scientists trying to calculate the half-life (the time it takes for half of a sample to decay) of phosphorus-32, took measurements of the sample once every day for five days. on what day should about half of the original amount of p-32 remain? (round answer to the nearest day.)
Answers
Day at which one-tenth of the original amount of P-32 remains i.e 10 g, t is 47 days.
The equation of above graph is y = -0.049x + 4.603 (y = mx +b)
Slope, average decay constant, m = -k = -0.049
decay constant, k = 0.049 /day
or it can be calculated by the integrated law equation :
ln [A] = -kt + ln [A]o
t = half life = t0.5
[A]o = 100 g
[A] at half-life = 100 g/2 = 50 g
k = 0.049/day
ln 50 = -0.049t0.5 + ln 100
3.912 = -0.049t0.5 + 4.605
3.912-4.605 = -0.049t0.5
-0.693 = -0.049 t0.5
half-life , t0.5 = -0.693/-0.049 = 14 days
day at which one-tenth of the original amount of P-32 remains i.e 10 g
ln [A] = -kt + ln [A]o
[A]o = 100 g
[A] = 10 g
k = 0.049/day
ln 10 = -0.049t+ ln 100
2.302 = -0.049t + 4.605
2.302-4.605 = -0.049t
-2.303 = -0.049 t
Day at which one tenth of original amount of P-32 is remained i.e 10 g , t = -2.303/-0.049 = 47 days
The slope of a line is a degree of its steepness. Mathematically, the slope is calculated as "upward push overrun" (trade-in y divided by using trade-in x).A numerical measure of a line's inclination relative to the horizontal. In analytic geometry, the slope of any line, ray, or line phase is the ratio of the vertical to the horizontal distance among any points on it (“slope equals upward push over run”).
The slope formulation is used to calculate the steepness or the incline of a line. The x and y coordinates of the strains are used to calculate the slope of the lines. it is the ratio of the alternatives within the y-axis to the change within the x-axis. The slope of a line is its vertical trade divided by means of its horizontal change, also referred to as upward thrust overrun. if you have 2 factors on a line on a graph the slope is the alternate in y divided by using the change in x.
To learn more about slope visit here:
brainly.com/question/3605446
#SPJ4

Related Questions
What element is shiny , solid at room temperature and has atoms with two valance electrons
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
gold think
Answer:
boron
Explanation:
The combustion of ethylene proceeds by the reaction
C2H4(g) + 3O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
When the rate of disappearance of O2 is 0.37 mol L-1 s-1, the rate of appearance of CO2 is ________ mol L-1s-1.
Answers
Thus, the rate of disappearance of O₂ is 0.37 mol L⁻¹ s⁻¹ , the rate of appearance of CO₂ is 0.2467 mol L⁻¹ s⁻¹
What is the rate of reaction?The rate at which a chemical reaction moves forward is known as the reaction rate in chemistry. It is frequently defined in terms of either the concentration of a reactant that is consumed in a unit of time or the concentration of a product that is generated in a unit of time (amount per unit volume).
The equation becomes:
C₂H₄(g) + 3O₂(g) → 2CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(g)
Rate of reaction = \(-\frac{d[C_2H_4]}{dt}\) = \(-\frac{1}{3} \frac{d[O_2]}{dt}\) = \(+\frac{1}{2} \frac{d[CO_2]}{dt}\) = \(+\frac{1}{2} \frac{d[H_2O]}{dt}\)
It is given that, the rate of disappearance of O₂ is 0.37 mol L⁻¹ s⁻¹.
So, \(-\frac{1}{3} \frac{d[O_2]}{dt} =\) \(+\frac{1}{2} \frac{d[CO_2]}{dt}\)
or, \(-\frac{1}{3} \frac{d[O_2]}{dt}\) × (-0.37 mol L⁻¹ s⁻¹) = \(\frac{d[CO_2]}{dt}\)
or, \(\frac{2}{3} \frac{d[O_2]}{dt}\) × (0.37 mol L⁻¹ s⁻¹) = \(\frac{d[CO_2]}{dt}\)
or, 0.2467 mol L⁻¹ s⁻¹ = \(\frac{d[CO_2]}{dt}\)
Thus, the rate of disappearance of O₂ is 0.37 mol L⁻¹ s⁻¹ , the rate of appearance of CO₂ is 0.2467 mol L⁻¹ s⁻¹
To know more about rate of reaction refer to:
https://brainly.com/question/24795637
#SPJ1
What is the mass of 3.01x 1022 molecules of phosphorus, P4 ? {R.AM for phosphorus is 31} *
Answers
To find the mass of 3.01 x 10^22 molecules of P4, we need to first calculate the number of moles of P4 in 3.01 x 10^22 molecules.
Number of moles = Number of molecules / Avogadro's number
Number of moles = 3.01 x 10^22 / 6.022 x 10^23
Number of moles = 0.005
Now that we know the number of moles, we can use the molar mass to calculate the mass:
Mass = Number of moles x Molar mass
Mass = 0.005 mol x 124 g/mol
Mass = 0.62 g
Therefore, the mass of 3.01 x 10^22 molecules of P4 is 0.62 g.
I need help with this question.
Instruction : Answer the following questions using the given options.
Questions :
1. The reaction between an acid and a base is an example of ___ reaction ?
a. Valence
b. Endothermic reaction
c. Chemical reaction
d. Exothermic reaction
2.The following are the factors affecting the rate of a chemical reaction except ___
a. catalyst
b. nature of reactants
c. activation energy
d. lights
3.___ gives a dense white fume when in contact with HCL
a. propane
b. ammonia
c. tetraoxosulphate(vi) acid d. water
Answers
Explanation:
The reaction between an acid and a base is known as a neutralisation reaction.
Reactant concentration. Increasing the concentration of one or more reactants will often increase the rate of reaction. ...
Physical state of the reactants and surface area. ...
Temperature. ...
Presence of a catalyst.
ammonia
An alkaline gas which produces dense white fumes when reacted with HCl gas is ammonia and fumes are of compound ammonium chloride.
BRAINILIEST PLEASE
LINKS WILL BE REPORTED PLEASE HELP
Certain bacteria live and grow on the roots of some plants and produce chemicals that are beneficial to the plants. Which of the following observations best supports the claim that this relationship is beneficial to the plants?
A.When the bacteria are removed from the plant roots and are grown in a laboratory setting, they fail to survive
B.The population size of the bacteria varies greatly depending on the chemistry of the soil and the type of the plant
C.Plants with a higher density of the bacteria on their roots have increased rates of survival and reproduction
D.The chemical produced by the bacteria can be created by humans and added to the soil where it reaches the roots of the plant
Answers
C. the denser the plants the better.
Answer:
C
Answer: Plants with higher density of the bacteria on their roots have increased rates of survival reproduction
Explanation:
Fill in the two blanks

Answers
Answer:
A.) Longer and Shorter
Explanation:
If the wavelength of a light wave is shorter that means the frequency will be higher.
That means that longer wavelengths have a lower frequency.
suppose that you add 25.6 g of an unknown molecular compound to 0.250 kg of benzene, which has a k f of 5.12 oc/m. with the added solute, you find that there is a freezing point depression of 3.54 oc compared to pure benzene. what is the molar mass (in g/mol) of the unknown compound?
Answers
If we add 25.6 g of an unknown molecular compound to the 0.250 kg of benzene, the molar mass of the unknown compound is 148.8 g/mol.
The Molality of the compound is given as :
ΔT = i Kf m
Where,
ΔT = freezing point depression = 3.54 °C
i = Van't Hoff factor of the Benzene = 1
Kf = constant of the freezing = 5.12 °C/m
m = molality = ?
m = ΔT / i Kf
m = 3.54 / 1 × 5.12
m = 0.69 mol
molality = moles / mass of benzene
moles = 0.172
The molar mass = mass / moles
The molar mass = 25.6 / 0.172
The molar mass = 148.8 g/mol
To learn more about molar mass here
https://brainly.com/question/16928753
#SPJ4
how does mechanical weathering affect the rate of chemical weathering
Answers
Mechanical weathering can significantly affect the rate of chemical weathering. When rocks are physically broken down into smaller fragments through processes like abrasion, frost wedging, or root expansion, the surface area of the rock increases.
This increased surface area provides more exposure to chemical agents like water, oxygen, and acids, accelerating the chemical weathering process.
The smaller particles resulting from mechanical weathering provide more contact points for chemical reactions to occur. Water can penetrate deeper into the rock, allowing chemical reactions to take place more readily.
Additionally, the fractured structure of the rock provides pathways for chemical agents to penetrate and react with the minerals, causing them to break down and dissolve more easily.
Overall, mechanical weathering enhances the effectiveness of chemical weathering by increasing the surface area and facilitating the access of chemical agents, leading to a faster breakdown of minerals and the transformation of rock over time.
To know more about Mechanical weathering, refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/29616569#
#SPJ11
What is the fluoride ion concentration for a saturated solution of BaF 2 if the K sp for BaF 2 is 1.8 × 10 -7 ?
Answers
\(\\ \rm\rightarrowtail BaF_2\longrightarrow Ba^{2+}+2F-\)
BaF_2 be xBa2+ is also xF- is 2xNow
\(\\ \rm\Rrightarrow K_{sp}=[Ba^2+][F-]^2\)
\(\\ \rm\Rrightarrow 1.8\times 10^{-7}=x(2x)^2\)
\(\\ \rm\Rrightarrow 4x^3=1.8\times 10^{-7}\)
\(\\ \rm\Rrightarrow x^3=0.45\times 10^{-7}\)
\(\\ \rm\Rrightarrow x=\sqrt[3]{0.000000045}\)
\(\\ \rm\Rrightarrow x=0.00376M\)
\(\\ \rm\Rrightarrow x=3.8\times 10^{-3}M\)
So
\(\\ \rm\Rrightarrow [F-]=2x=7.6\times 10^{-3}M\)
What is the mass in grams of 3.75 × 10 21 atoms of Li?
Answers
Answer:
The mass
Explanation:
the mass grams of 3.75 × 10 21 atoms of Li is
40. 21 atom of Li
PLEASE HELP THIS IS TIMED
Which of the following is a physical change?
CsF(s) + XeFo(s) → CsXeF;(s)
CO2 (s) + CO2(g)
O N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) → 2NH3 (g)
2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H20 (1)
Zn(s) + 2 MnO2(s) + H20(1) → Zn(OH)2(s) + Mn2O3(s)
Answers
This is a physical change because only the state of matter changes, not the chemical makeup.
Why is the mole important? Group of answer choices It can be applied to any type of object: molecules, atoms, ions, etc. It gives us a convenient way to express large numbers. It is useful when converting between grams and atoms or molecules. All of the above.
Answers
Answer: the mole
Explanation:
The mole is the unit of amount in Chemistry.
It provides a bridge between the atom and the macroscopic amounts of material that we work with in the laboratory.
Explain why this statement is false: “Because there is no change in composition during a physical change, the appearance of the substance will not change”
Answers
compare solution a and solution b in each label and drag the label to the appropriate concentration description.
olution A = 0.5mM and Solution B = 100mm
Solution A = 2 mM of n+3 and Solution B = 1 M n+1
Solution A = 3.5mg/dL and Solution B = 3.7mg/dL
Solution A = 0% (w/v) and Solution B = 0% (w/v)
Solution A = 10-3 M and Solution B = 10-5M
Solution A = 12.23% (w/v) and Solution B = 12.3% (w/v)
Substance A is more conentrated than B
Equal concentrations
Substance B is more concentrated than A
Answers
A) Solution B of 100 mM is more concentrated than Solution A of 0.5 mM.
B) Solution B of 3.7mg/dL is more concentrated than Solution A of 3.5mg/dL.
C) Solution A = 0% (w/v) and Solution B = 0% (w/v) equal concentrations.
D) Solution A of 10⁻³ M is more concentrated than Solution A of 10⁻⁵M.
E) Solution B of 12.3% (w/v) is more concentrated than Solution A of 12.23% (w/v)
What is concentration?In chemistry, concentration can be described as the abundance of components divided by the total volume of a solution. Several kinds of mathematical descriptions can be distinguished: mass concentration, number concentration, molar concentration, and volume concentration.
The concentration is defined as the kind of chemical mixture, but most frequently refers to solutes and solvents in solutions. The molar concentration has variants, such as osmotic concentration and normal concentration.
Molarity, molality, Normality, and weight/ volume percentage are also used to define the concentration of the solution.
Learn more about concentration, here:
https://brainly.com/question/10935668
#SPJ1
2. According to the graph below, what temperature will result in the highest rate of photosynthesis?
100+ Oxygen flow (LH)
80
60
40
20
0
Temperature (°C)
10
20
30
40
50
O A.5°C
O B. 40°C
O C.30°C
OD. 25°C
Answers
Answer:
D 25°c is the highest rate of photosynthesis.
ANSWER QUICK PLEASE I GIVE BRANLIEST

Answers
Answer:
Answer 3 is the correct answer.
Niels Bohr adapted the nuclear model.
Describe the change that Bohr made to the nuclear model.
Answers
Answer:
To remedy the stability problem, Bohr modified the Rutherford model by requiring that the electrons move in orbits of fixed size and energy.
Fill in the blank: We will not be using a physical textbook this year. Instead, we will be using the _______________ Curriculum through Canvas. * Hint: The response is two words.
Answers
Answer:
The answer are given below
Please mark Brainliest
Explanation:
Online
Virtual
No physical
Non Physical
The answers are given above are the best suited in this fill in the blank question. Above provided answers are four and the best suited answer can fit in the blank space provided in the question. Please mark brainliest.
What is a resistor?
1.A battery
2.A light bulb
3.A switch
Answers
Answer:2
Explanation:
If 100 grams of O2 are reacted, how many grams of P4 will also be reacted?
Answers
If 100 grams of Oxygen are reacted, 77.5 grams of P4 will also be reacted.
Calculating the number of moles in 100g of oxygen gas.
Mass of oxygen = 100 g
Molar mass of oxygen = 32.0 g/mol
Thus, moles of oxygen are -
Moles of oxygen = (Mass of oxygen/ Molar mass of oxygen)
Moles of oxygen = (100/32.0)
Moles of oxygen = 3.125 moles.
Here, the 5 moles of Oxygen need 1 mole of P4.
Moles of Phosphorous = 3.125/5 = 0.625 moles.
Therefore, from moles of P4 and molar mass of P4 = (124.0 g/mol)
Mass of Phosphorous = 0.625 * 124.0 = 77.5g
Hence, 77.5 grams of P4 will react with 100 grams of Oxygen.
To learn more about Moles and Mass
https://brainly.com/question/13860160
#SPJ4
What does this image represent?
A) A methyl group present in fatty acids
B) A ketone group present in fat molecules
C) An aldehyde group present in monosaccharides molecules
D) An acid group present in lipids

Answers
Answer:
D) An acid group present in lipids
2. Question I don’t understand on this one buttt

Answers
Answer:
1st question is B
Explanation:
metal is a good conductor of heat and electricity
If CaCl2 is added to the following reaction mixture at equlibrium, how will the quantities of each component compare to the original mixture after equilibrium is reestablished
Answers
when CaCl2 is added to the reaction mixture at equilibrium, the concentrations of CaCl2, Ca²⁺, and Cl⁻ will be higher than in the original mixture after equilibrium is reestablished.
Let's consider the following equilibrium reaction:
CaCl2 (aq) ⇌ Ca²⁺ (aq) + 2 Cl⁻ (aq)
When CaCl2 is added to the reaction mixture at equilibrium, the concentration of CaCl2 will increase. According to Le Chatelier's Principle, the reaction will shift to counteract this change in order to reestablish equilibrium. In this case, the reaction will shift to the right, consuming some of the added CaCl2 and producing more Ca²⁺ and Cl⁻ ions.
After equilibrium is reestablished, the quantities of each component will be as follows:
1. CaCl2: The concentration will be higher than in the original mixture, as some of the added CaCl2 will remain.
2. Ca²⁺: The concentration will be higher than in the original mixture, as the reaction shifted to the right to produce more Ca²⁺ ions.
3. Cl⁻: The concentration will also be higher than in the original mixture, as the reaction shifted to the right to produce more Cl⁻ ions.
To know more about equilibrium Visit:
https://brainly.com/question/30694482
#SPJ11
Which of the following elements will form positive ions Na N Cu Br
Answers
Answer:
Na, Cu, and Br will form positive ions
Explanation:
Na, Cu, and Br have more protons than electrons, so they will form positive ions.
Na, Cu, and Br are all elements that have an atomic number greater than their number of electrons. This means that they have more protons than electrons, so they will form positive ions when they react with other elements. Na will form Na+, Cu will form Cu+ and Br will form Br+.
What is the wavelength (in nm) of an electron with the following kinetic energies? (a) 20.0 ev (no response) nm (b) 200 ev (no response) nm (c) 2.00 kev (no response) nm (d) 20.0 kev (no response) nm (e) 0.200 mev (no response) nm (f) 2.00 mev (no response) nm which of these energies are most suited for study of the nacl crystal structure? (select all that apply.) 20.0 ev 200 ev 2.00 kev 20.0 kev 0.200 mev 2.00 mev none of these
Answers
The wavelength of an electron can be calculated using the formula: wavelength = h / (mass of electron * velocity). Since kinetic energy is equal to the mass of the electron multiplied by the velocity squared, we can also calculate wavelength by using the formula: wavelength = h / sqrt(2mass of electron kinetic energy).
To convert the kinetic energies given in electron volts (eV) to Joules (J), you can use the formula: 1 eV = 1.6 x 10^-19 J
(a) 20.0 eV = 3.2 x 10^-18 J, wavelength = h / sqrt(2mass of electron3.2 x 10^-18 J) = 2.4 x 10^-12 m or 2.4 pm (picometers)
(b) 200 eV = 3.2 x 10^-17 J, wavelength = h / sqrt(2mass of electron3.2 x 10^-17 J) = 2.4 x 10^-11 m or 24 pm
(c) 2.00 keV = 3.2 x 10^-14 J, wavelength = h / sqrt(2mass of electron3.2 x 10^-14 J) = 2.4 x 10^-8 m or 2.4 nm
(d) 20.0 keV = 3.2 x 10^-13 J, wavelength = h / sqrt(2mass of electron3.2 x 10^-13 J) = 2.4 x 10^-7 m or 24 nm
(e) 0.200 MeV = 3.2 x 10^-11 J, wavelength = h / sqrt(2mass of electron3.2 x 10^-11 J) = 2.4 x 10^-5 m or 0.24 nm
(f) 2.00 MeV = 3.2 x 10^-10 J, wavelength = h / sqrt(2mass of electron3.2 x 10^-10 J) = 2.4 x 10^-4 m or 2.4 nm
A lower energy electron will have a longer wavelength, while a higher energy electron will have a shorter wavelength. To study the crystal structure of NaCl, you would need to use a technique such as X-ray diffraction, which typically uses X-rays with energies in the range of a few keV to a few tens of keV. Based on this, 2.00 keV and 20.0 keV energies are most suited for study of the NaCl crystal structure.
To know more about wavelength of electrons visit :
https://brainly.com/question/17295250?referrer=searchResults
#SPJ4
to make 400 gram solution with a mass by a mass concentration of 6 % how much salt and water you need to mix
Answers
Answer:
\(400 \div 6 \\ \\ \)
Elements on the right side of the Periodic Table are mostly in what state of matter?
Answers
\(\huge\mathfrak\red {Answer:}\)
Elements on the right side of the periodic table are mostly Non - metals.
And Nonmetals exist in all three states of matter. The majority are gases, such as nitrogen and oxygen. Bromine is a liquid. A few are solids, such as carbon and sulfur.
\(\mathfrak\purple {Hope\: this\: helps\: you...}\)
10 moles of carbon dioxide has a mass of 440 g. What is the relative formula mass of carbon dioxide?
Answers
Answer: 44g
Explanation: The formular for finding Moles is ;
Moles = Mass / Molar Mass or Formular Mass.
Base on this question; Moles = 10, Mass = 440g, and Formular Mass = ?
Making 'Formular Mass', subject of the formular; we thus have;
Formular mass = Mass / Moles = 440/ 10 = 44g
QuestionWhich of the following sets of quantum numbers is permissible for an electrons in an atom?An=1,l=1,m=0,s=+ 21â Bn=3,l=1,m=â2,s=â 21â Cn=2,l=1,m=0,s=+ 21â Dn=2,l=0,m=0,s=1Medium
Answers
Correct option is (c). The set of quantum numbers is permissible for an electrons in an atom is n = 2, l=1, m=0, s= + 1/2.
There are total of four quantum numbers are used to describe completely the movement of each electron within an atom. The combination of all the quantum numbers in an atom is described by a wave function. Each of the electron in an atom has a unique set of quantum numbers. Quantum numbers can be used to determine the electron configuration of an atom and the probable location of the electrons of an atom. It is used to understand other characteristics of atoms such as ionization energy and the atomic radius. It describes the values of conserved quantities in the dynamics of a quantum system.
To learn more about Quantum numbers please visit:
https://brainly.com/question/2292596
#SPJ4
The correct question is,
Which of the following sets of quantum numbers is permissible for an electrons in an atom?
A. n=1, l=1, m=0, s =+ 1/2
B. n=3, =1, m=2, s= - 1/2
C. n=2, l=1, m=0, s= + 1/2
D. n=2, l=0, m=0, s=1
What is the vapor pressure of water at 75 °C? mmHg (whole number)
What is the vapor pressure of bromine at 300 K? mmHg (whole number)
At what temperature is the vapor pressure of mercury 500 mmHg? °C (whole number)
What is the vapor pressure of diether ether at the normal freezing temperature of water? mmHg (whole number)
At what temperature will ethanol boil when at 50 mmHg? °C (whole number)
What is the normal boiling point pressure for water in kPa? kPa (exact number)
What is the normal boiling point pressure for water in mmHg? mmHg (exact number)
What is the normal boiling point temperature in Celsius of n-Octane? °C (whole number)
What is the normal boiling point temperature in Kelvin of Ethylene glycol? K (whole number)
At which temperature would ethylene glycol boil when the atmospheric pressure is 0.20 atm? °C (Whole number)
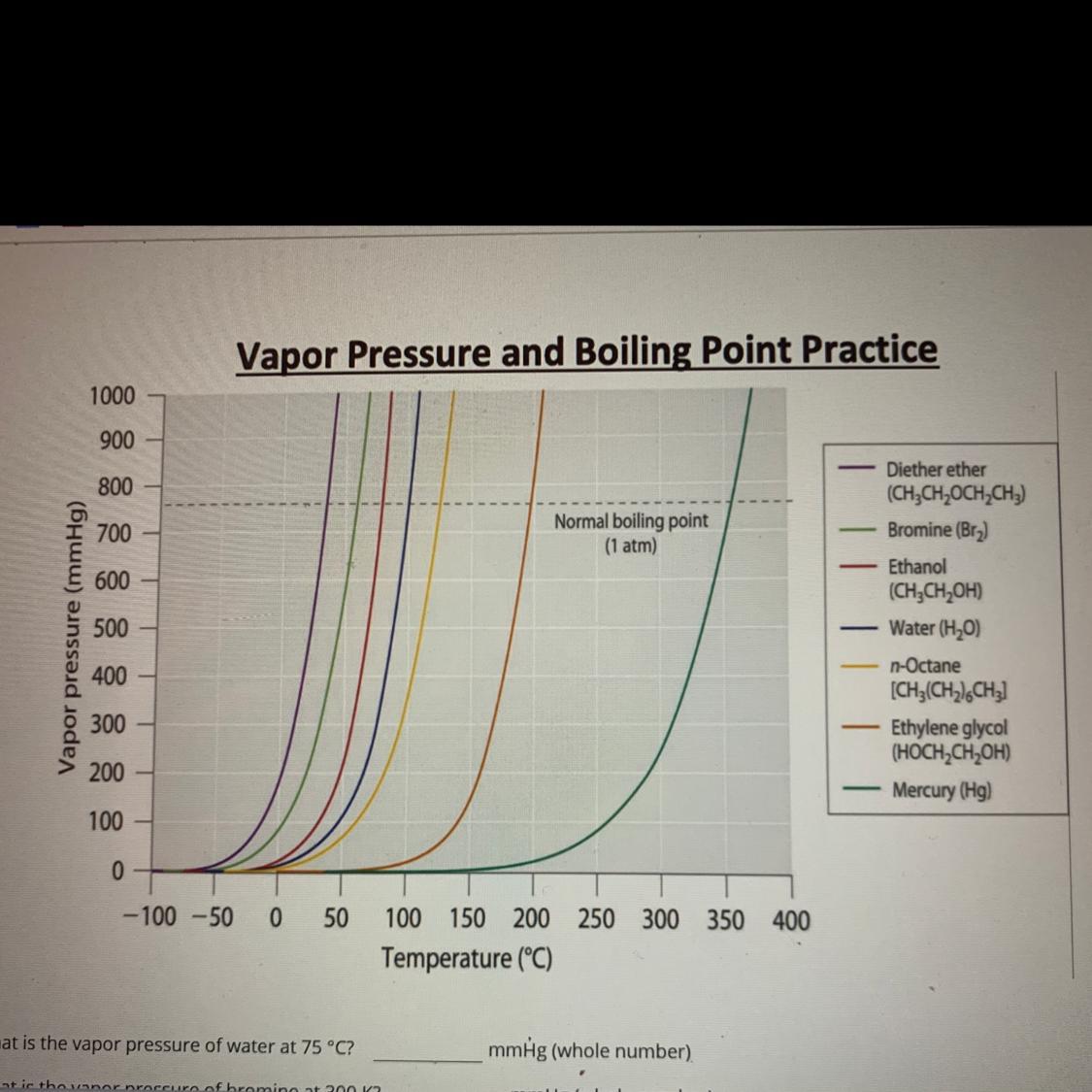
Answers
Answer: All the answers are given below.
Explanation:
The vapor pressure of water at 75°C is approximately 293 mmHg (whole number).
The vapor pressure of bromine at 300 K is approximately 240 mmHg (whole number).
The boiling point of mercury is 357°C at atmospheric pressure (760 mmHg), and the vapor pressure of mercury is 500 mmHg at a higher temperature than this. Therefore, the temperature at which the vapor pressure of mercury is 500 mmHg is greater than 357°C.
Diethyl ether's normal boiling point is 34.6°C, which is above the freezing temperature of water (0°C). At 0°C, the vapor pressure of diethyl ether is approximately 5.5 mmHg (whole number).
At a pressure of 50 mmHg, ethanol will boil at approximately 64°C (whole number).
The normal boiling point pressure for water is 101.3 kPa (exact number) at a temperature of 100°C.
The normal boiling point pressure for water is 760 mmHg (exact number) at a temperature of 100°C.
The normal boiling point temperature in Celsius of n-Octane is approximately 126°C (whole number).
The normal boiling point temperature in Kelvin of ethylene glycol is approximately 471 K (whole number).
To find the boiling point of ethylene glycol at a pressure of 0.20 atm, you can use the Clausius-Clapeyron equation. However, the equation requires knowing the vapor pressure of ethylene glycol at a known temperature. Without this information, it is not possible to calculate the boiling point.