Answers
Answer:
arsenic (As)
Explanation:
Related Questions
What limitations occurs for chalk in vinegar chemistry pd lab experiment?
Also the precautions to take
Need this asap!!
Answers
Answer:
When conducting a chemistry lab experiment using chalk (calcium carbonate) in vinegar (acetic acid), there are several limitations and precautions to be aware of:
Limitations of chalk in vinegar chemistry experiment:
Reaction rate: The reaction between chalk and vinegar is relatively slow, which may require a longer observation period or higher concentration of vinegar to observe significant changes within a reasonable time frame.
Solubility: Chalk may not dissolve completely in vinegar, resulting in incomplete reaction or difficulty in obtaining accurate results.
Product formation: The reaction between chalk and vinegar produces carbon dioxide gas, water, and calcium acetate. The carbon dioxide gas may escape into the atmosphere, leading to loss of product and inaccurate measurements.
pH: Chalk is a basic substance, and the reaction with vinegar, which is acidic, may result in neutralization, leading to a decrease in the overall acidity of the reaction mixture.
Precautions to take in chalk in vinegar chemistry experiment:
Ventilation: The reaction between chalk and vinegar produces carbon dioxide gas, which can displace air and potentially cause asphyxiation in a closed or poorly ventilated area. Conduct the experiment in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to ensure adequate air circulation.
Eye and skin protection: Vinegar is an acid and can cause skin and eye irritation. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and goggles, to protect yourself from contact with vinegar or any other chemicals used in the experiment.
Chemical handling: Handle the chemicals, including chalk and vinegar, with care, following proper lab safety protocols. Avoid ingestion, inhalation, or direct contact with the chemicals, and dispose of them properly according to local regulations.
Accuracy in measurements: Use calibrated and accurate measuring tools, such as graduated cylinders or burettes, to measure the amount of chalk, vinegar, and other reagents accurately. This will ensure the reliability and accuracy of the experimental results.
Observations: Make careful and detailed observations during the experiment, noting any changes in appearance, gas evolution, or other relevant observations. Take measurements at appropriate intervals and record the data accurately for analysis and interpretation.
It is important to follow good laboratory practices, including proper chemical handling, accurate measurements, and cautious observations, to ensure safe and reliable results in a chalk in vinegar chemistry lab experiment. Consult with a qualified instructor or supervisor for specific guidelines and precautions related to your experiment.
Identify the compound that contains an ionic bond.
*
O
H20
O CO2
O Naci
O CH3CH2OH
Answers
Answer:
Nacl compound contain ionic bonds because sodium is metal and chlorin is nonmetal
what are the colors of a rainbow
Answers
If there are 3.10 moles of O, how many moles of each of the compounds are present?
H2SO4
mol
C2H4O2
mol
NaOH
mol
Answers
Explanation:
The question pretty much requires us to find the amount of moles of each compounds based on the number of moles of O given.
H2SO4
1 mol of H2SO4 contains 4 mol of O
x mol of H2SO4 would contain 3.10 mol of O
x = 3.10 * 1 / 4 = 0.775 mol of H2SO4
C2H4O2
1 mol of C2H4O2 contains 2 mol of O
x mol of C2H4O2 would contain 3.10 mol of O
x = 3.10 * 1 / 2 = 1.55 mol of C2H4O2
NaOH
1 mol of NaOH contains 1 mol of O
x mol of NaOH would contain 3.10 mol of O
x = 3.10 * 1 / 1 = 3.10 mol of NaOH
1. The moles of \(H_2SO_4\) is 0.775 mol.
2. The moles of \(C_2H_4O_2\) is 1.55 mol.
3. The moles of \(NaOH\) is 3.10 mol.
Given:
Moles of O =3.10
Number of moles:It is defined as given mass over molar mass.\(\text{Number of moles}=\frac{\text{Given mass}}{\text{Molar mass}}\)1. Calculation for moles of \(H_2SO_4\):
1 mol of \(H_2SO_4\) contains 4 mol of O
x mol of \(H_2SO_4\) would contain 3.10 mol of O
x = 3.10 * 1 / 4 = 0.775 mol of \(H_2SO_4\)
2. Calculation for moles of \(C_2H_4O_2\) :
1 mol of \(C_2H_4O_2\) contains 2 mol of O
x mol of \(C_2H_4O_2\) would contain 3.10 mol of O
x = 3.10 * 1 / 2 = 1.55 mol of \(C_2H_4O_2\)
3.Calculation of moles of \(NaOH\) :
1 mol of \(NaOH\) contains 1 mol of O
x mol of \(NaOH\)would contain 3.10 mol of O
x = 3.10 * 1 / 1 = 3.10 mol of \(NaOH\)
Find more information about Number of moles here:
brainly.com/question/14464650
Question 1Propane gas is commonly used in household grills, barbecues, and camping stoves. Heat for these stoves is produced through thecombustion of propane gas (C3Hg) in the presence of Oz which produces carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). The density of thispressurized propane gas is usually around 0.52 kilograms of propane per liter. If you use 0.2 L of propane gas during a cookout,how much carbon dioxide in grams does this reaction produce? (Assume 02 is in excess)Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer.a416 gb 3128C2088d 104 gUnanswereda Savemartian
Answers
Answer:
\(312\text{ g}\)Explanation:
Here, we want to get the mass of carbon (iv) oxide produced
We start by writing the equation of reaction as follows:
\(C_3H_{8(g)}\text{+5 O}_{2(g)}\text{ }\rightarrow\text{ 3CO}_{2(g)}\text{ + 4H}_2O_{(g)}\)Now, we need to get the mass of propane that reacted
We can get that by multiplying the density of propane by its given volume
Mathematically, we have that as:
\(\begin{gathered} 0.52\text{ }\times0.2\text{ = 0.104 kg} \\ 1000\text{ g = 1kg} \\ 0.104\text{ kg = 0.104 }\times\text{ 1000g = 104 g} \end{gathered}\)From here, we get the actual number of moles of propane that reacted
We can get that by dividing the mass by the molar mass of propane
The molar mass of propane is 44 g/mol
The number of moles is thus:
\(\frac{104}{44}\text{ mol}\)From the balanced equation:
1 mole of propane gave 3 moles of carbon (iv) oxide
104/44 mol will give x moles
We have the value of x as:
\(x\text{ = }\frac{104}{44}\times\text{ 3 = }\frac{312}{44}\text{ mol}\)To get the mass of carbon (iv) oxide produced, we multiply the number of moles above by the molar mass of carbon (iv) oxide
The molar mass of carbon (iv) oxide is 44 g/mol
Thus, we have the mass as:
\(\frac{312}{44}\times44\text{ = 312 g}\)How many lone pairs in the correct electron dot structure of O3?
Answers
Answer:
Three lone pairs
Explanation:
From the left, O1 , has TWO lone pairs; O2 has ONE lone pairs; and O3 has THREE lone pairs
From the left, O1 , has TWO lone pairs; O2 has ONE lone pairs; and O3 has THREE lone pairs.
Students are studying various forms of matter. They just finished studying solids, liquids, and gases. Now they must draw a model that represents their
observations which model best represents what happens to gas molecules in a closed container?
b.
a
C
d.
ooo
Answers
Answer:d
Explanation:
the name of the acid present in milk
Answers
Answer:
lactic acidThe real acidity of milk is due to lactic acid. This is never found in milk when it is first drawn from the udder. It is produced by the action of the lactic acid organisms on the milk sugar. The so-called apparent acidity of milk is what gives fresh milk its acid reaction.

At STP the number of liters of O2 required to react with 11.2 liters of CH4 to form only CO2 and H2O is ________ liters.
Answers
The number of liters of oxygen, O₂, required at STP to react with 11.2 liters of CH₄ to form only CO₂ and H₂O is 22.4 liters.
What is the number of liters of O₂ required at STP to react with 11.2 liters of CH₄ to form only CO₂ and H₂O?The number of liters of O₂ required at STP to react with 11.2 liters of CH₄ to form only CO₂ and H₂O is determined from the balanced equation of the reaction as follows:
The balanced equation of the reaction of O₂ at STP CH₄ to form only CO₂ and H₂O is given below:
CH₄ + 2 O₂ (g) ----> CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂O (g)
From the balanced equation of the reaction of O₂ at STP CH₄, 2 moles of O₂ reacts with one mole of CH₄.
At STP, the volume of one mole of CH₄ is equal to 22.4 liters
The number of mole of CH₄ in 11.2 liters of CH₄ will be 11.2 / 22.4 = 0.5 moles
The moles of oxygen required will be 0.5 liters * 2 /1 = 1 mole of oxygen.
At STP, the volume of one mole of O₂ is equal to 22.4 liters.
Hence, 22.4 liters of oxygen are required.
Learn more about the volume of gases at STP at: https://brainly.com/question/26364483
#SPJ1
What are 3 elements similar to silver
Answers
Answer:
Copper, Sodium, and Francium
Explanation:
Gaseous butane (CH3(CH2)2CH3) will react with gaseous oxygen (02) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and gaseous water (H2O). Suppose 34.g of butane s mixed with 200. g of oxygen. Calculate the maximum mass of water that could be produced by the chemical reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.

Answers
The maximum mass of water that can be produced by the reaction is 43.3 g, rounded to three significant figures.
Determining the maximum mass of water producedThe balanced chemical equation for the reaction between butane and oxygen is:
C4H10 + 13/2 O2 → 4 CO2 + 5 H2O
From the equation, we can see that 1 mole of butane reacts with 13/2 moles of oxygen to produce 5 moles of water.
moles of butane = 34. g / 58.12 g/mol = 0.585 mol
moles of oxygen = 200. g / 32.00 g/mol = 6.25 mol
Determining the limiting reactant.
butane : oxygen = 0.585 mol : 6.25 mol
= 0.0936 : 1.00
stoichiometric ratio = 1 : 13/2
= 0.7692 : 1.00
Since the actual ratio is lower than the stoichiometric ratio for oxygen, it is the limiting reactant.
The maximum amount of water that can be produced is determined by the amount of limiting reactant (oxygen).
moles of water = 5/13 * 6.25 mol
= 2.403 mol
Finally, we can convert the moles of water to grams:
mass of water = 2.403 mol * 18.015 g/mol
= 43.3 g
Learn more on stoichiometry here https://brainly.com/question/14935523
#SPJ1
how do i get money in real life
Answers
Teaching, working at the restaurant, online work and freelancing are the work that make money.
How do I get money in real life?In real life, we can get money by doing teaching in the school or academy, working at the restaurant or any other public places. Freelancing and online teaching are the best jobs for making good money. Doing small business able you to make good money in a short period of time. Make deliveries on Amazon and start your own business. So there are a lot of jobs for making money and better your financial condition.
So we can conclude that teaching, working at the restaurant, online work and freelancing are the work that make money.
Learn more about money here: https://brainly.com/question/24373500
#SPJ1
Help please due today

Answers
Answer:
It is a becaues i am a doctor and i know about that
Explanation:Just here to help
A calorimetry experiment determined that the combustion of 1.01 g of H2(g) reacting with excess O2(g) gave qsoln = 143 kJ. Calculate ΔH for the reaction: H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O (l)
Answers
Answer:
089
Explanation:
I have no idea
Based on the data from the calorimetry experiment, the enthalpy change, ΔH of the reaction is -286 KJ .
What is enthalpy change, ΔH of a reaction?The enthalpy change, ΔH of a reaction is the amount of heat evolved or absorbed when reactant molecules react to form products.
From the calorimetry experiment, the determined heat of combustion of 1.01 g of H2(g) reacting with excess O2(g), qsoln = 143 kJ.
Heat is evolved in the reaction, therefore the qsoln = -143 kJ
Equation of reaction is given as:
H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O (l)
Molar mass of H = 1.01 g
Mass of H2 = 1.01 g × 2 = 2.02 g
ΔH of the reaction = -143 kJ × 2.02/1.01
ΔH of the reaction = -286 KJ
Therefore, the enthalpy change, ΔH of the reaction is -286 KJ .
Learn more about enthalpy change at: https://brainly.com/question/14047927
10. For the reaction
H₂(g) + O₂(g) → H₂O(l)
H=-286 kJ/mol
What is the enthalpy change when 10.4 mol of hydrogen gas reacts with excess oxygen?
a. 27.5 kJ
b.-27.5 kJ
c. 3.64 x 10-2 J
d. -2.97 × 10³ J
e. -1.48 x 10³ J
Answers
deprotonate enolate enone
what do these terms mean?
Answers
Deprotonation refers to the removal of a proton from a molecule, while an enolate is an anionic species formed by deprotonation of the α-carbon adjacent to a carbonyl group. An enone, on the other hand, is a molecule containing a carbon-carbon double bond and a carbonyl group.
"Deprotonate," "enolate," and "enone" are terms used in organic chemistry to describe specific reactions and functional groups. Let's break down each term:
Deprotonate: Deprotonation refers to the removal of a proton (H+) from a molecule. It is a process that involves the transfer of a proton from a molecule to a base. The resulting species is negatively charged and called an anion.
Deprotonation reactions are common in various organic reactions and play a crucial role in the formation of new bonds and the generation of reactive intermediates.
Enolate: An enolate is an anionic species that contains a carbon-carbon double bond and a negatively charged oxygen or nitrogen atom. Enolates are formed through deprotonation of the α-carbon adjacent to a carbonyl group (such as a ketone or aldehyde).
The formation of enolates is an important step in many organic reactions, such as aldol condensation and Michael addition, as enolates serve as nucleophiles or reactive intermediates.
Enone: An enone is a molecule that contains a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C) and a carbonyl group (C=O) adjacent to each other. Enones are carbonyl compounds that possess a conjugated double bond system. They exhibit unique reactivity due to the presence of both a double bond and a carbonyl group, making them valuable intermediates in organic synthesis.
Enones are involved in various reactions, including Michael additions, Diels-Alder reactions, and cycloadditions, to form complex organic compounds.
For more such question on Deprotonation. visit :
https://brainly.com/question/28480664
#SPJ8
The SI unit of pressure is the _______.
The boiling point of water is _______ on Mount McKinley than the boiling point of water in NYC.
At lower elevations, atmospheric pressure _______ compared to higher elevations.
Standard atmosphere or standard atmospheric pressure is equal to _______ Pa.
Answers
The SI unit of pressure is the Pascal (Pa).
The boiling point of water is lower on Mount McKinley than the boiling point of water in NYC.
What is Pressure?
Pressure is defined as the amount of force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. In other words, it is the force per unit area that an object exerts on another object. Pressure can be measured in various units such as pascal (Pa), bar, pounds per square inch (psi), and atmospheres (atm), among others. It is an important concept in physics and is used to describe many phenomena, including fluid dynamics, weather patterns, and even the behavior of gases in space.
At lower elevations, atmospheric pressure is higher compared to higher elevations.
Standard atmosphere or standard atmospheric pressure is equal to 101325 Pa.
Learn more about Pressure from given link
https://brainly.com/question/28012687
#SPJ1
BRAINLIEST AND 100 POINTS FOR THIS

Answers
Answer:
I need to see the chapter lol /:
Answer:
1: background sound.
2: room tone
3: middle-frequency
4: Feedback
5: lapel mic
6: line level
7: High impedance
Part E Why does the car stop? Where did the energy go?
Answers
When the moving car brakes to the stop the kinetic energy of car will be converted to the heat energy.
The mechanical brake will be applies to the friction force and it convert the kinetic energy of the car into the thermal energy that which then dissipates on atmosphere. The process of the braking will follow the principle of the conservation of the energy.
The conservation of the energy is the principle, that is expressed in its the most general form, and it is the first law of the thermodynamics. The first law of thermodynamics explains that "the energy of the universe remains the same."
To learn more about thermodynamics here
https://brainly.com/question/31303013
#SPJ1
This question is incomplete, the complete question is :
A car in motion has kinetic energy. A moving car is suddenly stopped. Why does the car stop? Where did the energy go?
A sample of hydrogen at 50.6
C exerts a pressure of 237.46 mmHg. If the gas is heated to 73.2 °C at constant volume, what will its new pressure be?
Answers
If the gas is heated to 73.2 °C at constant volume 253.7 mmHg will its new pressure.
What is the quick description of the ideal gas law?The rule that states that the sum of the absolute temperature of the gas and the universal gas constant is equal to the product of the pressure and volume of a single gramme of an ideal gas.
Using the ideal gas law, we may assume that hydrogen is acting optimally as follows:
As the gas is being heated solely and the volume is not changing, thus, n and V are constant and hence we may state
(P1V1) / T1 = (P2V2) / T2
P1 / T1 = P2 / T2
We can then plug in the given values and solve for P2:
P1 = 237.46 mmHg
T1 = 50.6 + 273.15 = 323.75 K (temperature in Kelvin)
T2 = 73.2 + 273.15 = 346.35 K
P2 = P1 * T2 / T1
P2 = 237.46 * 346.35 / 323.75
P2 = 253.7 mmHg.
If the gas is heated to 73.2 °C at constant volume 253.7 mmHg will its new pressure.
To know more about Ideal gas law visit:
https://brainly.com/question/28257995
#SPJ1
how would you confirm the presence of lead in an ore?
Answers
There are numerous ways to determine whether lead is present in an ore. Atomic absorption spectroscopy is a popular approach. With this method, an ore sample is dissolved in acid and then atomized in a flame or plasma.
The sample's atoms will absorb light at particular wavelengths that are peculiar to the element under investigation. The amount of light absorbed can be used to calculate how much lead is present in the sample. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy are further techniques. It is crucial to remember that these procedures call for specialized tools and training, thus they ought to only be carried out in a lab by qualified experts.
To know more about spectrometry, here
brainly.com/question/31075363
#SPJ1
what’s is the answer?

Answers
The energy of the photon of light can be obtained as 6.27 * 10^-20 J.
What is the energy of the photon?We know that a photon has to to do with a particular unit of light. We know that light can be said to be composed of very tiny corpuscles and these corpuscles of light is what we call the photon of the light.
We can be able to us the equation that is derived by Max Plank to be able to get the value of the energy of the photon of light. Now we know that a photon of light can have an energy that is able to be obtained by;
E = hf
h = Plank's constant
f = Frequency
Then;
E = 6.6 * 10^-34 Js * 9.5 * 10^13 Hz
= 6.27 * 10^-20 J
Thus as we can see from the parameters in the question, the energy of the photon is 6.27 * 10^-20 J.
Learn more about energy of the photon:https://brainly.com/question/2393994
#SPJ1
light energy travels in
Answers
Light energy travels in the form of waves.
when an alkane reacts with a halogen to form a halogenated compound, the reaction that occurs is a substitution reaction.
Answers
Yes, when an alkane reacts with a halogen, the reaction that occurs is a substitution reaction.
In this type of reaction, the halogen atom replaces a hydrogen atom in the alkane structure. The halogenated compound formed in this reaction is known as a halogenated hydrocarbon. This type of reaction is also known as halogenation.
The halogenation reaction can be carried out using a variety of methods, such as direct halogenation, radical halogenation, and electrophilic halogenation. The method used depends on the nature of the reactants and the desired product.
Learn more about halogenated compound
https://brainly.com/question/21500024
#SPJ4
What does this image represent?
Amine group
Carbonyl group
Ether group
Hydroxyl group
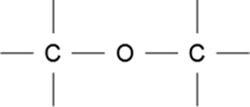
Answers

Answer:
ether group
Explanation: I looked it up
500.0 liters of a gas in a flexible-walled container are prepared at 0.92 atm and 473K. The gas is placed into a tank under high pressure. When the tank cools to 293K, the pressure of the gas is 3.0 atm. What is the volume of the gas?
P1V 1 T2=P 2 V 2 T 1
Question 17 options:
48 L
248 L
19 L
95 L
Answers
The volume of the gas in the tank at 293K and 3.0 atm pressure is 248 L. Hence, option B is correct.
Given:
T1 = 473K
T2 = 293K
P1 = 0.92 atm
P2 = 3.0 atm
The ideal gas law equation is:
PV = nRT
where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles of gas, R is the universal gas constant, and T is temperature.
n1 = (PV)/(RT)
= (0.92 atm × 500.0 L)/(0.0821 Latm/molK × 473K)
= 10.42 mol
Use the ideal gas law again to find the final volume of the gas in the tank under high pressure:
V2 = (n1 × R × T2)/P2
= (10.42 mol × 0.0821 Latm/molK × 293K)/(3.0 atm)
= 248 L
Therefore, the volume of the gas in the tank at 293K and 3.0 atm pressure is 248 L.
To learn more about pressure, follow the link:
https://brainly.com/question/31525061
#SPJ1
Answer:
Using the ideal gas law, PV=nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles, R is the gas constant, and T is temperature in Kelvin, we can solve for n:
n = PV/RT
We know that the initial volume is 500.0 L, pressure is 0.92 atm, and temperature is 473K. We can use this information to find the initial number of moles:
n1 = (0.92 atm x 500.0 L)/(0.08206 L atm/mol K x 473K) = 11.80 mol
Next, we can use the ideal gas law again to find the final volume. We know that the final pressure is 3.0 atm and the final temperature is 293K:
V2 = nRT2/P2
V2 = (11.80 mol x 0.08206 L atm/mol K x 293K)/3.0 atm = 95 L
Therefore, the volume of the gas at the lower temperature and higher pressure is approximately 95 L. Answer: 95 L.
(b) Two compounds, A and B, have the molecular formula C₂H6O. On treatment with Na metal, compound A releases H2 gas and compound B does not.
Can you give a reason to help to explain the observation better?
Answers
The observation that compound A releases H2 gas while compound B does not when treated with Na metal can be explained by considering the structural differences between the two compounds and their ability to undergo specific reactions.
Compound A and compound B both have the molecular formula C₂H₆O, which indicates that they both contain two carbon atoms, six hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom. However, the difference lies in the arrangement of these atoms within the molecules. One possible explanation for the observed difference is that compound A is an alcohol, specifically ethanol (CH₃CH₂OH), while compound B is an ether, such as dimethyl ether (CH₃OCH₃). The presence of the hydroxyl group (-OH) in ethanol enables it to undergo a reaction with sodium metal, known as the metal-acid reaction. In this reaction, the metal displaces the hydrogen from the hydroxyl group, forming sodium ethoxide (CH₃CH₂ONa) and releasing hydrogen gas (H₂). On the other hand, ethers like dimethyl ether lack the hydroxyl group and therefore cannot undergo the metal-acid reaction. Consequently, when compound B is treated with sodium metal, no hydrogen gas is released. The ability of compound A to release hydrogen gas while compound B does not when treated with sodium metal can be attributed to the presence of a hydroxyl group in compound A (ethanol), enabling it to undergo a metal-acid reaction, whereas compound B (dimethyl ether) lacks the necessary functional group and thus does not undergo this reaction.
For such more questions on structural
https://brainly.com/question/29117530
#SPJ11
What mass of water can be heated from 10.0 C to 38.0 Celsius by addition of 3,500j? (Specific heat capacity of water is 4.18 j/g C)
Answers
Mass of water : 29.904 g
Further explanationHeat can be formulated
Q=m.c.Δt
Q, heat, J
m,mass, g
c, specific heat, j/g C
Δt,temperature, C
Δt,temperature\(\tt 38-10=28^oC\)
mass of water\(\tt m=\dfrac{Q}{c.\Delta t}\\\\m=\dfrac{3500}{4.18\times 28}\\\\m=29.904~g\)
A change in the number of neutrons in an atom will change an isotope. What will happen when the number of protons changes in an atom?
Answers
A nitrogen-containing compound shows no absorption band at ∼3400cm−1 and no absorption bands between ∼1700cm−1 and ∼1600cm−1. what class of compound is it
Answers
Explanation:
A nitrogen-containing compound that shows no absorption band at around 3400 cm^−1 and no absorption bands between approximately 1700 cm^−1 and 1600 cm^−1 is likely an amide compound.
Amides typically exhibit a characteristic absorption band in the region of 3200-3500 cm^−1 due to the N-H stretching vibration. The absence of this absorption band suggests the absence of N-H bonds, which rules out compounds like primary or secondary amines.
The absence of absorption bands between 1700 cm^−1 and 1600 cm^−1 eliminates functional groups such as carbonyl compounds (e.g., aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters) and imines, which typically exhibit absorption in this region.
Therefore, based on the given information, it can be inferred that the compound is likely not an amine, carbonyl compound, or imine. Other classes of compounds that do not possess these characteristic absorption bands would need to be considered.