In a large forest with many animals, there are only a small number of apex predator bears. Which biotic factor limits the population of bears in the forest?
Answers
Answer:
According to a research paper by University of Minnesota, black bear habitat limits black bear populations, especially through the influences of shelter, food supply and social tolerances or territoriality of the animal. Shelter or cover is a prime factor. Black bears need cover for feeding, hiding, bedding, traveling, raising cubs and denning. With limits of space, adult bears will kill young bears or run them out of the area. These young bears must keep moving around until they die or find an area vacated by an adult1.
In general, density-dependent limiting factors tend to be biotic —living organism-related—as opposed to physical features of the environment. Some common examples of density-dependent limiting factors include competition within the population. When a population reaches a high density, there are more individuals trying to use the same quantity of resources..
Explanation:
Related Questions
Question 16
How does the skeletal system interact with the nervous system?
A the nervous system supplies the blood and oxygen to developing bones
B
the nervous system supplies nutrients and minerals to developing bones
С
the skeletal system controls the messages sent to the brain and spinal cord
D
the skeletal system provides protection for the brain and spinal cord
Answers
Answer:
D
the skeletal system provides protection for the brain and spinal cord
classify any 10 animals from your surroundings and write unique features of each
Answers
Answer:
Monkey- it likes to climb trees and makes funny sounds
Frog-it can jump high
elephant -it has a big trunk
tiger-Roaaarrrrr
lion- it eats meat
Sample of practical recording
Aim:
Material required :
Procedure :
Observation :
Inference:
Answers
Identify the characteristics of allosteric regulation of glycogen phosphorylase in the muscle and liver. Glycogen phosphorylase in muscle Glycogen phosphorylase in liver Activation generates glucose for the cell. Activation liberates glucose for export. b form is the default state. a form is the default state. Glucose binding induces T state. AMP binding induces R state.
Answers
The allosteric regulation of glycogen phosphorylase in muscle and liver exhibits distinct characteristics.
In muscle tissue, glycogen phosphorylase it activates generates glucose for the cell while in liver, glycogen phosphorylase it activates liberates glucose for export.
In muscle tissue, glycogen phosphorylase b form is the default state while in liver, glycogen phosphorylase a form is the default state.
In muscle tissue, glycogen phosphorylase is regulated by glucose binding, which induces a conformational change and leads to the T state (inactive form) of the enzyme while on the other hand in liver, glycogen phosphorylase is regulated by the binding of AMP (adenosine monophosphate), which induces the R state (active form) of the enzyme.
In muscle tissue, glycogen phosphorylase is regulated to provide glucose for energy production within the muscle cell. The default state of glycogen phosphorylase in muscle is the b form. When activated, it converts glycogen into glucose-1-phosphate, which can be used for glycolysis and ATP generation within the muscle.
In contrast, glycogen phosphorylase in the liver is regulated to liberate glucose for export to other tissues, particularly to maintain blood glucose levels. The default state of glycogen phosphorylase in the liver is the a form. Activation of glycogen phosphorylase in the liver results in the breakdown of glycogen, releasing glucose molecules that are transported to the bloodstream for distribution to other cells and tissues.
The binding of glucose induces the T state of glycogen phosphorylase in muscle, while the binding of AMP induces the R state. This means that glucose promotes the inactive form of the enzyme, whereas AMP promotes the active form. The exact mechanisms of allosteric regulation differ between muscle and liver, reflecting their distinct physiological roles in glucose metabolism and homeostasis.
In summary, allosteric regulation of glycogen phosphorylase in muscle and liver serves different metabolic purposes. In muscle, it generates glucose for intracellular energy production, while in the liver, it liberates glucose for export to other tissues to maintain blood glucose levels. The default states, regulatory molecules (glucose and AMP), and resulting enzyme conformations differ between muscle and liver, reflecting their specific metabolic functions.
For more such information on: allosteric regulation
https://brainly.com/question/12492497
#SPJ11
12. Which area of deep ocean research provides the most economic
benefit?
a sea-floor spreading
b. oil resource
C.new habitats
d hydropower
Answers
Answer: Oil resources
Explanation:hope this helps and happy early hallowen :D
identify the variable and non-variable regions within the antibody.
Answers
An antibody is a protein that plays a crucial role in our immune system by recognizing and binding to specific antigens. It is composed of four polypeptide chains, two heavy chains, and two light chains, which are linked by disulfide bonds.
The variable regions of the antibody are responsible for binding to the antigen, and they are located at the tips of the Fab (fragment antigen-binding) regions of the heavy and light chains. These variable regions are highly diverse and specific to different antigens. In contrast, the non-variable regions, also known as constant regions, are located in the Fc (fragment crystallizable) region of the heavy chains and are responsible for determining the effector functions of the antibody. The constant regions are the same in all antibodies of a particular class (e.g., IgG, IgM), and they interact with the immune system to recruit other cells and molecules to destroy the antigen. Understanding the variable and non-variable regions of antibodies is crucial for developing vaccines, therapies, and diagnostic tools for infectious diseases and cancers.
To Know more about antigens visit:
brainly.com/question/24384193
#SPJ11
If a cell with six chromosomes undergoes mitosis, it will produce____________ (number) daughter cells that contain ______________ (number) chromosomes.
Answers
Answer:
hii dear your answer is here
2 daughter cells with 6 chromosomes each.
Explanation:
If a cell with six chromosomes undergoes mitosis, it will produce 2 (number) daughter cells that contain 6 (number) chromosomes.
Mitosis is a type of cell division where one parent cell divides to produce two genetically identical daughter cells. In diploid organisms, mitosis produces diploid daughter cells.
If a cell with six chromosomes undergoes mitosis, it will produce TWO daughter cells that contain SIX chromosomes.A diploid (2n) organism has two copies of each chromosome in its somatic cells.Mitosis can be divided into the following stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.In conclusion, if a cell with six chromosomes undergoes mitosis, it will produce TWO daughter cells that contain SIX chromosomes.
Learn more in:
https://brainly.com/question/13536882?referrer=searchResults
Biology, concussion homework

Answers
1. When the brain is pushed on or disturbed inside the skull, a traumatic brain injury (TBI) known as a concussion results.
2. Depending on the severity of the damage, signs and symptoms of stroke may include headache, nausea, dizziness, disorientation, sensitivity to light or sound, blurred vision, ringing in the ears, memory problems, and mood or behavior changes.
3. A health care professional, such as a doctor or a certified athletic trainer, will often diagnose a concussion after evaluating the patient's symptoms and performing a physical examination.
4. It's important to get medical help right away if you suspect you've had a stroke. This can guarantee that you get the proper care and prevent any problems or long-term effects.
5. The best way to recover from a stroke is to get plenty of rest and avoid things that could make your symptoms worse. This may include skipping work or school, avoiding physical activity, and setting time limits on screen use.
6. You can avoid dangerous behavior, such as not wearing a seat belt, by wearing protective equipment when participating in sports or other high-risk activities, as well as by taking precautions to avoid falls and other accidents.
7. There is strong evidence that repeated head trauma, including concussion, can have long-term consequences, including the development of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), a degenerative brain disorder.
Learn more about concussion, here:
https://brainly.com/question/3758366
#SPJ1
The DNA sequence ATGCATGC will pair with which of the following RNA strands?a) UACGUACGb) CGAUCGAUc) AUGCAUGCd) TAGCTAGCe) UAGCTAGC
Answers
A key to understanding the structure and function of nucleic acids is the principle of complementary base pairing. In double-stranded DNA, adenine and thymine always pair (A-T), and cytosine and guanine always pair (C-G). On the other hand, uracil (U) is one of the four nucleotide bases in RNA, with the other three being adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, uracil pairs with adenine (U-A). In a DNA molecule, the nucleotide thymine (T) is used in place of uracil.
You can determine the sequence of a complementary strand if you are given the sequence of the template strand.
With this information, we can conclude that the correct answer is:
Answer:The DNA sequence ATGCATGC will pair with the following RNA strand:
a) UACGUACG
9. formulate a hypothesis in why the genetic counselor said ""not exactly"". you should use your textbook and omim as the reference.
Answers
A possible hypothesis for why a genetic counselor may have said "not exactly" is that the patient's genetic disorder or condition is likely to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
This could be due to a gene-environment interaction, which occurs when two or more genes interact with environmental factors to cause a disorder. Additionally, the genetic counselor may have been referring to the complexity of the underlying genetic basis of the disorder and the difficulty in understanding the exact cause of the disorder, even with the use of textbooks and OMIM (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man) as references.
To know more about genes please refer:
https://brainly.com/question/29367774
#SPJ4
Which ion is a found in a glass of water
Answers
In a glass of water, the most common ion found is the hydroxide ion (OH-) and the hydrogen ion (H+).
These ions are formed when water molecules dissociate through a process called self-ionization or autoionization.
In a glass of water, several ions can be found, originating from the dissociation of water molecules. The main ions present are hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-), resulting from the self-ionization of water.
Water molecules can break apart spontaneously into equal concentrations of H+ and OH- ions through a process called autoionization. This occurs when a water molecule donates a proton (H+) to another water molecule, forming H3O+ (hydronium ion) and OH-.
Additionally, other ions might be present in a glass of water depending on its source. For example, tap water can contain various dissolved ions like calcium (Ca2+), magnesium (Mg2+), sodium (Na+), chloride (Cl-), and bicarbonate (HCO3-). These ions come from minerals and other substances present in the water source, such as groundwater or surface water.
It's worth noting that the specific ion composition of water can vary depending on factors like location, treatment processes, and water source. However, the fundamental ions present in water are H+ and OH- resulting from the autoionization of water molecules.
For more such answers on Water
https://brainly.com/question/5060579
#SPJ8
Although we study the citric acid cycle as the final stage in the oxidation of carbon from glucose, an in-depth look at the cycle shows intermediates entering and leavi the cycle from a number of metabolic pathways. With all of these demands on the cycle, how does it maintain a minimal level of oxaloacetate (OAA) to allow the cycl function? a The rate of the cycle increases when the cell has high levels of NADH b OAA is formed directly via the deamination of glutamate c OAA is synthesized via pyruvate carboxylase in an anaplerotic reaction that occurs when acetyl CoA is present d isocitrate dehydrogenase is allosterically inhibited by ADP, which signifies the need for more energy e OAA can be formed by the condensation of two moles of acetyl CoA and occurs when the energy charge of the cell is high
Answers
C. When acetyl CoA is present, an anaplerotic process involving pyruvate carboxylase produces OAA.
Through anaplerotic reactions, which involve the synthesis of cycle-depleting intermediates like oxaloacetate (OAA), the citric acid cycle can be replenished. An enzyme called pyruvate carboxylase helps turn pyruvate into OAA, which can subsequently be combined with acetyl CoA to complete the cycle. When acetyl CoA is present, this reaction takes place, signalling that the cycle needs to be renewed.
As we discovered, an acetyl group can be added to any molecule, even the biggest ones that we are aware of. This includes molecules as small as an OH group, which produces acetic acid. As a result of its frequent use in organic chemistry reactions, it is crucial to understand this moiety.
To know more about acetyl ,visit
https://brainly.com/question/30470177?referrer=searchResults
#SPJ4
The respiratory system is responsible for:?
transporting materials (e.g., nutrients and oxygen) throughout the body.
breaking down large food into molecules that can be used by the cells of the body.
obtaining oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide.
producing movement of body parts.
Answers
Answer:
obtaining oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide(gaseous exchange)
Please someone help. Also don’t pay attention to the questions.
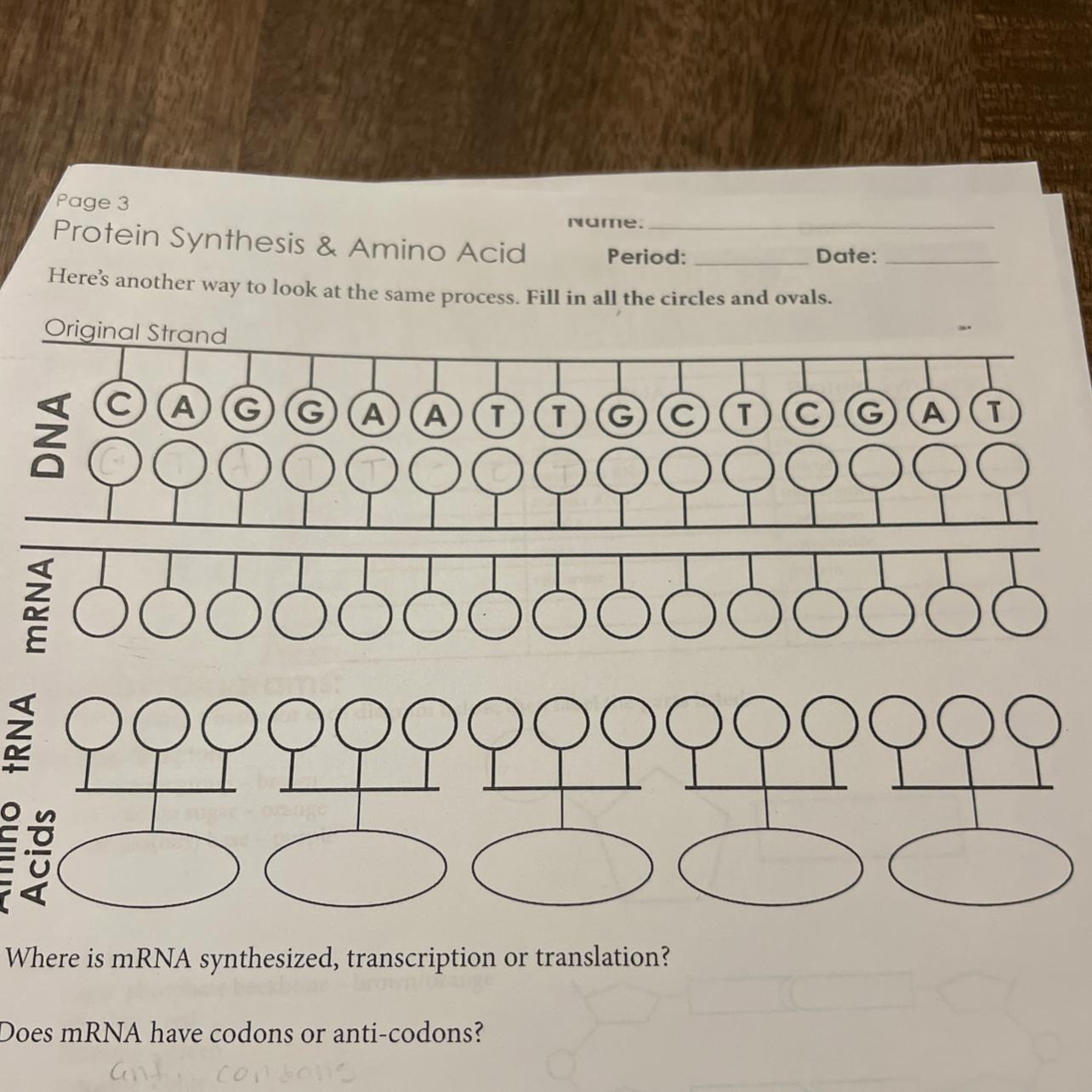
Answers
DNA sequence of
\(5^'\) CAGGAATTGCTGAT \(3^'\) will be
\(3^'\)GTCCTTAACGAGCTA \(5^'\)
What is DNA sequence?DNA sequencing is defined as the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence - the order of nucleotides in DNA which includes any method or technique that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine A, guanine G, cytosine C and thymine T. For complimentary strand of DNA during DNA replication, A binds with T and C binds with G.
For above given information,
DNA \(5^'\) CAGGAATTGCTGAT \(3^'\)
\(3^'\)GTCCTTAACGAGCTA \(5^'\)
mRNA \(5^'\) CAG GAA UUG CUC GAU \(3^'\) (These are Codons)
tRNA GUC CUU AAC GAG CUA (These are Anti-codons)
For Amino acids,
The codon CAG represents the amino acid glutamine
The codon GAA represents the amino acid glutamine
The codon UUG represents the amino acid leucine
The codon CUC represents the amino acid leucine
The codon GAU represents the amino acid aspartic acid.
Thus, DNA sequence of
\(5^'\) CAGGAATTGCTGAT \(3^'\) will be
\(3^'\)GTCCTTAACGAGCTA \(5^'\)
Learn more about Amino acids, here:
https://brainly.com/question/14583479
#SPJ1
Medication is a persistent pattern of medication misuse that causes harm.a. Trueb. False
Answers
Medication is a persistent pattern of medication misuse that causes harm.a. False
The correct definition of medication misuse is the use of medication in a way that is not consistent with its intended purpose or in a manner that is inconsistent with medical or social norms. Medication misuse can lead to harm or negative consequences, but it does not necessarily imply a persistent pattern of misuse.
However, when medication misuse becomes a persistent pattern and causes significant harm to the individual's health, relationships, work, or other areas of their life, it can be classified as a substance use disorder or addiction. It is important to seek medical help and support if medication misuse becomes problematic.
Learn more about Medication
https://brainly.com/question/11098559
#SPJ4
What technique is used to assess frequency changes seen when a skeletal muscle generates different levels of force production?
Answers
The technique used to assess frequency changes seen when a skeletal muscle generates different levels of force production is electromyography (EMG).
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique that involves the placement of electrodes on the surface of the skin or directly into the muscle to measure the electrical activity produced by muscle fibers during contraction.
By analyzing the frequency and amplitude of the EMG signal, researchers can gain insights into the recruitment and activation patterns of muscle fibers during different levels of force production. This information can help identify changes in motor unit activation and muscle fiber recruitment, which are important factors in understanding the mechanisms underlying muscle performance and fatigue.
Learn more about Electromyography (EMG) here: https://brainly.com/question/22373134
#SPJ11
when are chromosomes (dna) copied?
Answers
Answer:
Interphase begins with G1 (G stands for gap) phase. During this phase, the cell makes a variety of proteins that are needed for DNA replication. During S phase, which follows G1 phase, all of the chromosomes are replicated. Following replication, each chromosome now consists of two sister chromatids.
Have a good day. :)
Answer:
Chromosome replication
Explanation:
Chromosome replication is a key event during the cell cycle that must be completed before a cell divides. To reproduce successfully, every cell must replicate its chromosome and distinguish these sister chromosomes from one another.
explain the genetic hypothesis that existed before mendel's time by placing the correct word in each sentence.
Answers
Before Mendel's time, the genetic hypothesis was based on the theory of blended inheritance.
This theory suggested that offspring inherited a blend of their parents' traits, which resulted in a gradual and continuous change in the population over time. According to this hypothesis, traits were controlled by particles called pangenes that were present in all parts of the body and were passed down to offspring through the bloodstream.
However, this hypothesis did not account for the observed patterns of inheritance, such as the reappearance of traits in later generations or the occurrence of rare traits. Therefore, Mendel's experiments with pea plants provided a new understanding of inheritance based on the principles of segregation and independent assortment.
Here you can learn more about blended inheritance
https://brainly.com/question/30759531#
#SPJ11
What is not an example of proteins??
Answers
Answer:Glucose is not an example of proteins.
Explanation:
Which term describes a single female arctic The group of polar bears that live along the eastern coast of Russia makes upfox?
Answers
The term that describes a single female arctic fox is a vixen.
A vixen is a female fox, including the arctic fox, that is not pregnant or nursing young. It belongs to the Canidae family and is found in the tundra and other Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere.The Arctic fox is a small, compact, and sturdy mammal that can survive in some of the world's harshest environments.
The population of Arctic foxes that lives along the eastern coast of Russia is not referred to as a group of polar bears. It is known as a population, a community, or a family.A population is a group of animals of the same species that live in the same area and interact with one another.
A family of arctic foxes is made up of a male and female adult and their offspring. They live together in underground dens that are used for shelter and protection.Arctic foxes are considered a keystone species in the Arctic region because they play a crucial role in the ecosystem. They feed on small animals like lemmings and voles, which helps to regulate their populations. In addition, they are a food source for larger predators like wolves and polar bears, which helps to maintain balance in the food web.
For more such questions on arctic fox, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/27754416
#SPJ8
in a basic staining procedure, which is the correct order? group of answer choices smear, fix, stain fix, stain, decolorize fix, smear, stain smear, decolorize, stain smear, stain, fix
Answers
In a basic staining procedure, the correct order is: smear, fix, stain. The staining process is essential for observing and identifying microorganisms under a microscope.
Here's a brief explanation of each step:
1. Smear: The sample containing the microorganism is spread thinly on a clean microscope slide to create a uniform layer. This helps in even distribution of the organisms, allowing for easier observation under the microscope.
2. Fix: The smear is then fixed on the slide, which involves the use of heat or chemicals to adhere the cells to the slide and to kill the microorganisms. Fixation also preserves the cells' structures, preventing them from undergoing changes during the staining process.
3. Stain: Finally, a dye or stain is applied to the fixed smear. The stain imparts color to the cells, making them more visible under the microscope. Basic stains, like crystal violet or methylene blue, are positively charged and bind to the negatively charged cell components, such as the cell wall and nucleic acids. This highlights the cells and their structures, enabling better visualization and identification of the microorganisms.
In summary, the correct order for a basic staining procedure is to create a smear, fix the sample, and then apply the stain. This process allows for easier observation and identification of microorganisms under a microscope.
For more such questions on Staining.
https://brainly.com/question/28633620#
#SPJ11
A lending library has a fixed charge for the first three days and an additional charge for each day thereafter. Saritha paid ₹27 for a book kept for seven days, while Susy paid ₹21 for the book she kept for five days. Find the fixed charge and the charge for each extra day.
Answers
Answer:
See the attachment.
Hope u understand

In the given question, 5₹ is the fixed charge and 3₹ is the charge for each extra day.
A fixed charge is a fee or cost that remains constant and does not vary with changes in usage or consumption.
Let the fixed charge for the first three days be x and the charge for each extra day be y.
From the given information, we can set up two equations:
For Saritha: \(\rm 3x + 4y = 27 -----(equation 1)\)
For Susy: \(\rm 3x + 2y = 21 -----(equation 2)\)
We can solve for x and y by using elimination or substitution:
Using elimination, we can multiply the second equation by 2 and subtract it from the first equation:
\(\rm 3x + 4y = 27\)
\(\rm - (6x + 4y = 42)\)
Solving above equations, we get:
\(\rm -3x = -15\)
\(\rm x = 5\)
Substituting x = 5 into one of the equations, we can solve for y:
\(\rm 3(5) + 4y = 27\)
\(\rm 15 + 4y = 27\)
\(\rm 4y = 12\)
\(\rm y = 3\)
Therefore, the fixed charge is ₹5 and the charge for each extra day is ₹3.
Learn more about fixed charge here:
https://brainly.com/question/33211058
#SPJ4
Which phase of the cell cycle could you identify most readily with a light microscope
Answers
1. Are there any teratogens that you are exposed to on an everyday basis? If s which ones? 2. Do you think it's possible to avoid ALL teratogens? If so, how might you go about this? If not, why not? 3. Is it important for expectant fathers to avoid teratogens? Why or why not?
Answers
Teratogens are substances or conditions that can cause birth defects in developing fetuses. Exposure to these teratogens may increase the risk of birth defects and other developmental disorders. There are several teratogens that an individual may be exposed to on an everyday basis. Some of these common teratogens include alcohol, tobacco smoke, caffeine, pesticides, and some prescription and over-the-counter drugs.
It is not possible to avoid all teratogens completely. However, there are certain measures that one can take to reduce the risk of exposure. For example, pregnant women can avoid smoking, alcohol consumption, and exposure to harmful chemicals. They can also eat a healthy diet and get enough rest to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Expectant fathers should also take precautions to avoid teratogens as they can also have an impact on the health of the developing fetus. For example, exposure to lead and certain chemicals may increase the risk of birth defects and developmental disorders. Therefore, it is important for both parents to take measures to minimize their exposure to teratogens and create a healthy environment for the developing fetus.
In conclusion, exposure to teratogens can have a significant impact on the health of a developing fetus. While it may not be possible to avoid all teratogens, there are steps that can be taken to minimize exposure and ensure a healthy pregnancy. Both expectant mothers and fathers should be aware of the risks associated with teratogens and take steps to reduce their exposure.
Learn more about Teratogens:
https://brainly.com/question/6676255
#SPJ11
Hemoglobin contains four __________ groups, each of which has a(n) __________ at its center, acting as the binding site for oxygen. heme; iron globin; nitrogen heme; carbon globin; iron
Answers
Hemoglobin contains four heme groups, each of which has an iron atom at its center, acting as the binding site for oxygen.
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that is responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. Its structure consists of four subunits, each of which contains a heme group. The heme group is a complex molecule that consists of a porphyrin ring and an iron ion (Fe2+) at its center.
The iron ion within the heme group is crucial for the binding and transportation of oxygen. When oxygen is inhaled, it enters the lungs and binds to the iron ions in the heme groups of hemoglobin. This forms an oxygenated form of hemoglobin called oxyhemoglobin. Oxyhemoglobin is bright red in color and is transported by the bloodstream to various tissues and organs where oxygen is needed.
In the tissues, the oxygen is released from the oxyhemoglobin, and the hemoglobin molecule returns to its deoxygenated form, called deoxyhemoglobin. The released oxygen can then be utilized by the cells for various metabolic processes. This cycle of oxygen binding and release is essential for oxygen delivery to tissues and organs throughout the body.
Therefore, hemoglobin's ability to bind oxygen is facilitated by the presence of four heme groups, each containing an iron atom at its center. These iron atoms act as binding sites for oxygen molecules, allowing hemoglobin to efficiently transport oxygen to where it is needed in the body.
To know more about Hemoglobin refer here
https://brainly.com/question/31765840#
#SPJ11
what are a structural difference Characteristics that triglycerides and phospholipids have in common
Answers
explain organic Farming
Answers
Organic farming is an agricultural approach that emphasizes the use of natural and environmentally friendly practices to cultivate crops and raise livestock. It aims to minimize the use of synthetic inputs such as chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs) while promoting sustainable farming methods.
In organic farming, soil health and fertility are prioritized through techniques like crop rotation, cover cropping, and composting. These practices enhance soil structure, increase nutrient content, and promote beneficial microorganisms, leading to long-term soil health and reduced erosion.
Organic farmers rely on biological pest management methods, such as beneficial insects, crop diversity, and cultural practices, to control pests and diseases. They avoid the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides, which helps to protect biodiversity and minimize chemical residues in food and the environment.
The organic farming approach promotes ecological balance, biodiversity conservation, and sustainable production methods while striving to provide consumers with organic products that are free from synthetic chemicals and GMOs. It also encourages the adoption of regenerative practices to mitigate the environmental impacts of conventional agriculture.
Know more about Organic farming here:
https://brainly.com/question/29233846
#SPJ8
5’ GCGACUAAAUUU 3’
What is the sequence of amino acids that will be translated from the mRNA
Answers
The process of mRNA translation is present in essentially all biological systems. Following the transcription of the genetic information from the DNA to the mRNA, the genetic codons are translated from mRNA to protein via ribosome translocation in this process.
What amino acids that will be translated from the mRNA?The mRNA is then dragged into the ribosome, where it is translated into an amino acid sequence, utilizing the tRNAs as adaptors to add each amino acid. In the proper order to the end of the expanding polypeptide chain when its codons come into contact with the ribosome's active site.
Therefore, 3’ CGCTGATTTAAA 5’ is the sequence of amino acids that will be translated from the mRNA.
Learn more about mRNA here:
https://brainly.com/question/12903143
#SPJ1
3. How can genetic engineering be beneficial to human society?
There may be unknown side effects.
Genes coded for diseases could be eliminated.
Bacteria and viruses could grow stronger.
Genes can be completely changed.
Answers
The ability to eradicate diseases through genetic engineering might be advantageous to human society.
What are genetic engineering's social advantages?With improved agricultural yields and the ability to fend off pests, droughts, and floods, genetic technologies are revolutionizing the way we grow food. Along with raising life expectancy and quality of life, they are also providing fresh approaches to the fight against cancer and many other inherited disorders.
Which three advantages do genetic modifications offer?Increased crop yields, lower production costs for food or drugs, less need for pesticides, improved nutrient composition and food quality, disease and pest resistance, greater food security, and medical advantages for the world's expanding population are a few advantages of genetic engineering in agriculture.
To know more about genetic visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/5757079
#SPJ1
Sort the following Into whether they occur In metaphase l/anaphase Sort the following into whether they occur in metaphase l/anaphase I of meiosis, in metaphase/anaphase of mitosis, or both. anaphase I bivalents are formed a cell division follows homologous chromosomes separate from one another the number of chromosomes will be reduced overall centromeres will divide in two a telophase will follovwthe number of chromosomes stays the same overal crossing over occurred just before Metaphase/anaphase of mitosis Metaphase/anaphase of meiosis Mitosis and meiosis
Answers
The events of Metaphase I/Anaphase I of Meiosis are: bivalents are formed; the number of chromosomes will be reduced overall; crossing over occurred just before. The events of Metaphase/Anaphase of Mitosis are: centromeres will divide in two; the number of chromosomes stays the same overall; homologous chromosomes separate from one another. Events of both mitosis and meiosis are: a cell division follows; a telophase will follow.
Meiosis is the type of cell division that forms four daughter cells from one parent cell which are haploid in the ploidy. The process occurs in two parts: meiosis I and meiosis II.
Mitosis is the cell division that occurs is somatic cells where the ploidy of cells remains the same. This results in 2 daughter cells from a parent cell.
To know more about mitosis, here
brainly.com/question/26678449
#SPJ4