To learn more about planetary body, Click here: brainly.com/question/32117026
#SPJ11
a soccer ball is kicked at an angle of 64° to the horizontal with an initial speed of 15 m/s. assume for the moment that we can neglect air resistance. (a) for how much time is the ball in the air?
Answers
Time taken by the soccer ball in the air when we neglect the air resistance is 2.75s
projectile motion - It is the motion of an object which projected into the air and moving under the gravity.
a soccer ball is kicked at an angle of 64° to the horizontal
initial speed = 15 m/s
Initial velocity in vertical direction is given as
\(V_{v} = V_{0}sin \theta\)
\(V_{v} = 15sin(64)\)
\(V_{v}\) = 15× 0.8987
= 13.48m/s
time taken to reach the maximum height is given by
T =\(V_{v}\) /g
where
\(V_{v}\) is the velocity
g is the gravity
Ball comes downward with the same speed
then that time period is given by.
2\(V_{v}\) /g
= 2× 13.48 /9.8
T = 2.75s
Time taken by the soccer ball in the air when we neglect the air resistance is 2.75s
To know more about projectile
https://brainly.com/question/14607185
#SPJ4
a reaction that happens when one substance breaks down into two or more substances
Answers
Answer:
decomposition reaction
Explanation:
decomposition reactions occurs when one substance breaks down, or decomposes, into two or more substances
You walk 100m due north. You then turn and walk 55m due east. You then make another turn and walk 12m due south. What is the resultant vector for your walk?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Important here is to know that due north is a 90 degree angle, due east is a 0 degree angle, and due south is a 270 degree angle. Then we find the x and y components of each part of this journey using the sin and cos of the angles multiplied by each magnitude:
\(A_x=100cos90\\A_x=0\\B_x=55cos0\\B_x=55\\C_x=12cos270\\C_x=55\)
Add them all together to get the x component of the resultant vector, V:
\(V_x=55\)
Do the same to find the y components of the part of this journey:
\(A_y=100sin90\\A_y=100\\B_y=55sin0\\B_y=0\\C_y=12sin270\\C_y=-12\)
Add them together to get the y component of the resultant vector, V:
\(V_y=88\)
One thing of import to note is that both of these components are positive, so the resultant angle lies in QI.
We find the final magnitude:
\(V_{mag}=\sqrt{55^2+88^2}\) and, rounding to 2 sig dig's as needed:
\(V_{mag}=\) 1.0 × 10² m; now for the direction:
\(\theta=tan^{-1}(\frac{88}{55})=\) 58°