suppose a 32 mh inductor has a reactance of 95 ω.What would be the frequency in Hz
Answers
The frequency of a 32 mh inductor that has a reactance of 95 ω is approximately 476.6 Hz.
The frequency at which the parasitic capacitance of the inductor resonates with the ideal inductance of the inductor resulting in an extremely high impedance is the frequency of an inductor.
To find the frequency (f) in hertz (Hz) corresponding to a given inductor reactance (X) in ohms (Ω), we can use the formula:
f = X / (2πL),
where L is the inductance in henries (H). In this case, the inductor has an inductance of 32 mH, which is equivalent to 0.032 H, and a reactance of 95 Ω. Plugging these values into the formula:
f = 95 Ω / (2π * 0.032 H) ≈ 476.6 Hz.
Therefore, the frequency is approximately 476.6 Hz.
To know more about frequency, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/29739263
#SPJ11
Related Questions
an 7m 11 sec issc wave spectra can be approximated by 5 regular amplitudes and frequencies waves as follows: 1.1m, 0.35 rad/s; 1.4m, 0.45 rad/s; 1.1m, 0.55 rad/s; 1.0 m, 0.7rad/s
Answers
The given wave spectrum can be approximated by the combination of these 5 waves. Each wave has a specific amplitude and frequency, which together create the overall shape of the wave spectrum.
The given wave spectrum consists of 7m 11 sec issc wave with 5 regular amplitudes and frequencies waves. The amplitudes and frequencies of the waves are as follows:
Wave 1: Amplitude = 1.1m, Frequency = 0.35 rad/s
Wave 2: Amplitude = 1.4m, Frequency = 0.45 rad/s
Wave 3: Amplitude = 1.1m, Frequency = 0.55 rad/s
Wave 4: Amplitude = 1.0m, Frequency = 0.7 rad/s
To understand the overall wave spectrum, we need to consider the contributions of each individual wave.
The given wave spectrum can be approximated by the combination of these 5 waves. Each wave has a specific amplitude and frequency, which together create the overall shape of the wave spectrum.
By adding the contributions of each wave, we can visualize the resulting wave spectrum. For example, if we were to graph the amplitude of the waves over time, we would see the combined effect of all 5 waves.
We can consider an analogy. Imagine a group of people playing different musical instruments. Each person represents a wave with their own unique sound (amplitude) and rhythm (frequency). When they play together, their individual contributions create a harmonious melody, just like the combination of waves in the given wave spectrum.
The given wave spectrum can be approximated by the combination of 5 regular amplitudes and frequencies waves. Each wave contributes to the overall shape of the spectrum, and by considering their individual effects, we can understand the behavior of the wave spectrum as a whole.
To know more about spectrum visit:
brainly.com/question/13435566
#SPJ11
Can someone please help for a , what am I meant to do
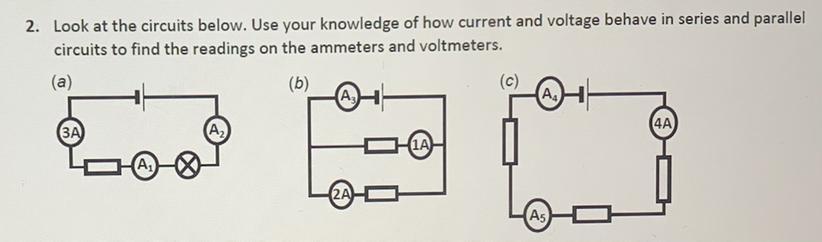
Answers
give three examples of objects in equilibrim found in the class room and draw an approximate scale diagram for the object
Answers
Table at rest, Books on a table, See-saw are objects in equilibrium found in the class room.
What is an object in equilibrium?There is no net force acting on an object and it is said to be in equilibrium if the size and direction of the forces acting on it are precisely balanced. If an object is moving with a constant velocity, it is in equilibrium because its acceleration is zero. The fundamental function of an object in equilibrium is a zero acceleration.
Are all stationary objects in equilibrium?Two forces are in equilibrium when they are acting on an object that is stationary or moving at a constant speed. The body will accelerate if the forces have a result rather than canceling each other out.
To know more about net force :
https://brainly.com/question/18109210
#SPJ9
Consider a 1.5-m-high and 2.4-m-wide double-pane window consisting of two 3-mm-thick layers of glass (k = 0.78 W/m.K) separated by a 12-mm-wide stagnant air space (k = 0.026 W/mK). Determine the steady rate of heat transfer through this double-pane window and the temperature of its in- ner surface for a day during which the room is maintained at 21°C while the temperature of the outdoors is -5°C. Take the convection heat transfer coefficients on the inner and outer sur- faces of the window to be h, = 10 W/m²K and h2 = 25 W/m².K, and disregard any heat transfer by radiation,
Answers
The temperature of the inner surface of the window will be lower than the room temperature, 21°C.
The steady rate of heat transfer through a double-pane window is determined by the heat conduction through the glass layers, convection to the outdoor air, and convection to the room air. The temperature of the inner surface of the window will depend on the temperature difference between the outdoors and the room.
The heat transfer rate, Q, through the double-pane window can be calculated using the overall heat transfer coefficient U:
Q = U × (Area of window) × (Temperature difference)
The overall heat transfer coefficient can be calculated using the equation below:
U = 1/[(1/h1) + (L/k) + (1/h2)]
Where h1 and h2 are the convection heat transfer coefficients on the inner and outer surfaces of the window, respectively; L is the thickness of the air space between the two glass layers; and k is the thermal conductivity of the air space.
Given the parameters in the question, the overall heat transfer coefficient is calculated to be U = 1.30 W/m2K. Thus, the heat transfer rate through the double-pane window is
Q = 1.30 × (2.4 m × 1.5 m) × (26 K) = 72 W.
The temperature of the inner surface of the window can be calculated by considering the heat transfer balance between the room air and the outdoor air. The rate of heat transfer from the outdoors is
Qout = h2 × (2.4 m × 1.5 m) × (26 K) = 90 W.
The rate of heat transfer to the room air is
Qin = h1 × (2.4 m × 1.5 m) × (26 K) = 36 W.
Thus, the rate of heat transfer to the room air is 72 W - 90 W = -18 W.
for such more question on temperature
https://brainly.com/question/26866637
#SPJ11
The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection will ______.Select one:a.never be equalb. always add up to 90 degreesc.always add up to 180 degreesd.always be equal
Answers
The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection will always be equal.
When a ray of light reflects off a surface, the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence.
Use DeMorgan's Theorem, as well as any other applicable rules of Boolean algebra, to simplify the following expression so there are no more complementation bars extending over multiple variables: \[ \
Answers
The expression to be simplified is, A + BC + ABCD. Using De Morgan's theorem, we can convert complementation bars extending over multiple variables into complementation bars over single variables. The De Morgan's theorem states that the complement of a product is equal to the sum of complements. De Morgan's Theorem:
1. (AB) = A + B2. (A + B) = A B The steps to simplify the given expression using De Morgan's theorem are as follows: A + BC + ABCD = A + (BC + ABCD) = A + (BC). (ABCD) = A + (B + C) (A + B + C + D) = A + AB + AC + BC + BD = A + AC + BC + BD.
Hence, the simplified expression is A + AC + BC + BD. Thus, using DeMorgan's Theorem and other applicable rules of Boolean algebra, the given expression is simplified to A + AC + BC + BD.
To know more about Morgan's Theorem here:
https://brainly.com/question/33579332
#SPJ11
A plane flies with an average velocity of -98 m/s for 45.0 s. What was its displacement
Answers
Answer:-4410 m
Explanation:
Displacement = velocity*time
Displacement = -98 m/s * 45 s
Displacement = -4410 m
6. The speed of sound waves in air is 330 m/s. A sound wave has a frequency of 750 Hz.
a. What is its wavelength as it travels through air?
b. What is its period?
Answers
Answer:
Wavelength = 0.44 meter
Time period = 0.0013 seconds
Explanation:
Given:
Speed of sound = 330 m/s
Frequency = 750 Hz
Find:
Wavelength
Time period
Computation:
Wavelength = Velocity / Frequency
Wavelength = 330 / 750
Wavelength = 0.44 meter
Time period = 1 / Frequency
Time period = 1/750
Time period = 0.0013 seconds
Kinetic theory told us that gas particles are moving constantly and bumping into anything in their path. The collisions of these particles in the gas result in ___________ .
a
Energy conversion
b
Pressure
c
Creation of new forms of matter
d
Potential energy
Answers
Answer:
a
Explanation:
because if gas particles move they move with speed and that is because they are free,so when they bump into something,they bump into it with force so it converts the energy
which has an effect on acceleration (speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction)?
Answers
Explanation:
If acceleration points in the same direction as the velocity, the object will be speeding up. The acceleration points in the same direction as the velocity if the car is speeding up, and in the opposite direction if the car is slowing down.

What is the force that counteracts the thrust force for flight?
Answers
The force which counteracts the thrust force for the flight is known as the drag force, as it opposes the flow.
What is drag force?Drag is a force that opposes an object's relative motion to a fluid environment in the field of fluid dynamics. It may be among two liquid film (or surfaces) or in between a liquid and a flat wall. The drag force is influenced by velocity, as opposed to other resistive forces like dry contact, which are essentially independent of it.
When a flow is moving at low or high speed, the drag force is equal to the speed for low pressure and to the square of the velocity for high-speed flow. Although viscous friction is what ultimately causes drag, turbulent drag is unaffected by viscosity.
A force in physics is an input that has the power to change an object's motion. A mass-containing object's velocity can vary, or accelerate, as a result of a force. Intuitively, a push or a pull can also be used to describe forces.
To know more about drag force:
https://brainly.com/question/12774964
#SPJ5
The drag force, which resists the flow, is the force that balances the propulsion force for flight.
What is Drag force?In the study of fluid dynamics, drag is a force that opposes an object's relative motion to a fluid environment. It could be situated between two liquid surfaces (or films) or between a liquid and a flat wall.
Unlike other resistive forces like dry contact, which are largely independent of velocity, the drag force is affected by it.
For low pressure and high speed flows, respectively, the drag force is equal to the speed for low pressure and the square of the velocity. Although drag is ultimately caused by viscous friction, turbulent.
Thus, The drag force, which resists the flow, is the force that balances the propulsion force for flight.
Learn more about Drag force, refer to the link:
https://brainly.com/question/13258892
#SPJ6
Two men push a bobsled with a total force of 250 Newtons. The
combined mass of the men and the bobsled is 230 kilograms.
Ignoring friction, what is the acceleration of the bobsled??(
F = ma)
Answers
Answer:
\(0.78m \: per {s}^{2} \)
the nec allows what maximum number of receptacle outlets to be connected on a 120-volt residential lighting or small-appliance branch circuit?
Answers
The quantity of outlets that must be installed on each of the branch circuits has no set maximum.
Technically, a 15 amp circuit breaker may support any number of outlets. A good guideline is 1 outlet per 1.5 amps, up to 80% of the circuit breaker's capability. As a result, we advise no more than 8 outlets on a 15 amp circuit. You see, the number of outlets that can be installed on a single 20 amp circuit is not explicitly capped by the National Electrical Code (NEC). A lighting and appliance branch circuit panelboard may have up to 42 overcurrent devices fitted (excluding the main device), in accordance with NEC.
Learn more about circuit here-
https://brainly.com/question/12608516
#SPJ4
Which one of the following statements concerning the buoyant force on an object submerged in a liquid is true
Answers
The buoyant force depends on the volume of the liquid displaced.
A force that is generated upward by the water that an object displaces is known as buoyancy.
It is directly proportional to the volume (weight) of water that is being displaced by an object, in accordance with Archimede's principle
Therefore, the force of buoyancy pushing an object up increases as an object displaces more water.
Where;
Fb is the amount of buoyant force a liquid exerts on an object.
gravity-induced acceleration, or g.
p equals the liquid's density.
v is the liquid's displacement volume.
h is the height of water that an object has moved.
A stands for the floating object's surface area.
The buoyancy unit of measurement is the Newton (N).
Additionally, the buoyant force acting on a fluid is directly inversely correlated to its density, meaning that as a liquid's density falls, buoyancy increases, and vice versa.
Therefore, the assertion that the buoyant force on an item submerged in a liquid relies on the volume of the liquid displaced is valid.
Learn more about buoyant force here brainly.com/question/21990136
#SPJ4.
4 is just for reference - i need 5. For the function f(x)=x−tan x with 0 ≤ x ≤ π 2 , the values of x= 0.0, 0.15708, 0.31416, 0.3927, 0.5236, 0.7854, 1.0472 were used to determine the corresponding values of f(x). Find the discrete least squares polynomial of the 2nd degree that will fit the data. (15 points) (5) For the same data in part (4) above, find the discrete least squares trigonometric polynomial, S4(x). (15 points)
Answers
1. The discrete least squares polynomial of the 2nd degree that fits the data is f(x) = -0.553x^2 + 1.025x + 0.022. 2. The discrete least squares trigonometric polynomial S4(x) is S4(x) = 0.026 + 0.994cos(x) + 0.995cos(2x) - 0.118sin(x) - 0.012sin(2x).
1. To find the discrete least squares polynomial of the 2nd degree, we use the method of least squares to minimize the sum of the squared differences between the given data points and the polynomial.
The resulting polynomial is f(x) = -0.553x^2 + 1.025x + 0.022.
2. To find the discrete least squares trigonometric polynomial, S4(x), we express the polynomial in terms of trigonometric functions (cos and sin) to fit the given data points.
Using the method of least squares, we minimize the sum of the squared differences between the data points and the trigonometric polynomial.
The resulting polynomial is S4(x) = 0.026 + 0.994cos(x) + 0.995cos(2x) - 0.118sin(x) - 0.012sin(2x).
These polynomials provide the best fit for the given data points using the least squares method.
To know more about polynomial, refer here :
https://brainly.com/question/29110563#
#SPJ11
Given that q=12 micro coulomb and d=16m find the direction and magnitude of the net electrostatic force exerted on the point charge where q1=+q q2=-2. 0q q3=+30q
Answers
Electrostatic force the force between static charges.Net force is 12056.9 q N in the positive y-direction, found by vector summing forces from charges q1, q2, and q3.
To find the net electrostatic power applied on the point charge, we want to compute the power applied by every one of different charges and afterward find the vector amount of these powers.To start with, we can compute the power applied on the point charge by q1. We can utilize Coulomb's regulation to track down the extent of the power:
F1 = k * q1 * q/\(d^2\)
Where k is the Coulomb steady (\(9 x 10^9 N m^2/C^2\)). Connecting the qualities, we get:
F1 = \(9 x 10^9 * 12 x 10^-6 * q/(0.016)^2\)
F1 = 2535.94 q N
The heading of the power applied by q1 is towards the point charge, since q1 is positive.Then, we can ascertain the power applied on the point charge by q2. Since q2 is negative, the power will be the other way of the vector joining the two charges. Utilizing Coulomb's regulation once more, we get:
F2 = k * q2 * q/\(d^2\)
F2 = \(9 x 10^9 * (- 2.0) * 12 x 10^-6 * q/(0.016)^2\)
F2 = - 5071.88 q N
The extent of the power is more noteworthy than the power applied by q1, yet the heading is inverse.At long last, we can compute the power applied on the point charge by q3. Utilizing Coulomb's regulation once more, we get:
F3 = k * q3 * q/\(d^2\)
F3 =\(9 x 10^9 * 30 * 12 x 10^-6 * q/(0.016)^2\)
F3 = 11462.5 q N
The heading of the power applied by q3 is towards the point charge, since q3 is positive.To find the net power, we really want to add these three vectors. Since the heading of the power applied by q2 is inverse to that of q1 and q3, we want to take away it from the amount of the other two vectors. Composing the vectors in part structure and adding them, we get:
Fnet = (2535.94 - 5071.88) I + (0) j + (11462.5) k
Fnet = - 2535.94 I + 11462.5 k
The greatness of the net power is:
|Fnet| = \(sqrt((- 2535.94)^2 + (0)^2 + (11462.5)^2) = 12056.9 q N\)
The heading of the net power is towards the positive y-pivot, since there is no part of the power in the x-bearing. Accordingly, the net electrostatic power applied on the point charge is 12056.9 q N in the positive y-course.
To learn more about numerical on electrostatic force, refer:
https://brainly.com/question/8635934
#SPJ4
A wire is placed within a magnetic field, and a current starts to flow through
the wire. Which statement about the magnetic field must be true?
O A. The field is produced by permanent magnets,
O B. The field is moving
C. The field is produced by induced magnetism.
OD. The field is not moving
PLEASE PLEASE HELP QUICK
Answers
Answer:
B. The field is moving
An object has gravitational potential energy due to its?
Answers
An object has gravitational potential energy due to its an position relative to the gravitational field it is in.
The gravitational potential energy is determined by the mass of the object, the gravitational constant, and the distance between the object and the source of the gravitational field.
Gravitational potential energy is a type of potential energy that an object can have due to its position in a gravitational field. It is the energy that is stored in an object due to its position in a gravitational field and can be converted into other forms of energy.
Learn more about gravitational potential energy:
https://brainly.com/question/15896499
#SPJ4
What is the name of the process on a neuron that carries electrical impulses toward the cell to be stimulated?.
Answers
Answer:
axon
Explanation:
Three people trying to move a box. Which set of forces will result in a net force on the box of 20 N to the right?

Answers
we have that from the Question"Three people trying to move a box. Which set of forces will result in a net force on the box of 20 N to the right?" it can be said that
The set of forces which will result in a net force on the box of 20 N to the right isOption DFrom the Question we are told
Three people trying to move a box. Which set of forces will result in a net force on the box of 20 N to the right?
Generally the equation for Net Force is mathematically given as
Fn=Fx+Fy...
Therefore
The force from the option that give a Net Force of 20 to the right is
\(Fn=(28+10)-(18)\\\\Fn=20N\)
Therefore
The set of forces which will result in a net force on the box of 20 N to the right is
Option D
For more information on this visit
https://brainly.com/question/19007362?referrer=searchResults
Answer: The correct answer is A
55N, 16N, 17N
Explanation: I took the quiz
Which two statements describe force?

Answers
Answer:
I think its C and D
Explanation:Force is like a energy that moves stuff. :)
what fluid property is responsible for the development of the velocity boundary layer? for what kinds of fluids will there be no velocity boundary layer in a pipe?
Answers
Fluid viscosity is the property of the fluid that is responsible for the development of the velocity boundary layer. Non-viscous fluids do not exhibit the property of velocity boundary layer in a pipe.
What is fluid viscosity?
Thickness of a fluid is called its viscosity. In liquids, velocity boundary layer is formed due to viscosity.
Viscosity is also termed as the flow rate of a liquid. If a liquid has a high flow rate then its viscosity is low and vice versa.
The fluid viscosity can be measured by using viscometer. The formula to measure viscosity is F = μA. u/y
Here F is force, μ is fluid viscosity, A is the area and u/y sheer deformation rate.
On the contrary, a non-viscous fluid is one that has less thickness and can flow easily.
For example, water is a non-viscous fluid.
If you need to learn more about velocity click here:
https://brainly.com/question/25905661
#SPJ4
A bell hanging at the top of a tower has 8,550 J of gravitational potential energy. It has a mass of 20 kg. If the bell falls to the ground so that all of its potential energy gets converted to kinetic energy, what will it's final velocity be?
Answers
The gravitational potential energy (PE) of an object is given by the formula:
PE = mgh
where m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the object above some reference point.
In this case, the bell has a PE of 8,550 J and a mass of 20 kg. We can rearrange the above formula to solve for the height h:
h = PE/(mg)
Substituting the given values, we get:
h = 8,550 J / (20 kg x 9.81 m/s^2) ≈ 43.4 meters
This is the height from which the bell falls. When the bell falls to the ground, all of its PE is converted to kinetic energy (KE). The formula for KE is:
KE = (1/2)mv^2
where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity.
Setting the PE equal to the KE, we get:
PE = KE
mgh = (1/2)mv^2
Simplifying and solving for v, we get:
v = √(2gh)
Substituting the values for g and h, we get:
v = √(2 x 9.81 m/s^2 x 43.4 m) ≈ 29.4 m/s
Therefore, the final velocity of the bell when it hits the ground is approximately 29.4 m/s.
a 5.0 kg ball is dropped from a height of 12.0 m above one end of a uniform bar that pivotsat its center. the bar has mass 8.0 k and is 4.0 m in length. at the other end of the bar sitsanother 5.0 kg ball, unattached to the bar. the dropped ball sticks to the bar after the collision.how high will the other ball go after the collision?
Answers
To solve this problem, we can apply the principle of conservation of angular momentum.Since the final angular velocity is zero, the bar will not rotate after the collision. Therefore, the other ball will not rise after the collision, and it will remain at the same height.
The angular momentum (L) of an object can be calculated as the product of its moment of inertia (I) and angular velocity (ω):
L = I × ω
For the system consisting of the bar and the two balls, the initial angular momentum is zero, and after the collision, the angular momentum is given by:
L = I × ω
The moment of inertia (I) of the system is the sum of the moment of inertia of the bar and the moment of inertia of the two balls.
The moment of inertia of the bar (I\(_{bar}\)) about its center can be calculated as:
I\(_{bar}\) = × m\(_{bar}\) × L²
where m\(_{bar}\) = 8.0 kg is the mass of the bar and L = 4.0 m is the length of the bar.
The moment of inertia of each ball (I\(_{ball}\)) about the pivot point can be calculated as:
I\(_{ball}\) = m\(_{ball}\) × R²
where m\(_{ball}\)= 5.0 kg is the mass of each ball, and R is the distance from the pivot point to the ball.
Since the balls are attached to the ends of the bar, the distance from the pivot point to each ball is half the length of the bar:
R = \(\frac{L}{2}\)= \(\frac{4}{2}\) = 2.0 m
Now, let's calculate the total moment of inertia :
I\(_{bar}\)= (1/12) × 8.0 kg × (4.0 m)²
= 8/3 kg·m²
I\(_{ball}\)= 5.0 kg × (2.0 m)²
= 20 kg·m²
I\(_{ball}\)= I\(_{bar}\) + 2 × I\(_{ball}\)
= 8/3 kg·m² + 2 * 20 kg·m²
= 8/3 kg·m² + 40 kg·m²
= 8/3 kg·m² + 120/3 kg·m²
= 128/3 kg·m²
After the collision, the system will rotate about the pivot point with an angular velocity (ω). The angular velocity can be calculated from the conservation of angular momentum equation:
L\(_{initial}\) = L\(_{final}\)
0 = I\(_{initial}\) × ω\(_{initial}\) + I\(_{ball}\) × ω\(_{final}\)
Since the initial angular velocity is zero, we can solve for the final angular velocity:
I\(_{ball}\) *ω\(_{final}\)= 0
Now, let's calculate the final angular velocity (ω\(_{final}\)):
ω\(_{final}\)= 0 / (I\(_{total}\) + I\(_{ball}\))
= 0 / (128/3 kg·m² + 20 kg·m²)
= 0 / (128/3 kg·m² + 60/3 kg·m²)
= 0 / (188/3 kg·m²)
= 0
Since the final angular velocity is zero, the bar will not rotate after the collision.
Therefore, the other ball will not rise after the collision, and it will remain at the same height.
To know more about angular momentum
https://brainly.com/question/4126751
#SPJ4
brain
the pressure at the ground floor to be 270 KPa.
A man's brain is approximately 0.33 m above his heart. If the density of human blood
is 1.05 X 109 Kg/m², determine the pressure required to circulate blood between the
heart and the brain.
Answers
which type of energy does a ball falling through the air have?
Answers
Answer:
the answer would be kinetic energy
Describe the electric and magnetic fields of an electromagnetic wave.
Answers
- Electricity can be static, like the energy that can make your hair stand on end
- An electric field is a vector quantity and can be visualized as arrows going toward or away from charges.
-An electric field is a region of space around an electrically charged particle or object in which an electric charge would feel force.
Magnetic:
-Magnetic fields force moving electrically charged particles in a circular or helical path.
-A magnetic field is basically used to describe the distribution of magnetic force around a magnetic object.
-a surrounding area where magnetic forces occur.
Class 11
Physics
Motion in a Plane
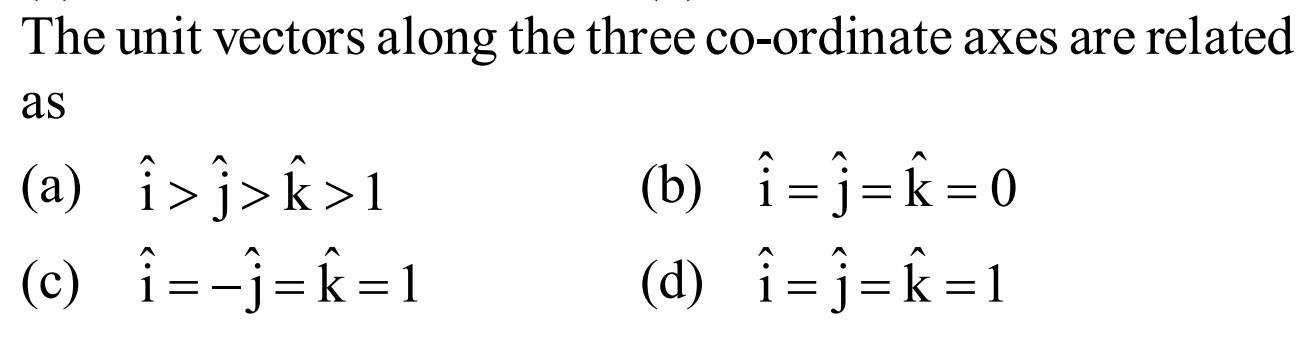
Answers
The unit vectors along the three co-ordinate axes are described as. i > j > k > 1. is D. i = j = k = 1
What is the unit vector along the vector?A vector that has a volume of 1 is a unit vector. It is also known as a direction vector because it is generally used to denote the direction of a vector. The vectors i, j, k, stand the unit vectors along the x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis respectively.
What is the unit vector along y-axis?
There are three essential unit vectors which are commonly employed and these are the vectors in the direction of the x, y and z-axes. The unit vector in the direction of the x-axis is i, the unit vector in the direction of the y-axis is j and the unit vector in the demand of the z-axis is k.
To learn more about unit vectors, refer
https://brainly.com/question/2094736
#SPJ9
A merry-go-round moves in a circle at a constant speed. Is the merry-go-round accelerating? Explain your answer.
Uniform Circular Motion:
Uniform Circular motion is the motion of a body that moves at constant angular velocity. Some examples of bodies that move at uniform circular motion are the blades of a fan set at a constant setting and the motion of a compact disc while the player is on.
Answers
The merry-go-round is accelerating since it is moving in a circle despite the fact that it is moving at a constant speed. The fact that an object moves in a circle does not always imply that it is moving at a constant speed. When an object moves in a circle, it changes direction, and this alteration of direction implies that the object is accelerating.
Even if the speed remains constant, it is still accelerating because the velocity is changing. This is referred to as centripetal acceleration. Centripetal acceleration is the acceleration caused by a force that pulls an object towards the center of the circle. Centripetal force is required for a body to move in a circle. A merry-go-round moves in a circle at a constant speed. This implies that the speed of the merry-go-round does not vary. However, the direction of motion changes continuously, indicating that the merry-go-round is constantly accelerating. Therefore, the merry-go-round is accelerating despite the fact that it is moving at a constant speed.
to know more about Centripetal acceleration visit:
https://brainly.com/question/8825608
#SPJ11
The eficiency of a
simple machine can never be 100% why?
Answers
Answer:
Systems always tend toward a state of decreasing order unless more energy is provided into the system to counteract this tendency.