Answers
Answer:
True
Explanation:
Answer:
true true true true true
Explanation:
true true true
Related Questions
A frictionless plane is 10.0 m long and inclined at 36.0°. A sled starts at the bottom with an initial speed of 6.00 m/s up the incline. When the sled reaches the point at which it momentarily stops, a second sled is released from the top of the incline with an initial speed Vi. Both sleds reach the bottom of the incline at the same moment.
(a) Determine the distance that the first sled traveled up the incline. m
(b) Determine the initial speed of the second sled. m/s
Use the equation for the position of the second sled as a function of time to find the speed that makes it reach the bottom of the slope in the same time that the first sled takes to slide back down.
Answers
If a frictionless plane is 10.0 m long and inclined at 36.0°.
The sled traveled 8.17 m up the incline.The initial speed of the second sled is about 5.68 m/sHow to find the initial speed?We can use conservation of energy to find the distance that the first sled travels up the incline. The potential energy of the sled at the bottom of the incline is zero, and its kinetic energy is:
KE = (1/2)mv^2
where m is the mass of the sled and v is its speed. At the point where the sled stops, all of its kinetic energy has been converted into potential energy, so we can write:
mgh = (1/2)mv^2
where h is the height that the sled has traveled up the incline. Solving for h, we get:
h = (v^2)/(2g)
where g is the acceleration due to gravity. Using the given values, we have:
h = (6.00 m/s)^2 / (2 * 9.81 m/s^2) = 1.83 m
So the first sled travels a distance of 10.0 m - 1.83 m = 8.17 m up the incline.
b. To find the initial speed of the second sled, we can use conservation of energy again. At the top of the incline, the sled has potential energy:
PE = mgh
where h is the height of the incline. As the sled slides down the incline, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy:
KE = (1/2)mv^2
where v is the speed of the sled at the bottom of the incline. We can equate these two expressions and solve for v:
mgh = (1/2)mv^2
v = sqrt(2gh)
Using the given values, we have:
v = sqrt(2 * 9.81 m/s^2 * 10.0 m * sin(36.0°)) = 12.2 m/s
So the second sled must be released from the top of the incline with an initial speed of 12.2 m/s.
The position of the sled as a function of time is given by:
y = -0.5gt^2 + Vi*t + h
where y is the vertical position of the sled, t is the time, Vi is the initial speed of the sled, and h is the height of the incline. At the bottom of the incline, y = 0, so we can solve for the time it takes for the second sled to reach the bottom:
0 = -0.5gt^2 + Vi*t + h
t = (Vi ± sqrt(Vi^2 - 2gh)) / g
Since we want both sleds to reach the bottom at the same time, we set the time for the first sled to slide down the incline equal to this expression for t and solve for Vi:
t = sqrt(2h/g) = sqrt(2 * 1.83 m / 9.81 m/s^2) = 0.619 s
0 = -0.5gt^2 + Vi*t + h
Vi = (h - 0.5gt^2) / t
Vi = (1.83 m - 0.5 * 9.81 m/s^2 * (0.619 s)^2) / 0.619 s
Vi = 5.68 m/s
So the initial speed of the second sled is about 5.68 m/s
Learn more about initial speed here:https://brainly.com/question/24493758
#SPJ1
18. The displacement of an object moving 330 km North for 2 hours and an additional 220
km North for 5 hours is
a. 110 km North
b. 220 km North
c. 330 km North
d. 550 km North
19. When something falls to the ground, it accelerates. This acceleration is called the acceleration due to
gravity and is symbolized by the letter g. What is the value of g on Earth's surface?
a. 9.8 m/s2
b. 9.8 m/s
c. - 9.8 m/s2
d. about 20 m/s2
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
1) Displacement of the object will be gotten using simply adding the distances since they are goinf in the same direction (positive y direction)
Displacement= 330km + 220km
Displacement = 550km North
2) For a falling body, the body will possess positive acceleration due to gravity because it is falling under the influence of gravitational force. If a body is not under the influence of gravity and is thrown up, such body wont come back down. Hence the value of acceleration due to gravity of a body falling to the ground is +9.8 m/s² (note that the unit of acceleration is m/s²)
What is the speed of the plane wave defined by sin(ωt−kx) with ω=3376.7 Thz and k=11.79μm−1?
Answers
The speed of the plane wave defined by sin(ωt−kx) is 2.864 × 10⁸ m/s
Speed of a wavethe speed of the plane wave defined by sin(ωt−kx) is v = ω/k where
ω = angular frequency of wave and k = wave number of waveNow ω = 3376.7 Thz = 3376.7 × 10¹² Hz and k = 11.79μm⁻¹ = 11.79 × 10⁶ m⁻¹
So, substituting the values of the variables into v, we have
v = ω/k
v = 3376.7 × 10¹² Hz/11.79 × 10⁶ m⁻¹
v = 286.4 × 10⁶ m/s
v = 2.864 × 10⁸ m/s
The speed of the plane wave defined by sin(ωt−kx) is 2.864 × 10⁸ m/s
Learn more about speed of a plane wave here:
https://brainly.com/question/2847127
The Sun's energy comes from which nuclear reaction?
A. Nuclear fission
B. Gamma decay
C. Positron emission
D. Nuclear fusion
SUBMIT
Answers
Explanation: The sun is a main-sequence star, it generates its energy by nuclear fusion of hydrogen nuclei into helium.
Sun's energy comes from the nuclear fusion taking place inside. In nuclear fusion two light nuclei fuses together to form a heavy nuclei with the release of greater amount of energy.
What is nuclear fusion :Nuclear fusion is the process of combining two light nuclei to form a heavy nuclei. In this nuclear process, tremendous energy is released. This is the source of heat and light in stars.
On the other hand, nuclear fission is the process of breaking of a heavy nuclei into two lighter nuclei. Fission also produces massive energy. But in comparison, more energy is produced by nuclear fusion.
Nuclear fission is used in nuclear power generators. The light energy and heat energy comes form the nuclear fusion of hydrogens to form helium nuclei. Hence, option D is correct.
Find more on nuclear fusion:
https://brainly.com/question/12701636
#SPJ2
A toy car travels at 5.3 m/s. The car travels a distance of 17.8 m. How long did it
take to travel that distance?
Answers
Explanation:
Assuming constant speed:
Distance = speed × time
17.8 m = (5.3 m/s) t
t = 3.36 s
If an object is placed between a convex lens and its focal point, which type of image will be produced?
Answers
If the car has a mass of 0.2 kg, the ratio of height to width of the ramp is 12/75, the initial displacement is 2.25 m, and the change in momentum is 0.58 kg*m/s, how far will it coast back up the ramp before changing directions
Answers
Answer:
l = 0.548 m
Explanation:
For this exercise we compensate by finding the speed of the car
p = m v
v = p / m
v = 0.58 / 0.2
v = 2.9 m / s
this is how fast you get to the ramp, let's use conservation of energy
starting point. Lowest point
Em₀ = K = ½ m v²
final point. Point where it stops on the ramp
\(Em_{f}\) = U = m g h
mechanical energy is conserved
Em₀ = Em_{f}
½ m v² = m g h
h = \(\frac{m v^2}{2 g}\)
let's calculate
h = \(\frac{0.2 \ 2.9^2}{2 \ 9.8}\)
h = 0.0858 m
to find the distance that e travels on the ramp let's use trigonometry, we look for the angle
tan θ = y / x
tan θ = 12/75 = 0.16
θ = tan⁻¹ 0.16
θ = 9º
therefore
sin 9 = h / l
l = h / sin 9
l = 0.0858 / sin 9
l = 0.548 m
A laboratory measurement finds 200 μg of hemoglobin per μL of blood. Hemoglobin, the blood protein that transports oxygen, has a molecular weight of 64 kDa or 64,000 u , where 1 dalton ( Da ) = 1 atomic mass unit ( u ) = 1.66×10^−24g . Estimate the number of hemoglobin proteins in one red blood cell. Express your answer in hemoglobin per red blood cell.
Answers
One red blood cell contains an estimated 251 molecules of haemoglobin, according to our estimation.
What size does a red blood cell typically have?The average red blood cell has a diameter of 6 to 8 micrometres, according to the American Society of Haematology, and a volume of 113-268 μm³ or 113-268x10⁻¹² L.
Let's first change the haemoglobin concentration from grammes per litre to grammes per litre so that it has the same units as the molecular weight:
200 μg/μL x 1 g/1000 μg x 10⁶ μL/L = 0.2 g/L
Next, let's translate hemoglobin's molecular weight from kDa to grammes per molecule:
64 kDa x 1000 Da/kDa x 1.66x10⁻²⁴ g/Da = 1.06x10⁻²⁰ g/molecule
Using Avogadro's number, we can now determine how many haemoglobin molecules are present in a single litre of blood (\(6.022*10^{23}\) molecules/mol): 0.2 g/L x 1 mol/1.06x10⁻²⁰ g x \(6.022*10^{23}\) molecules/mol = 1.13x10¹⁵ molecules/L.
Divide the total number of molecules in 1 litre of blood by the volume of red blood cells to get the amount of haemoglobin molecules per red blood cell. The typical red blood cell count range, according to the American Society of Haematology, is between 4.5-5.5 million cells/L, which translates to 4.5-5.5x10¹² cells/L.
When we divide the quantity of red blood cells in 1 L by the quantity of haemoglobin molecules, we get:
1.13x10¹⁵ molecules/L / 4.5x10¹² cells/L = 251 Red blood cell haemoglobin molecules, rounded to the closest integer.
To know more about hemoglobin, visit:
brainly.com/question/15011428
#SPJ1
what is hookies law of elasticity
Answers
Hooke's law of elasticity is a principle in physics that states that the force required to extend or compress a spring by some distance is proportional to that distance. It is named after the English physicist Robert Hooke, who first stated the law in 1678. Hooke's law is often written as F = -kx, where F is the force applied to the spring, x is the distance it is stretched or compressed, and k is the spring constant, a measure of the stiffness of the spring.
Suppose 10.0 g of ice at -10.0C is placed into 300.0 g of water in a 200.0-g copper calorimeter. The final temperature of the water and copper calorimeter is 18.0C.
1) What was the initial common temperature of the water and copper? (Express your answer to three significant figures.)
Answers
The initial common temperature of the water and copper is approximately 2.68°C.
To find the hidden typical temperature of the water and copper, we need to use the norm of protection of energy, which communicates that energy can't be made or obliterated, recently moved or changed beginning with one design then onto the following.
The force lost by the ice as it breaks up is identical to the power obtained by the water and the calorimeter. We can impart this using the recipe:
Q_ice = Q_water + Q_calorimeter
where Q_ice is the force lost by the ice, Q_water is the power procured by the water, and Q_calorimeter is the force gained by the calorimeter.
We can determine the power lost by the ice using the recipe:
Q_ice = m_ice * L_f
where m_ice is the mass of the ice and L_f is the force of blend of water, which is 333 J/g.
Q_ice = (10.0 g) * (333 J/g) = 3330 J
We can sort out the force obtained by the water using the condition:
Q_water = m_water * c * (T_f - T_i)
where m_water is the mass of the water, c is the specific power breaking point of water, which is 4.184 J/g°C, T_f is the last temperature of the water and calorimeter, and T_i is the hidden ordinary temperature of the water and calorimeter.
Q_water = (300.0 g) * (4.184 J/g°C) * (18.0°C - T_i)
We can figure the force obtained by the calorimeter using the recipe:
Q_calorimeter = m_calorimeter * c_calorimeter * (T_f - T_i)
where m_calorimeter is the mass of the calorimeter, which is 200.0 g, c_calorimeter is the specific force breaking point of copper, which is 0.385 J/g°C, T_f is the last temperature of the water and calorimeter, and T_i is the hidden ordinary temperature of the water and calorimeter.
Q_calorimeter = (200.0 g) * (0.385 J/g°C) * (18.0°C - T_i)
Subbing these circumstances into the norm of conservation of energy, we get:
m_ice * L_f = m_water * c * (T_f - T_i) + m_calorimeter * c_calorimeter * (T_f - T_i)
Tending to for T_i, we get:
T_i = T_f - [(m_ice * L_f)/(m_water * c + m_calorimeter * c_calorimeter)]
T_i = 18.0°C - [(10.0 g) * (333 J/g)/(300.0 g * 4.184 J/g°C + 200.0 g * 0.385 J/g°C)]
T_i = 2.68°C
As needs be, the basic ordinary temperature of the water and copper was 2.68°C (conveyed to three immense figures).
To learn more about temperature, refer:
https://brainly.com/question/31909880
#SPJ1
The force between a pair of charges is 900 newtons. The distance between the charges is 0.01 meters. If one of the charges is 2e-10 C what is the strength of the other charge ?
Answers
Answer:
\( \fbox{strength \: of \: the \: other \: charge = - 0.0196 Ke \: Coulomb}\)
Explanation:
Given:
Force between pair of charges= 900 newtons
The distance between the charges = 0.01 meters
Strength of Charge first q1 = 2e-10 Coulomb
To find:
Strength of Charge second q2 = ____ Coulomb?
Solution:
We know that,
Force between two charges separate by distance r is given by the equation,
\(|F| = K_e \frac{q1 \cdot \: q2}{ {r}^{2} } \\ 900 =K_e \frac{(2e - 10)\cdot \: q2}{ {0.01}^{2} } \\ 900 \times {10}^{ - 4} = K_e {(2e - 10)\cdot \: q2} \\ q2 = \frac{9 \times {10}^{ - 2} }{(2e - 10) K_e} \\ \\ \fbox{We \: know \: that \: e = 2.71 } \\ substituting \: the \: value \: \\ q2 = \frac{9 \times {10}^{ - 2} }{(2 \times 2.71 - 10)K_e} \\ q2 = \frac{0.09}{ - 4.58 K_e} \\ q2 = \frac{-0.0196}{K_e}\: coulomb\)
\( \fbox{strength \: of \: the \: other \: charge = - 0.0196 Ke \: Coulomb}\)
Thanks for joining brainly community!
Friction is actually caused by what?
A. The electrostatic interaction between the molecules on the two surfaces moving across each other which is seen as normal forces on a microscopic scale.
B. The ratio of the mass is between the object.
C. The amount of force used to move one object where a higher force creates higher friction.
D. The interaction between the chemical bonds of the materials the objects are made of.
Answers
Answer:
The atomic number
The electrostatic interaction between the molecules on the two surfaces moving across each other which is seen as normal forces on a microscopic scale.
A block with mass 0.470 kg sits at rest on a light but not long vertical spring that has spring constant 85.0 N/m and one end on the floor. A second identical block is dropped onto the first from a height of 4.40 m above the first block and sticks to it. What is the maximum elastic potential energy stored in the spring during the motion of the blocks after the collision? What is the maximum distance the first block moves down after the second block has landed on it?
Answers
Answer: 0.487 m.
Explanation: First, we need to find the velocity of the second block just before it lands on the first block. We can use the conservation of energy:
mgh = (1/2)mv^2
v = sqrt(2gh)
where m = 0.470 kg, g = 9.81 m/s^2, and h = 4.40 m. Plugging in these values, we get:
v = sqrt(2 × 9.81 × 4.40) = 9.76 m/s
Since the second block sticks to the first block, the two blocks move together as one object. The maximum compression of the spring occurs when the velocity of the blocks becomes zero, and all of the kinetic energy has been converted to elastic potential energy.
The total mass of the two blocks is 0.470 kg + 0.470 kg = 0.940 kg. Using the conservation of energy again, we can find the maximum compression of the spring:
(1/2)mv^2 = (1/2)kx^2
where k = 85.0 N/m is the spring constant, and x is the maximum compression of the spring. Solving for x, we get:
x = sqrt((mv^2)/k) = sqrt((0.940 kg × (9.76 m/s)^2) / 85.0 N/m) = 0.487 m
Therefore, the maximum elastic potential energy stored in the spring is:
(1/2)kx^2 = (1/2) × 85.0 N/m × (0.487 m)^2 = 10.0 J
The maximum distance the first block moves down after the second block has landed on it is equal to the maximum compression of the spring, which is 0.487 m.
Construct a ray diagram to determine the image.
A thin lens is located centered over a 14 cm ruler at the 7 cm mark. A black dot is located at 5.5 cm on the left side of the lens and at 8.5 cm on the right side of the lens. An arrow is located at the 3.0 cm mark.
Where is the image located?
At 8.3 cm on the ruler
At 9.4 cm on the ruler
At 10.7 cm on the ruler
At 11.5 cm on the ruler
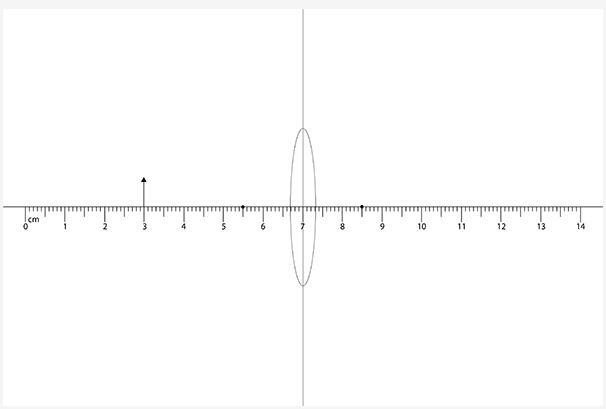
Answers
The distance of the image formed by the lens is at 10.7 cm on the ruler.
option C.
What is the location of the image?The distance of the image is calculated by applying lens formula as shown below;
1/f = -1/u + 1/v'
where;
f is the focal length of the lens v is the image distance u is the object distanceFrom the diagram, the focal length of the lens = 8.5 cm
the object distance = 3 cm
The image distance is calculated as follows;
1/v' = 1/f + 1/u
1/v' = 1/8.5 + 1/3
1/v' = 0.45
v' = 1/0.45
v' = 2.21 cm
The position of the image on the rule is calculated as follows;
v = v' + 8.5 cm
v = 2.21 cm + 8.5 cm
v = 10.71 cm
Thus, the ray - diagram shows the position or distance of the image formed.
Learn more about ray diagram here: https://brainly.com/question/15506795
#SPJ1

What is the largest atom of period 4
Answers
The largest atom of period 4 is Potassium (K).
What are the elements of period 4?
One of the chemical elements in the fourth row (or period) of the periodic table of the elements is known as element of period 4. The periodic table is organized into rows to show recurrent (periodic) tendencies in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number rises.
One element is present in each of the eighteen groups, making up the fourth period's 18 elements, which start with potassium and end with krypton. d-block, which includes transition metals, makes its first appearance in the table.
Learn more about periodic table; refer the link:
https://brainly.com/question/11155928
#SPJ1
What would make oppositely charged objects attract each other more?
o increasing the positive charge of the positively charged object and increasing the negative charge of the negatively
charged object
o decreasing the positive charge of the positively charged object and decreasing the negative charge of the negatively
charged object
O increasing the distance between the positively charged object and the negatively charged object
O maintaining the distance between the positively charged object and the negatively charged object
Answers
Answer:
First choice
Explanation:
F orce = C q1 q2 / r^2 to increae the force you can increase either charge or DECREASE the distance between them
A 75.0 kg man pushes on a 500,000 kg wall for 250 s but it does not move.
a. How much work does he do on the wall? ____________
b. How much energy is used?__________
c. How much power is exerted?____________
Answers
Since no work is done, the power exerted is zero. Therefore, the man exerts no power on the wall.
What is force?In physics, force is defined as any action that can change the motion of an object or cause an object to accelerate. Force is a vector quantity, meaning that it has both magnitude (size or strength) and direction. The unit of force in the International System of Units (SI) is the Newton (N), which is defined as the amount of force required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram at a rate of one meter per second squared (1 N = 1 kg × 1 m/s^2). Force can be measured using a variety of instruments, such as spring scales, strain gauges, or force plates. Some common types of forces include gravitational force, electromagnetic force, frictional force, and normal force. The study of forces and their effects on the motion of objects is known as mechanics and is a fundamental concept in physics.
Here,
a. The man does not do any work on the wall because the wall does not move. Work is only done when there is a displacement in the direction of the force applied.
b. Since no work is done, no energy is used or transferred.
c. The power exerted by the man can be calculated using the formula:
Power = Work / Time
To know more about force,
https://brainly.com/question/29044739
#SPJ9
A uniform brick of length 24 m is placed over the edge of a horizontal surface with a maximum overhang of 12 m attained without tipping.

Answers
The maximum overhang possible for the two bricks (without tripping) is 15m.
What is the detailed solution to the above question?Given,
Length of the brick (L) = 24m
Maximum overhang = 12m
Length of second brick = 24m
Maximum overhang for two bricks =?
Now,
Generally, the equation for the value x (mid-point joining the bricks) is given as,
x = 0.25 × L
=0.25 × 12
= 3m
Hence,
The maximum overhang possible for the two bricks (without tripping) will be,
L₀ = L/2 + x
= 24/2 + 3
= 12 + 3
= 15m
Therefore, The maximum overhang possible for the two bricks (without tripping) is 15m.
Learn more about overhang length, here:
https://brainly.com/question/26390576
#SPJ1
After coming down a slope, a 60-kg skier is coasting northward on a level, snowy surface at a constant 15 m>s. Her 5.0-kg cat, initially running southward at 3.8 m>s, leaps into her arms, and she catches it. (a) Determine the amount of kinetic energy converted to internal energy in the Earth reference frame. (b) What is the velocity, measured in the Earth reference frame, of an inertial reference frame in which the cat’s kinetic energy does not change?
Answers
The velocity, measured in the Earth reference frame, of an inertial reference frame in which the cat's kinetic energy does not change is equal to the velocity of the skier before the collision. The velocity of the skier before the collision is 15 m/s.
What is law of conservation of momentum?According to the law of conservation of momentum, the total momentum before the collision must be equal to the total momentum after the collision. This can be expressed as m1*v1 + m2*v2 = (m1 + m2)*vf, where m1 and m2 are the masses of the skier and the cat respectively, v1 is the velocity of the skier, and vf is the velocity of the skier and the cat after the collision.
The kinetic energy converted to internal energy in the Earth reference frame can be determined by applying the law of conservation of momentum.
The amount of kinetic energy converted to internal energy can be calculated as follows:
m1*v1 = (m1 + m2)*vf
vf = (m1*v1)/(m1 + m2)
KE = (1/2)*m2*v2²
KE converted = KE initial - KE final
KE converted = (1/2)*m2*v2² - (1/2)*m2*((m1*v1)/(m1 + m2))²
KE converted = (1/2)*m2*v2² - (1/2)*m2*((60*15)/(60 + 5))²
KE converted = (1/2)*5*3.8² - (1/2)*5*(15²/65)
KE converted = 28.8 - 22.15
KE converted = 6.65 J
The velocity, measured in the Earth reference frame, of an inertial reference frame in which the cat's kinetic energy does not change is equal to the velocity of the skier before the collision.
For more questions related to kinetic energy
https://brainly.com/question/8101588
#SPJ1
1. The development of what anatomical structure is one current idea for how the Cambrian Explosion began (the so-called Evolutionary Big Bang)? The
Answers
Answer:
One idea is how, on an astronomical level, the planets can be observed to spread apart continuously.
Explanation:
Throughout various studies, many have observed that the planets continuously grow distant from each other. In fact, it is observed through our technological advances that the very galaxies are slowly drifting apart. Thus, indicating there must have been some big bang to set these galaxies and planets in motion.
A positively charged rod is brought near a NEUTRAL metal sphere. Which of the following will happen, and why? A. The sphere is attracted to the rod because negative charges move to the side closest to the rod. B. Nothing, because the sphere is neutral. C. The sphere is attracted to the rod because it picks up some negative charge from the air D. The sphere is repelled from the rod because it picks up some of the rods positive charge.
Answers
The correct answer is option A. Because, When a positively charged rod is brought near a neutral metal sphere, the electrons in the metal sphere are attracted to the positively charged rod.
Since opposite charges attract each other, the negatively charged side of the sphere is attracted to the positively charged rod, causing the sphere to move towards the rod. . This redistribution of charges results in an attractive force between the rod and the sphere. The negative charges (i.e. electrons) in the metal sphere do not move to the side closest to the rod in order to repel it. This phenomenon is known as electrostatic induction, and it is a common example of how electric charges can influence each other without physical contact. Hence we know that the correct answer is option: A.
To know more about electrostatic induction, here
brainly.com/question/27716037
#SPJ4
Enter a curve slower than the posted speed if your vehicle has a high center of gravity or if surface _____________ is less than ideal.
a. traction
b. speed
c. energy
d. maneuvers
Answers
a. traction
If your vehicle has a high center of gravity or if the surface traction is less than ideal, it is important to enter a curve slower than the posted speed. This is because vehicles with a high center of gravity or poor surface traction are more prone to instability and are more likely to roll over or lose control when negotiating sharp turns or curves at high speeds.
Traction refers to the friction or grip between the tires of a vehicle and the road surface. Poor surface traction can be caused by a variety of factors, such as wet or slippery roads, loose gravel or debris, or worn or damaged tires. When surface traction is poor, it becomes more difficult for the tires to maintain contact with the road and to transmit the forces of acceleration, braking, and steering to the road.
By entering a curve slower than the posted speed, you can reduce the lateral forces acting on your vehicle and give your tires more time to grip the road. This can help you maintain control and stability, and reduce the risk of accidents or injuries. It is important to always adjust your speed and driving style to suit the conditions of the road and the capabilities of your vehicle.
To Learn More About Centripetal Force
https://brainly.com/question/14249440?referrer=searchResults
PLEASE HELP SOON! For the circuit below , the battery has 4.2V calculate power giving and power receiving

Answers
For this circuit, the voltage is 4.2 V. then power given is 0.9 W and receiving across 55Ω resistance is 0.07 W and that of 30Ω resistance is 0.14 W. Resistor are connected in parallel, its equvalent resistance is R₁R₂/R₁+R₂.
Both resistor are connected in parallel hence their equivalent resistance in parallel combination is given as,
R = 55*30/(55+30)
R = 19.4 Ω
Power given to the circuit is,
P = V²/R = 4.2/19.4 = 0.9 W
Receiving power taken from 55Ω resistor
P = V²/R = 4.2/55 = 0.07 W
Receiving power taken from 30Ω resistor
P = V²/R = 4.2/30 = 0.14 W
To know more about Power :
https://brainly.com/question/29869646
#SPJ1.
what were your preparetion before going the different physical fitness test?
Answers
Answer:
Avoid heavy strenuous exercise for the 24 hours prior to testing. Do not exercise at all on the day of testing to ensure you are well rested. Wear appropriate clothing for the conditions (e.g. shorts/track pants and t-shirt/singlet/sports top) and non-slip athletic footwear with laces securely fastened
If f is a linear function, f(0.1) = 10.5, and f(0.4) = −6.6, find an equation f(x) for the function.
Answers
The linear equation f(x) for the function is found as :
f(x) = -57x + 16.5.
How to find equation of linear function?The linear function is one that has the formula f(x) = mx + b, in which m denotes the line's slope and b its y-intercept. When two points of such a linear function are supplied, we can get the function by utilizing the two points to determine the line's slope, or m.Then plugging the slope along with one of the awarded numbers into the equation f(x) = mx + b, where b is the unknown. The last step is to enter m as well as b into f(x) = mx + b.For the stated question:
f(0.1) = 10.5, and f(0.4) = −6.6
Slope m = (-6.6 - 10.5) / (0.4 - 0.1)
m = -57
The standard equation is:
10.5 = -57(0.1) + c
c = 16.5
linear equation f(x):
f(x) = -57x + 16.5
Thus, the linear equation f(x) for the function is found as :
f(x) = -57x + 16.5.
To know more about the Linear Functions, here
https://brainly.com/question/2030026
#SPJ1
A bullet traveling at 5.0 x10^2 meters per is brought to rest by an impulse of 50 Newton*seconds. Find the mass of the bullet.
Answers
The bullet stops moving on hitting on a surface. Hence, the impulse here is equal to the momentum. Therefore, the mass of the bullet is 0.1 Kg.
What is impulse?Impulse in physics is the change in momentum. It is the product of the force and change in time.
hence, impulse = f. dt
When the bullet is travelling with a velocity of 500 m/s it has a momentum. When it brought to rest, momentum become zero. Thus, the momentum is equal to the impulse here.
Therefore, f.dt = m. v
f.dt = 50 N s
v = 500 m/s
m = 50 N s/500 m/s = 0.1 Kg
Therefore, the mass of the bullet is 0.1 Kg.
Find more on impulse:
https://brainly.com/question/904448
#SPJ1
the radiation that is least damaging to humans is
Answers
The radiation that is least damaging to humans is non-ionizing radiation.
What is non ionizing radiationNon-ionizing radiation refers to the type of radiation that does not have enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms or molecules, thus not causing significant damage to biological tissues.
Examples of non ionizing radiation include radio waves, microwaves, visible light and low energy ultraviolet (UV) radiation. while excessive exposure to any form of radiation can have adverse effects, non-ionizing radiation is generally considered to be less harmful compared to ionizing radiation, which includes X-rays and gamma rays.
Learn more about non-ionizing radiation at
https://brainly.com/question/9621276
#SPJ1
A man walks 8 m east in 12 seconds . What is the man's velocity ?
Answers
Answer:
0.67m/s due east
Explanation:
Given parameters:
Displacement of the man = 8m east
Time taken = 12s
Unknown:
Velocity of the man = ?
Solution:
The velocity of a body is the rate of displacement per time;
Velocity = \(\frac{Displacement}{time}\)
Velocity = \(\frac{8}{12}\) = 0.67m/s due east
A stone is allowed to fall from the top of the tower 100m high at the same moment another stone is projected vertically upward with a velocity of 25m/s. Where and when will the two cross each other
Answers
Answer:
both the stone will meet at a distance of 80 m from the top of tower.
Explanation:
let "t" = time after which both stones meet
"S" = distance travelled by the stone dropped from the top of tower
(100-S) = distance travelled by the projected stone.
◆ i) For stone dropped from the top of tower
-S = 0 + 1/2 (-10) t²
or, S = 5t²
◆ ii) For stone projected upward
(100 - S) = 25t + 1/2 (-10) t²
= 25t - 5t²
Adding i) and ii) , We get
100 = 25t
or t = 4 s
Therefore, Two stones will meet after 4 s.
◆ ¡¡¡) Put value of t = 4 s in Equation i) , we get
S = 5 × 16
= 80 m.
Thus , both the stone will meet at a distance of 80 m from the top of tower.
(Hope this helps can I pls have brainlist (crown)☺️)
the reading on a mercury barometer at mombasa is 760mms.calculate the pressure at mombasa(density of mercury=1.36x10 power 4kg/m3
Answers
Answer:
The pressure at Mombasa is 101.396 KPascal.
Explanation:
Given: Reading on barometer = 760 mm
= 0.76 m
Density of mercury = 1.36 x \(10^{4}\) kg/\(m^{3}\)
In this case, the pressure can be expressed as:
P = σhg
Where: σ is the density of mercury, h is height of mercury in the barometer, and g is the acceleration due of gravity.
But, g = 9.81 m/\(s^{2}\)
So that,
P = 1.36 x \(10^{4}\) x 0.76 x 9.81
= 101396.16 Pascal
P = 101.395 KPascal
The pressure at Mombasa is 101.396 KPascal.