Answers
Answer:
The drop in temperature overnight causes a decrease in the average kinetic energy of the air molecules inside the tires. According to the ideal gas law, this leads to a decrease in tire pressure. The low tire pressure light in vehicles is triggered when the pressure falls below a certain threshold, alerting the driver to check and adjust the tire pressure.
Explanation:
The ideal gas law, represented by the equation PV = nRT, relates the pressure (P), volume (V), number of moles (n), and temperature (T) of an ideal gas. In this case, we can analyze how the drop in temperature affects the tire pressure.
When the temperature drops, according to the ideal gas law, the pressure of a gas will decrease if the volume and the number of moles remain constant. This is because the decrease in temperature causes a decrease in the average kinetic energy of the gas particles, leading to less frequent and less forceful collisions with the tire walls, resulting in a decrease in pressure.
In the context of the tire pressure, the air inside the tires behaves as an ideal gas. When the temperature drops overnight, the air inside the tires also cools down, causing a decrease in its temperature. As a result, the average kinetic energy of the air molecules decreases, leading to a decrease in pressure inside the tires.
The low tire pressure light comes on as a result of this drop in pressure. The tire pressure monitoring system in modern vehicles is designed to detect significant deviations from the recommended tire pressure. When the pressure drops below a certain threshold, typically due to temperature changes or a puncture, the light is triggered to alert the driver to check and adjust the tire pressure.
Therefore, the drop in temperature overnight causes a decrease in the average kinetic energy of the air molecules inside the tires, resulting in a decrease in tire pressure, which triggers the low tire pressure warning light.
Hope this helps!
Related Questions
This problem explores the behavior of charge on conductors. We take as an example a long conducting rod suspended by insulating strings. Assume that the rod is initially electrically neutral. For convenience we will refer to the left end of the rod as end A, and the right end of the rod as end B. In the answer options for this problem, "strongly attracted/repelled" means "attracted/repelled with a force of magnitude similar to that which would exist between two charged balls.A small metal ball is given a negative charge, then brought near (i.e., within about 1/10 the length of the rod) to end A of the rod. What happens to end A of the rod when the ball approaches it closely this first time?
Answers
Answer:
rod end A is strongly attracted towards the balls
rod end B is weakly repelled by the ball as it is at a greater distance
Explanation:
When the ball with a negative charge approaches the A end of the neutral bar, the charge of the same sign will repel and as they move they move to the left end, leaving the rod with a positive charge at the A end and a negative charge of equal value at end B.
Therefore rod end A is strongly attracted towards the balls and
rod end B is weakly repelled by the ball as it is at a greater distance
According to the Keynesian view, manipulating foreign sector spending is not a reliable way to move the U.S. economy toward a more acceptable equilibrium because __________.
Answers
According to the Keynesian view, manipulating foreign sector spending is not a reliable way to move the U.S. economy toward a more acceptable equilibrium because it does not address the fundamental causes of economic instability.
Keynesian economics focuses on the role of domestic demand in driving economic growth and stability. The government can use fiscal and monetary policy to stimulate aggregate demand and promote full employment. However, changes in foreign sector spending can be unpredictable and beyond the control of domestic policymakers. For instance, an increase in foreign demand for U.S. exports could boost economic growth and employment in the short run, but it may not be sustainable if the foreign demand later decreases. Similarly, a decrease in foreign demand for U.S. exports could have negative short-term effects on the economy, but it may not necessarily lead to a long-term decline. In short, Keynesian economics emphasizes the importance of domestic demand management and stabilizing the economy through government intervention. While changes in foreign sector spending can have some impact on the economy, they are generally seen as unreliable and unpredictable, and therefore not a reliable tool for achieving economic stability in the long run.
For such more questions on reliable
https://brainly.com/question/27968241
#SPJ11
In a head-on collision, a car stops in 0.14 s from a speed of 17.6 m/s. The driver has a mass of 70 kg, and is, fortunately, tightly strapped into his
seat. What is the magnitude of the average force applied to the driver by his seat belt during that fraction of a second? Round to two decimal places and express the answer in Sl units.
Answers
The rate at which an object's velocity with respect to time changes is known as its acceleration. Accelerations are vector quantities. The direction of the net force acting on an object determines its acceleration.
Velocity is the rate at which an object is changing position as perceived from a certain point of view and as measured by a particular unit of time. It is defined as the direction at which an object is traveling.
acceleration = (Velocity f - Velocity i) / time
= - 17.6 / 0.14 m/s
= - 125.714 m/s
A force is an influence that has the power to change an object's motion. A force can cause an object with mass to move at a different speed or accelerate. A push or a pull makes natural sense to describe force. Forces have both magnitude and direction because they are vector quantities.
Force = mass x acceleration
= 70 x (- 125.714 m/s) N
= - 8800 N
To know more about colliding forces, click on the link below:
https://brainly.com/question/10626372
#SPJ13
How do you think the research will help you grow into your future profession?
Answers
it allows u to know things and remember them when you need to. It also helps you recognize ur skills and allows you to be an easy problem solver when u know the concept because u did some research and know the answer to a question.
Explanation:
1. Why did the quantum theory of light explain the outcome of the photoelectric effect experiment?
a. The quantum theory of light showed why high intensity light was needed to give the electrons enough energy to escape the material
b. The material only ejects electrons when there is enough of a distribution of energy across the surface, as described by quantum theory
c. The quantum theory explained why the waves needed less momentum in order to impact the electrons and knock them off
d. The material only absorbed a certain frequency of the light and the quanta of light are defined by the frequency
2. Why do lamps of different elements have different colored light?
a. The chemicals in the light are not affected by the electricity running through them and are only naturally luminescent
b. They gases have different energy levels that light can be emitted from, which produce different wavelengths (colors) of light
c. The gases chemically bond under the effects of the electricity and the release of the energy from this bonding produces the light colors
d. The electricity from the device is quantized and can only be accepted by certain wavelengths, so the remaining wavelengths are the colors we see
Answers
question 1 is option D
question 2 is option B
Explanation for question 1: The quantum theory of light, as proposed by Albert Einstein, explained the outcome of the photoelectric effect experiment by proposing that light travels in discrete packets of energy called photons, and that the energy of a photon is directly proportional to its frequency. In the photoelectric effect, the material only absorbs photons with a certain minimum frequency, called the threshold frequency. When a photon with sufficient energy is absorbed by an electron in the material, the electron is ejected with kinetic energy equal to the energy of the photon minus the energy required to overcome the binding energy of the electron to the material. This explains why increasing the intensity of the light does not increase the kinetic energy of the ejected electrons, but increasing the frequency of the light above the threshold frequency does.
Explanation for question 2: When an electric current is passed through a gas or vapor, some of the electrons in the gas are excited to higher energy levels. When these electrons return to their lower energy levels, they emit light in the form of photons. The energy of the emitted photons corresponds to the energy difference between the excited state and the lower energy state. Different elements have different electron configurations and energy levels, and therefore they emit light at different wavelengths (colors) when excited.
For example, sodium vapor lamps emit yellow light because the excited sodium atoms emit photons with a characteristic wavelength in the yellow part of the spectrum. Mercury vapor lamps emit blue-green light because the excited mercury atoms emit photons with a characteristic wavelength in the blue-green part of the spectrum.
A single-phase 60-Hz overhead power line is symmetrically supported on a horizontal cross arm. Spacing between the centers of the conductors acing between the centers of the conductors (say, a and b) is 2.5 m. A telephone line is also symmetrically supported on a horizontal cross arm 1.8 m directly below the power line. Spacing between the centers of these conductors (say, c and d) is 1.0 m.
4 x 10^7 ln âDad. Dln/Dnk. Dtet
where, for example, Dud denotes the distance in meters between conductors a and.
a. Hence, compute the mutual inductance per kilometer between the power line and the telephone line.
b. Find the GO-Hz voltage per kilometer induced in the telephone line when the power line carries 150 A.
Answers
Complete question is;
A single-phase 60-Hz overhead power line is symmetrically supported on a horizontal cross arm. Spacing between the centers of the conductors acing between the centers of the conductors (say, a and b) is 2.5 m. A telephone line is also symmetrically supported on a horizontal cross arm 1.8 m directly below the power line. Spacing between the centers of these conductors (say, c and d) is 1.0 m.
The mutual inductance per unit length between circuit a-b and circuit c-d is given as 4 x 10^(-7) ln √((D_ad × D_bc)/(D_ac × D_bd)) H/m
where, for example, D_ad denotes the distance in meters between conductors a and d.
a. Hence, compute the mutual inductance per kilometer between the power line and the telephone line.
b. Find the 60-Hz voltage per kilometer induced in the telephone line when the power line carries 150 A
Answer:
A) M = 1.01 × 10^(-4) H/km
B) v_cd = 5.712 V/km
Explanation:
A) From the distances given in the question, we can deduce that;
D_ac = √(((2.5/2) - (1/2))² + 1.8²)
D_ac = 1.95 m
Also;
D_ad = √(((2.5/2) + (1/2))² + 1.8²)
D_ad = 2.51 m
I_a and I_b are put of phase by 180°. Thus, due to a and b, the flux linkages to c and d is given as;
φ_cd = 4 x 10^(-7)I_a( ln (2.51/1.95))
Mutual inductance per km is given as;
M = φ_cd/I_a
Thus;
M = 4 x 10^(-7)( ln (2.51/1.95))
M = 1.01 × 10^(-7) H/m
Per km;
M = 1.01 × 10^(-7) × 1000
M = 1.01 × 10^(-4) H/km
B) voltage per km is gotten by;
v_cd = ωMI
Now, ω = 2πf = 2π × 60 = 377 rad/s
Thus;
v_cd = 377 × 1.01 × 10^(-4) × 150
v_cd = 5.712 V/km
Physics help please

Answers
Answer:
what's your question?
Explanation:
I'm standby to answering your question.
Why do people do drugs?
Answers
People use drugs for many reasons: they want to feel good, stop feeling bad, or perform better in school or at work, or they are curious because others are doing it and they want to fit in. The last reason is very common among teens.Drugs excite the parts of the brain that make you feel good. But after you take a drug for a while, the feel-good parts of your brain get used to it. Then you need to take more of the drug to get the same good feeling. Soon, your brain and body must have the drug just to feel normal. You feel sick, awful, anxious, and irritable without the drug. You no longer have the good feelings that you had when you first used the drug. This is true if you use illegal drugs or if you misuse prescription drugs. Misuse includes taking a drug differently than how your doctor tells you to (taking more or crushing pills to "shoot up" or snort), taking someone else’s prescription, or taking it just to get “high.”
Water flows at a speed of 13 m/s through a pipe that has a diameter of 1.2 m. What is the
diameter of the smaller end of the pipe that the water comes out with a speed of 30 m/s?
Answers
The diameter of the smaller end of the pipe is approximately 0.78 meters.
To determine the diameter of the smaller end of the pipe, we can use the principle of conservation of mass. According to this principle, the mass flow rate of water should remain constant throughout the pipe.
The mass flow rate is given by the equation:
Mass flow rate = density of water * cross-sectional area * velocity
Since the density of the water remains constant, we can write:
Cross-sectional area1 * velocity1 = Cross-sectional area2 * velocity2
Given that the velocity1 is 13 m/s, the diameter1 is 1.2 m, and the velocity2 is 30 m/s, we can solve for the diameter2 using the equation:
(pi * (diameter1/2)^2) * velocity1 = (pi * (diameter2/2)^2) * velocity2
Simplifying the equation:
(1.2/2)^2 * 13 = (diameter2/2)^2 * 30
Calculating the equation:
(0.6)^2 * 13 = (diameter2/2)^2 * 30
0.36 * 13 = (diameter2/2)^2 * 30
4.68 = (diameter2/2)^2 * 30
Dividing both sides by 30:
0.156 = (diameter2/2)^2
Taking the square root of both sides:
0.39 = diameter2/2
Multiplying both sides by 2:
0.78 = diameter2
To learn more about diameter
https://brainly.com/question/32968193
#SPJ8
Order the substances from least dense at the top (1) to most dense at
the bottom (5).
Carbon
dioxide
Lead
Water
Helium
Gold
1
O
O
O
O
2
O
O
O
O
3
O
O
O
4
O
O
O
O
O
*
50 puntos
5
O
O
O
O
Answers
The most denser among the given materials is gold and the least dense one is helium. The order of density from least to most dense is helium, carbon dioxide, water, lead and gold.
What is density?Density of a substance is the measure of its mass per unit volume. It describes how closely packed its particles. density depends on the bond type, temperature and pressure.
The density of helium is very low and it is the lightest element after hydrogen. It density is about 0.00017 g/ml. Density of carbon dioxide is 0.0019 g/ml and the density of water is 1 g/ml.
Gold is a denser metal and its density is about 19.3 g/ml and that of lead is 11.3 g/ml. Hence, the order of density from least to most dense is He < carbon dioxide< water< lead < gold.
To find more on density, refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/15164682
#SPJ1
An astronaut floating in space is trying to use her jetpack to get back to her space station, but she is being pulled away by a nearby planet, as shown in the image below. Her jetpack provides a constant thrust of 165 N. If she angles her jetpack in such a way that it cancels out the vertical force due to the planet's gravity, what is her net horizontal force?
A. 132.6 N toward the space station
B. 53.3 N away from the space station
C. 98.5 N toward the space station
D. 112.8 N away from the space station

Answers
Answer:
C. 98.5N toward the space station
Explanation:
Fx= Fjet×cos(20) - Fplanet × cos(45) = 98.5
Because the result is positive so she is going toward the space station
Engineers are working on a design for a cylindrical space habitation with a diameter of 7.50 km and length of 29.0 km. The habitation will simulate gravity by rotating along its axis. With what speed (in rad/s) should the habitation rotate so that the acceleration on its inner curved walls equals 8 times Earth's gravity
Answers
Answer:
The speed will be "0.144 rad/s".
Explanation:
Given that,
Diameter,
d = 7.50 km
Radius,
R = \(\frac{7.5}{2} \ Km\)
Acceleration on inner curve,
= 8 times
Now,
As we know,
⇒ \(\omega^2R=8g\)
or,
⇒ \(\omega=\sqrt{\frac{8g}{R} }\)
On substituting the values, we get
⇒ \(=\sqrt{\frac{8\times 9.8}{\frac{7.5}{2}\times 10^3 } }\)
⇒ \(=\sqrt{\frac{78.4}{3750} }\)
⇒ \(=\sqrt{0.0209}\)
⇒ \(=0.144 \ rad/s\)
What do we call the material such as air that light travels through
Answers
Answer:
Transparent or Translucent
Explanation:
help please i’m stuck

Answers
Answer:
no entiendo el inglés soryyy
When the moving sidewalk at the airport is broken, as it often seems to be, it takes you 42 s to walk from your gate to baggage claim. When it is working and you stand on the moving sidewalk the entire way, without walking, it takes 73 s to travel the same distance. How long (to the nearest second) will it take you to travel from the gate to baggage claim if you walk while riding on the moving sidewalk?
Answers
The traveling time from the gate to baggage will be 32.71 secs.
Let the total distance be x feet.
Speed while walking = x/54 feet per second
Speed on the sidewalk = x/83 feet per second
Therefore, total speed while walking on a moving sidewalk =
=x/54+x/83
=(83x+54x)/(54 × 83)
=137x/4482
=x/33.7
Hence, the travel time will be 32.71 secs.
Learn more about speed here
https://brainly.com/question/4931057
#SPJ1
Two equal charges q1=q2= -6uC are on the y-axis at y1=3cm and y2= -3cm. What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field on the x-axis at x=4cm. If a test charge q0=2uC is placed at x =4cm find the force the test charge experiences?
Answers
The electric field charges, q₁, and q₂, which are each -6×10⁻⁶ μC, gives:
First part:
The magnitude of the electric field at x = 4 cm is -3.456×10⁷ N/CThe direction of the electric field is towards the origin, along the x-axisSecond part:
The force experienced by the charge is 69.12 NWhat is an electric field?An electric field is the field around a particle that is electrically charged and which exerts a force on charged particles within the field.
The given information are:
The electric charges, q₁ = q₂ = -6 μC
The location of the charge q₁ = y₁ = 3 cm on the y-axis
Location of the charge q₂ = y₂ = -3 cm
First part:
The required location of the point where the electric field magnitude and direction is required is x = 4 cm
The electric field formula is: \(\displaystyle{E = \frac{k\cdot q}{r^2}\)
Where:
k = The electrostatic constant ≈ 9 × 10⁹ N·m²/C²
The distances, r, of the charges from the required point are therefore obtained using Pythagorean theorem as follows:
r = √(3² + 4²) = 5
r = 5 cm = 0.05 m
Which gives;
\(\displaystyle{E = \frac{9 \times 10^9\times (-6) \times 10^{-6}}{(0.05)^2} = -2.16\times 10^{7}\)
Given that the magnitude of the electric field along the y-axis cancel out, the magnitude of the electric field along the x-axis is found as follows:
\(E_x = 2 \times -2.16\times 10^{7}\times \dfrac{4}{5} = -3.456 \times 10^7\)
The magnitude of the electric field at x = 4 is -3.456 × 10⁷ N/C
Second part: The magnitude of the test charge is q₀ = 2 × 10⁻⁶ μC
The force of an electric field, F = E × q
The force experienced by the test charge is therefore:
F = -3.456 × 10⁷ × 2 × 10⁻⁶ = -69.12
The force the test charge experiences is 69.12 N acting towards the origin from the point x = 4 cm.
Learn more about electric fields and charges here:
https://brainly.com/question/14372859
#SPJ1
REAL ANSWERS ONLY PLS

Answers
Answer:
The statement of the student is correct.
Since B attained a higher velocity in a short amount of time, that is it accelerated faster(having a larger slope).
Slope = dy/dx
That is, Velocity
Time
which is acceleration.
That's my guess.
Hope it's right.
Why does an iceberg have more HEAT than a cup of coffee.
Answers
Explanation:
Although the iceberg has less internal energy per mass, its enormously greater mass gives it a greater total energy than that in the small cup of coffee
Answer:
The hot coffee has a higher temperature, but not a greater internal energy. Although the iceberg has less internal energy per mass, its enormously greater mass gives it a greater total energy than that in the small cup of coffee.
Explanation:
50 j of work was performed in 20 seconds. How much power was used to preform this task
Answers
Answer:
Power = 2.5 [W]
Explanation:
To be able to solve this problem we must remember that power is defined as the relationship of the work done in a given time interval.
\(P=W/t\)
where:
P = power [W] (units of watts)
W = work = 50 [J]
t = time = 20 [s]
Now replacing:
\(P=50/20\\P=2.5[W]\)
Answer:
2.5
Explanation:
Two objects have the same center point of the circle, but are located at different positions away from the center point. Each object is moving with uniform circular motion.
Which would describe the tangential speed of the objects?
both objects would have the same tangential speed
the object with the smaller radius has a faster tangential speed
the object with the larger radius has a faster tangential speed
both objects would have oscillating tangential speeds
Answers
The object with the larger radius has a faster tangential speed. Tangential speed is related to both rotational speed and radial distance from the rotating axis.
What is uniform circular motion?Uniform circular motion is a type of motion of a particle around a circle at a constant speed. The magnitude of the speed of the particle is constant.While the direction is changing continuously.
Tangential speed is related to both rotational speed and radial distance from the rotating axis.
The object with the larger radius has a faster tangential speed.
Hence, option C is correct.
To learn more about the uniform circular motion, refer to the link;
brainly.com/question/2285236
#SPJ1
Answer:
the object with the larger radius has a faster tangential speed
Explanation:
Edge.22
how much metal is needed to cast a cubical metal box
Answers
If metal is required to cast the cubical metal box, it would require 784cm3 of solid static electricity iron.
What exactly is static electricity?Unbalanced electric charge on such a material's surface is known as static electricity. In contrast for dynamic (moving) electricity, which takes the shape of electric currents, static electricity is defined as being fixed or immovable. A typical atom is neutral, meaning it has an equal number of protons and electrons.
What effects does static electricity have on the body?Although static electricity does not directly endanger human life, it can nonetheless shock us and, if we were on an elevated surface, might inflict serious injuries.
To know more about static electricity visit:
https://brainly.com/question/12791045
#SPJ4
Two blocks of mass m1=1.8kg and m2=1.2kg are connected via a pulley as shown. Assuming the blocks are at rest at t=0, what is the velocity of block 1 at t=1.0 second, and is it moving up or down?

Answers
Answer:
2m/s
Explanation:
18-T=1.8a
T-12=1.2a
solving simultaneously
acceleration a=3m/s^2
velocity= a×t=2×1=2m/s
A mass weighing 4 pounds is attached to a spring whose constant is 2 lb/ft. The medium offers a damping force that numerically equal to the instantaneous velocity. The mass is initially released from a point 1 ft above the equilibrium position with a downward velocity of 14 feet/second. Determine the time at which the mass passes through the equilibrium position
Answers
Answer:
the time at which it passes through the equilibrum position is:
t = 0.1 second
Explanation:
given
w= 4pounds
k(spring constant) = 2lb/ft
g(gravitational constant) = 10m/s² = 32ft/s²
β(initial point above equilibrum) = 1
velocity = 14ft/s
attached is an image showing the calculations, because some of the parameters aren't convenient to type.

The time at which the mass passes will be "0.1 s".
EquilibriumAccording to the question,
Mass weighing, w = 4 pounds
Spring constant, k = 2 lb/ft
Gravitational constant, g = 10 m/s² = 32 ft/s²
Point above equilibrium, β = 1
Velocity = 14 ft/s
By using equation of motion,
→ x(t) = (-1 + gt)
By substituting the values,
0 = (-1 + 10t)
-1 + 10t = 0
By adding "1" both sides, we get
-1 + 10t + 1 = 1
10t = 1
t = \(\frac{1}{10}\)
= 0.1 s
Thus the above answer is right.
Find out more information about equilibrium here:
https://brainly.com/question/517289
Harry is reading an online summary of the law of reflection. The site states that after light hits a mirror, the angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected ray and the normal, which is the surface of the mirror.
Which statement corrects an error on the site?
Answers
Answer:
A
Explanation:
A toddler weighs 10 kg and raises herself onto tiptoe (on both feet). Her feet are 8 cm long with each ankle joint being located 4.5 cm from the point at which her feet contact the floor. While standing on tip toe:
(a) what is the upward normal force exerted by the floor at the point at which one of the toddler's feet contacts the floor?
(b) what is the tension force in one of her Achilles tendons? (c) what is the downward force exerted on one of the toddler's
ankle joints?
Answers
Answer:
a.49 n
b. 63 n
c. 112 n
Explanation:
a.10 times 9.8 from gravity/2 = 49 n
b. 49n times 4.5/8-4.5 = 63 n
c 49n + 63 n = 112 n
By what factor must you increase the intensity of a sound in order to hear a 1.0-dB rise in the sound level?
Answers
Answer:
The right approach will be "1.3". A further explanation is given below.
Explanation:
As we know,
In Decibels, the change in sound volume will be:
= \(10log\frac{I_1}{I_2}\)
Now,
According to the question,
⇒ \(1=10 log \frac{I_1}{I_2}\)
By applying cross multiplication and putting the value of log, we get
⇒ \(10^{\frac{1}{10} }=\frac{I_1}{I_2}\)
⇒ \(1.26=\frac{I_1}{I_2}\)
⇒ \(\frac{I_1}{I_2}=1.3\)
a 250.0 g snowball of radius 4.00 cm starts from rest at the top of the peak of a roof and rolls down a section angled at 30.0 degrees
Answers
Answer:
The response to this question is as follows:
Explanation:
The whole question and answer can be identified in the file attached, please find it.
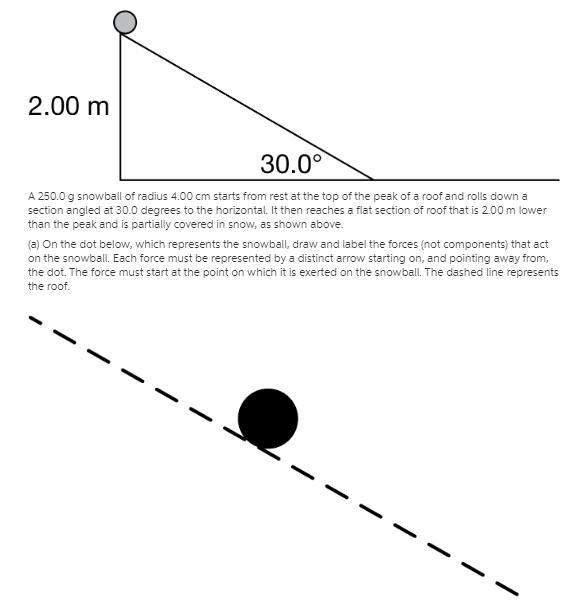

The force diagram of all the forces acting on the snowball include the normal force acting upwards, the weight of the snowball acting downwards and the frictional force acting horizontal.
The given parameters;
mass of the snow ball, m = 250 gradius of the snow ball, r = 4 cmangle of inclination of the plane, θ = 30 ⁰The force diagram of all the forces acting on the snowball is calculated as follows;
↑ N
⊕ → F
↓ W
Where;
N is the normal force on the snowballF is the frictional force on the snowballW is the weight of the ballThus, the force diagram of all the forces acting on the snowball include the normal force acting upwards, the weight of the snowball acting downwards and the frictional force acting horizontal.
Learn more here:https://brainly.com/question/3624253
Four resistors are arranged in a circuit, as shown. There is aconstant voltage V across the voltage source. The current I is 0.25 ampere,(a) Find the equivalent resistance of the four resistors.(b) Find the voltage V across the voltage source.(c) Find the voltage across resistor R2.(d) Find the power dissipated by resistor R2.

Answers
We are given 2 resistors in parallel and 3 resistors in series. The equivalent resistance for parallel resistors is determined using the following formula:
\(\frac{1}{R_{23}}=\frac{1}{R_2}+\frac{1}{R_3}\)Solving for the equivalent resistance:
\(R_{23}=\frac{R_3R_2}{R_3+R_2}\)Replacing the values we get:
\(R_{23}=\frac{(40)(60)}{40+60}\)Solving the operations:
\(R_{23}=24\)Now we use this resistance in series with resistances 1 and 4 to determine the equivalent resistance of the circuit using the following formula:
\(R_{1234}=R_1+R_{23}+R_4\)Replacing the values:
\(R_{1234}=16+24+12\)Solving the operations:
\(R_{1234}=52\)Therefore, the equivalent resistance of the 4 resistors is 52 Ohm.
For part B we are asked to determine the voltage V across the circuit. To do that we will use Ohm's law, which is:
\(V=IR\)Where "I" is the current and "R" is the equivalent resistance. Replacing the values:
\(\begin{gathered} V=(0.25A)(52\text{Ohm)} \\ V=13V \end{gathered}\)Therefore, the voltage across the circuit is 13 Volts.
For part C. We will use Kirchhoff law to determine the current in the second loop of the circuit. This says that the sum of the voltages in a loop must be equal to zero, this means for the first loop:
\(V-R_1I-I_2R_2-I_{}R_4=0\)Now, since the drop in voltage is equivalent to:
\(V_2=I_2R_2\)We can solve for this value in Kirschhoff's law:
\(I_2R_2=V-IR_4-IR_1\)Replacing the values:
\(V_2=13-(0.25)(12)-(0.25)(16)\)Solving the operations:
\(V_2=6\)Therefore, the voltage drop in resistance 2 has a magnitude of 6 volts.
For part D, we will use the following formula:
\(P=VI\)Where "P" is the power dissipated, "V" the voltage drop, and "I" the current, since we don't know the current but the resistance we can rewrite the formula as:
\(P=\frac{V^2}{R}\)Replacing the values:
\(P_2=\frac{(6)^2}{60}=0.6\)Therefore, the power dissipated in resistance 2 is 0.6 J.
What is the resistance at 20°C of a 2.0-meter length of tungsten wire with a cross-sectional area of 7.9 10^-7
meter^2
Answers
Answer:
1.4 * 10 ^-1 Ω
Explanation:
Hi,
For this question, we gotta use the formula
R = pL/A
p = The resistivity of your material at 20°C
L = length of the wire
A = cross-sectional area
The resistivity of tungsten is 5.60 * 10^-8 at 20°C
By plugging the values, we get:
R = (5.60 * 10^-8)(2.0)/(7.9*10^-7) = 1.4 * 10 ^-1 Ω
can someone please help this is due today
Answers
- 1. The mass movement of erosion and disposition of glaciers
Glaciers move, there a form of variety of landforms
by removing rock and soil, glaciers deposit material
that is rock when they retreat or melt, gravity causes material to move
downslope
- 2. which mass movement of glaciers took place on Earth (Ex. 1901-1959; 1973-Present)
9 June 1876 that's the only one i know.
- 3. two facts are events of earth's surface past
only earth's sustains liquid surface water, About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean.
- 4. earths present two facts
- 5. They scrape away at the surface of the land, erode rock and sediment, carry it from one place to another, and leave it somewhere else.
- 6. a description, in your own words, the benefits and risks of living in areas that are prone to flooding
Atlanta is known for floods, if I were living in an area that are prone
to flooding, it's a risking thing to be living in but Atlanta is a nice place
to be living in if I we're living in Atlanta, I would stay in places that
have big houses are at least somewhere higher off ground, its big
risk living in areas that are prone to flood's I've never expected a
flood but I've seen some online i would stay on higher ground level
definitely.!
Year of the flood: 2009
between Willoe Road and Atlanta Street
flooding impacted the Atlanta metropolitan area September 15-22, 2009, as a result of multiple days of prolonged rainfall.
the rest i think you can do lol
make sure you write it on paper okay