Given the wavefunction of a standing wave: y(x,t) = A sin(πx)cos(2πt), where x and y are in meters and t is in seconds. The position of the second anti-node from the end x = 0 is at
Answers
the distance of the second anti-node from the end x = 0 is given by:(2 × 2 - 1)λ/4 = 3/8 meters
Answer: 3/8 meters
The given wave function is:
y(x,t) = A sin(πx)cos(2πt)We need to determine the position of the second anti-node from the end x = 0.
The formula for the anti-nodes of a standing wave is given by:
L = (2n - 1)λ/4
Here,L = Length of the string
n = Node number
λ = Wavelength
For the given wave function:
y(x,t) = A sin(πx)cos(2πt)We can see that the wave function is of the standing wave in the string fixed at both ends. Therefore, both ends of the string are nodes. Now, we need to find the position of the second anti-node from the end x = 0.We know that for the standing wave in the string fixed at both ends, the nth anti-node will be at the distance of (2n - 1)λ/4 from one of the ends.
Therefore, the second anti-node from the end x = 0 will be at the distance of (2 × 2 - 1)λ/4 from x
= 0.Now,λ = 2L/n
λ = 2(1/2)/2λ = 1/2
Therefore, the distance of the second anti-node from the end x = 0 is given by:(2 × 2 - 1)λ/4 = 3/8 meters
Answer: 3/8 meters
learn more about wave function here
https://brainly.com/question/28447252
#SPJ11
Related Questions
please help answer the question in the image!!!

Answers
Answer:
C (only)
Explanation:
Often, we consider the 0 position on a graph like this to be the starting point. However, the position on this graph is indicated as positive at time = 0. The motion shown can be described in each stage as follows.
A: moving away from the starting position toward the reference position (position = 0)
B: stationary at the reference position
C: moving away from the reference position toward the starting position
D: stationary at a point just short of the starting position
E: moving away from the starting position toward, then beyond, the reference position
how much does a 115 kg barbell weigh in newtons? (~ indicates "approximately")
Answers
A 115 kg barbell weighs approximately 1,127 newtons. To convert kilograms to newtons, we need to multiply the weight in kilograms by the force of gravity, which is approximately 9.8 m/s^2.
So, 115 kg x 9.8 m/s^2 = 1,127 newtons.
This means that if you were to lift a 115 kg barbell, you would need to exert a force of approximately 1,127 newtons to lift it off the ground. It's important to note that the weight of the barbell may vary slightly depending on the specific model and brand. However, the calculation above is a good estimate for the weight of a typical 115 kg barbell.
To Learn more about newton. Click this!
brainly.com/question/13709335
#SPJ11
If a 0.5 kg ball is thrown up with 250 J of kinetic energy, how high will it go?
(HINT: At the ball's highest point it has stopped.)
KE = 1/2mv2
G = 9.8 m/s2
Answers
Answer:
51.02m
Explanation:
KE = 1/2mv2
Where k.e = 250J
mass = 0.5 kg
g = 9.8 m/s2
250= 1/2×0.5×v^2
250= 0.5×0.5×v^2
250= 0.25v^2
v^2 = 250/0.25
v^2 = 1000
v =√1000
v = 31.62m/s
v^2= u^2-2gh........... (1)
Since the object will stop at it highest point, hence it final velocity there will be zero and since it is moving up against the gravity g= -9.8m/s^2. That was why the formula in equation 1 has a negative sign
From h = u^2/2g
Where v = 31.62m/s
g = 9.8m/s^2
H = (31.62m/s)^2/9.8×2
H= 1000/19.6
= 51.02m
Hence the height of it travelling will be
51.02m
Iron man crashes into a parked car with a force of 8,000 newtons, resulting in a acceleration of 1.14 m/s. if the car has a mass of 1000 kg what is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the car tires and the road?
Answers
Answer:
0.8
Explanation:
F=uR
F=8,000N
R= 1000*10=10000
u=F/R
u= 8000/10000
u=0.8
HELPPPP PLSSS I NEED HELP
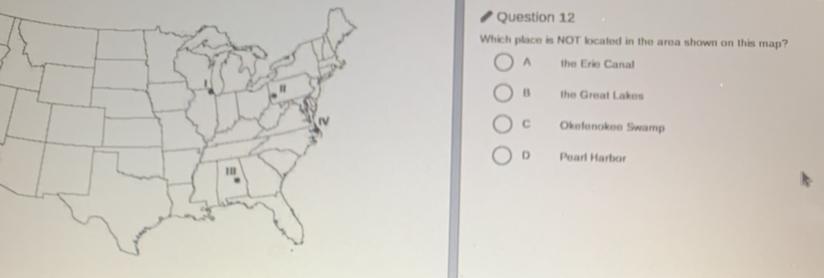
Answers
Answer:
D. Pearl Harbor
Explanation:
A 75.0 kg log floats downstream with a speed of 1.80 m/s. Eight frogs hop onto the log in a series of inelastic collisions. If each frog has a mass of 0.30 kg and an upstream speed of 1.3 m/s, what is the change in kinetic energy for this system
Answers
The change in kinetic energy for this system is - 11.69 J.
What is the change in the kinetic energy of the system?
The change in the kinetic energy of the system is calculated by applying the following kinematic equation as shown below.
ΔK.E = K.Ef - K.Ei
where;
K.Ei is the initial kinetic energy of the systemK.Ef is the final kinetic energy of the systemThe initial kinetic energy of the logs and the frogs is calculated as follows;
K.Ei = ¹/₂ (75)(1.8²) + 8(¹/₂)(0.3)(1.3²)
K.Ei = 123.53 J
The final kinetic energy of the system depends on the final velocity of the system. The final velocity of the system after the collision is calculated as follows;
m₁u₁ + m₂u₂ = v (m₁ + m₂)
(75 x 1.8) + (8 x 0.3)(-1.3) = v (75 + 8 x 0.3)
135 - 3.12 = 77.4v
131.88 = 77.4v
v = 131.88 / 77.4
v = 1.7 m/s
K.Ef = ¹/₂(m₁ + m₂)v²
K.Ef = ¹/₂(75 + 0.3x8)( 1.7² )
K.Ef = 111.84 J
The change in kinetic energy = 111.84 J - 123.53 J = - 11.69 J
Learn more about change in kinetic energy here: https://brainly.com/question/1932411
#SPJ1
The number of circular pieces of filter paper used in Experiment 2 was:

Answers
The number of circular pieces of filter paper used in Experiment 2 was 15.
The third option is correct.
What is a filter paper?Filter paper is described as a semi-permeable paper barrier placed perpendicular to a liquid or air flow which is used to separate fine solid particles from liquids or gases.
The various properties of filter paper includes:
wet strength, porosity, particle retention, volumetric flow rate, compatibility, efficiency and capacity.The number of circular pieces of filter paper used in Experiment 2 taking note of the number of trials is 15.
Learn more about filter papers at: https://brainly.com/question/30226734
#SPJ1
1) Prove that the total energy of a binary system where both objects (m1,m2) are moving can be expressed asE= \frac{1}{2}\mu \upsilon ^{2} - \frac{GM\mu }{r}where the reduced mass\mu = \frac{m_{1}m_{2}}{m_{1}+m_{2}}is orbiting around a mass M = m1 + m2 fixed at the origin. Do not assume circular orbits; your solution should apply to the general case of elliptical orbits.
Hint:
Step 1: Start from the total orbital energy of the system where both objects are moving as we discussed in
class: E = {
Answers
To prove that the total energy of a binary system where both objects (m1, m2) are moving can be expressed as E= 1/2μv² - GMμ/r, we start from the total orbital energy of the system, which is given by:
E = -GMm1m2/2r
where G is the gravitational constant, r is the distance between the two objects, and m1 and m2 are the masses of the objects. This expression assumes circular orbits, but we need to generalize it to elliptical orbits.
To do this, we use the concept of reduced mass, which is a way of simplifying the two-body problem by treating the motion of the two objects as if they were orbiting around their center of mass. The reduced mass μ is defined as:
μ = m1m2/(m1 + m2)
Using this definition, we can rewrite the expression for the total orbital energy as:
E = -GMμ/2r
Now, we need to relate this to the kinetic energy of the system. Since both objects are moving, we need to consider their relative motion. The velocity of m1 relative to m2 is given by:
v = v1 - v2
where v1 and v2 are the velocities of m1 and m2, respectively. Using the concept of reduced mass, we can rewrite this as:
v = (m2/(m1 + m2))v1 - (m1/(m1 + m2))v2
Now, we can express the kinetic energy of the system as:
K = 1/2m1v1² + 1/2m2v2²
Substituting the expression for v in terms of v1 and v2, and using the definition of reduced mass, we get:
K = 1/2μv²
where v is the relative velocity of the two objects. Therefore, the total energy of the system can be expressed as:
E = K + U = 1/2μv² - GMμ/2r
where U is the gravitational potential energy of the system, which is given by -GMμ/r.
To simplify this expression further, we can use the fact that the angular momentum of the system is conserved. Since the system is two-dimensional, the angular momentum vector is perpendicular to the plane of motion, and its magnitude is given by:
L = m1m2v0r
where v0 is the magnitude of the relative velocity at the minimum separation distance. Using the definition of reduced mass, we can rewrite this as:
L = μv0r
Solving for v0, we get:
v0 = L/(μr)
Substituting this expression into the equation for the total energy, we get:
E = 1/2μv² - GMμ/r = 1/2μ(v² - 2GM/r) + GMμ/r
Now, we recognize that the term in parentheses is just the square of the relative velocity minus the escape velocity from a distance r, so we can write:
E = 1/2μ(v - √(2GM/r))^2
This expression shows that the total energy of the binary system is a function of the relative velocity of the objects and the distance between them, and it holds for elliptical orbits as well as circular orbits.
Learn more about binary here:
https://brainly.com/question/19802955
#SPJ11
A dog runs down his driveway with an initial speed of 5.0 m/s for 8 seconds then uniformly increases his speed to 10 m/s in 5 seconds, how long is the driveway? SHOW WORK
Answers
Answer:
to find the displacement, or delta x (change in position) on a velocity graph, you can find the area under the line on the graph: between 1 and 8 seconds, the dog was going at 5m/s, so 5m/s x 8s=40m, for the second part, you have to find the area of both a triangle and a rectangle, so the rectangle would be 5m/s x 5s=25m and the area under the triangle would be (5m/s x 5s)/2=25m/2=12.5m -you divide by 2 because it's a triangle
-afterwards, you would add the area of the 2 sections together, so 40m+25m+12.5m=77.5m
Explanation:
What is the equivalent resistance (total resistance) of the series circuit shown?

Answers
Answer:
In a series circuit, the equivalent resistance is the algebraic sum of the resistances. The current through the circuit can be found from Ohm's law and is equal to the voltage divided by the equivalent resistance. The potential drop across each resistor can be found using Ohm's law.
Which of the following is not a major sub-field of physics?
Electricity and magnetism.
Thermodynamic.
Statistic.
Optic.
Helppp!!!
Answers
Answer: The answer is Statistic.
Explanation:
The branch of physics that deals with newton’s laws of motion, the law of gravitation, Maxwell’s kinetic theory, and thermodynamics. Classical physics is mostly related to energy and matter which are considered as different entities. The main branches of classical physics are Acoustics, optics, classical mechanics, and electromagnetic.
Answer:
Statistic.
Explanation:
Which of the following statements are true of thermal energy and kinetic
energy?
Check all that apply.
A. All the molecules or atoms in motion have kinetic energy.
B. Each molecule or atom in motion has kinetic energy.
C. Each molecule or atom in motion has thermal energy.
D. All the molecules or atoms in motion have thermal energy
Answers
Answer:
a
all the molecules or atoms in motion has kinetic energy
How much electricity is used to boil 600 g of water if the kettle has a power of 1500 W? The water boiled for 3 minutes and 9 seconds. Water density is 1000 kg/m3, specific heat of water is 4200 J/(kg· oC).
Answers
Answer:
The electrical energy consumed in boiling the water is 0.0788 kWh
Explanation:
Given;
mass of the water, m = 600 g = 0.6 kg
power rating of the kettle, P = 1500 W = 1.5 kW
specific heat capacity of water, c = 4,200 J/kg⁰C
density of water, = 1000 kg/m³
time taken to boil the water, t = 3 mins + 9 s = (3 x 60s) + 9 s = 180 s + 9 s = 189 s = \(189 \ s \times \frac{1 hr}{3.600 \ s} = 0.0525 \ hr\)
The electrical energy consumed in boiling the water is calculated as;
E = P x t
E = 1.5 kW x 0.0525 hr
E = 0.0788 kWh
Therefore, the electrical energy consumed in boiling the water is 0.0788 kWh
On the moon, the acceleration due to gravity is one-sixth that of earth. That is gmoon = gearth /6 = (9.8 m/s2 )/6 = 1.63 m/s2 . What effect, if any, would this have on the period of a pendulum of length L? How would the period of this pendulum differ from an equivalent one on earth?
Answers
You are sharing a house with a few roommates. One of them plays on the basketball team, and is exactly 200 cm tall. The heights of you and the other roommates are 188 cm, 175 cm, and 160 cm. You want to buy the minimum height mirror that will allow all of you to see your entire selves, when the mirror is mounted in a fixed position on the wall. Assume each person's eyes are at a level 95% of their height. How tall a mirror should you buy
Answers
Answer:
119 cm
Explanation:
Given heights : 200cm , 188 cm , 175 cm, 160 cm
since the eyes are at 95% level
95% of 200 cm = 190 cm
95% of 160 cm = 152 cm
hence the allowable height of mirror = 200 - ( 5 + 76 ) = 119 cm
and The mirror should be hung 75cm from the floor

1.The lunch lady pushes a 100 kg zombie with 300 N of force. How much is the zombie accelerated?
2. Pushing over the file cabinet to keep out the zombies requires 1000 N of force. The cabinet accelerates at 20 m/s 2 . What is the mass of the cabinet?
Answers
Answer:
1. A=3.00m/s 2.m=50kg
Explanation:
1. Use the formula a=f/m
a=300/100
a=3
2.Use the formula m=f/a
m=1000/20
m=50kg
1. Acceleration is calculated to be equal to, a=3.00m/s
2. Mass of the cabinet is, m=50kg
What is acceleration and force?Rate of change of velocity of the object in the same straight line is known as acceleration. Acceleration is any process where the velocity changes. There are only two ways to accelerate that is either to change your speed or direction or change both of them.
Physical influence that is when applied to an object causes it to accelerate in the direction from where it was applied is known as force.
1. Given :
m = 100kg, force= 300N
Using the formula :
a=f/m
a=300/100
a=3 m/s
2. Given,
F= 1000N, a= 20m/s
Using the formula :
m=f/a
m=1000/20
m=50kg
To know more about force, mass and acceleration, refer
https://brainly.com/question/20005124
#SPJ2
A force of 355 N is applied to an object that accelerates at a rate of 7.8 m/sec2 . What is the mass of the object ?
Answers
Answer:
A force of 355 N is applied to an object that accelerates at a rate of 7.8 m/sec2 . What is the mass of the object ?
Explanation:
A 2250 kg cartraveling to the east slows down uniformly from 20 m/s to 5 m/s. How long does it take to decelerate if the braking force is 7500 N to the west?
A. 3 seconds
B. 4.5 seconds
C. 6 seconds
D. 7.5 seconds
Answers
The time taken for the car to decelerate is 4.5 seconds.
option B.
What is the acceleration of the car?
The acceleration of the car is calculated from Newton's second law of motion as follows;
F = ma
a = F / m
a = ( 7500 ) / ( 2250 )
a = 3.33 m/s²
The time taken for the car to slow down is calculated as follows;
v = u + at
at = v - u
t = ( v - u ) / a
where;
v is the final velocity u is the initial velocityt = ( 20 - 5 ) / 3.33
t = 4.5 seconds
Learn more about time of motion here: https://brainly.com/question/2364404
#SPJ1
About how long does it take earth to make a make 1 revolution around the sun a a day be a week see a month d a year
Answers
Comparing the reactants and the products of a chemical reaction, which observation can best be used to argue that the reaction is endothermic?(1 point)
The volume of the reactants is greater than the volume of the products.
The total energy of the reactants is equal to the total energy of the products.
There are fewer chemical bonds in the reactants than there are chemical bonds in the products.
The temperature of the reactants is greater than the temperature of the products.
Answers
Answer:
D) The temperature of the reactants is greater than the temperature of the products.
Explanation:
All the answers:
1. A) The reactants are unlit charcoal, and the products are charcoal that has already burned and released its energy
2. C) sugar + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
3. D) iron + oxygen → rusted iron + energy
4. A) an endothermic reaction, because ice absorbs heat to become liquid water
5. D) The temperature of the reactants is greater than the temperature of the products.
We can argue that a reaction is endothermic when the temperature of the reactants is greater than the temperature of the products.
What is an endothermic reaction?An endothermic reaction is a chemical reaction accompanied by the absorption of heat.
Comparing the reactants and the products of a chemical reaction, which observation can best be used to argue that the reaction is endothermic?
The volume of the reactants is greater than the volume of the products. False. There is no relation between the volume and the endothermicity.The total energy of the reactants is equal to the total energy of the products. False. If the total energy is equal, there is no heat (energy) absorption.There are fewer chemical bonds in the reactants than there are chemical bonds in the products. False. We must consider not only the number of bonds, but also their energies, to establish if a reaction is endothermic.The temperature of the reactants is greater than the temperature of the products. True. If the reaction is endothermic and absorbs heat from the surroundings, the temperature of the reactants will be greater than the temperature of the products.We can argue that a reaction is endothermic when the temperature of the reactants is greater than the temperature of the products.
Learn more about endothermic reactions here: https://brainly.com/question/1995950
hen approaching a curve, it is best to: A. Search for possible collision traps and escape paths B. Stay close to the centerline if there is oncoming traffic C. Squeeze the clutch lever to slow down D. Shift to a higher gear
Answers
Squeezing the clutch lever to slow down is best to be done when approaching a curve and is denoted as option C.
What is Clutch?This is a mechanical device which used in the engagement and disengagement of transmission system in a vehicle.
Slowing down will give the driver more time to maneuver the curves so as to prevent accident. This is why it is imperative to squeeze the clutch in such road condition.
Read more about Clutch here https://brainly.com/question/14318041
#SPJ1
A student is constructing a stream table to investigate how erosion by a meandering stream is affected by the slope of the land. The student uses the equipment shown.
What should the student vary for the different trials of the experiment?
Responses
A The number of blocks stacked beneath the tray The number of blocks stacked beneath the tray
B The sediment size of sand used in the stream table The sediment size of sand used in the stream table
C The volume of water that enters the stream table and collects in the bucket The volume of water that enters the stream table and collects in the bucket
D The size of the hole in the bottom of the container of water
Answers
A student is constructing a stream table to investigate how erosion by a meandering stream is affected by the slope of the land should vary, the number of blocks stacked beneath the tray. Option A
What is the purpose of the experiment?The purpose of the experiment is to investigate how the slope of the land affects erosion by a meandering stream. By varying the number of blocks stacked beneath the tray, the student can change the slope of the land and observe how this affects the behavior of the stream and the resulting erosion.
Varying the sediment size, the volume of water, or the size of the hole in the bottom of the container would not directly address the question of how slope affects erosion by a meandering stream.
Learn more about erosion from
https://brainly.com/question/26960499
#SPJ1
A 1232 kg car moving north at 25.6 m/s collides with a 2028 kg car moving north at 17.5 m/s . They stick together. In what direction and at what speed do they move after the collision?
Answers
Answer:
I. Angle = 41.7° Northeast.
II. Vr = 7.08m/s
Explanation:
Let the two cars be denoted by A and B
Given the following data;
Mass of car A = 1232 Kg
Velocity of car A = 25.6 m/s
Mass of car B = 2028 Kg
Velocity of car B = 17.5m/s
First of all, we would solve for momentum;
Momentum = mass × velocity
Momentum, M1 = 1232 × 25.6
Momentum, M1 = 31539.2 Kgm/s
Momentum, M2 = 2028 × 17.5
Momentum, M2 = 35490 Kgm/s
Now, let's find the resultant momentum using the Pythagoras theorem;
R² = M1² + M2²
R² = 31539.2² + 35490²
R² = 994721136.6 + 1259540100
R² = 2254261237
Taking the square root of both sides, we have
Resultant momentum, R = 47479.06 Kgm/s
To find the direction;
Angle = tan¯¹(M1/M2)
Angle = tan¯¹(31539.2/35490)
Angle = tan¯¹(0.89)
Angle = 41.7° Northeast.
To find the speed;
R = (M1 + M2)Vr
47479.06 = (31539.2 + 35490)Vr
47479.06 = 67029.2Vr
Vr = 47479.06/67029.2
Vr = 7.08m/s
a wave with wavelength of 3 m long oscillates 1.5 times each second. what's the speed of the wave? (in m/s)
Answers
A wave of 3 m in length oscillates 1.5 times every second. The wave moves at a pace of 4.5 m/s.
What use does wavelength serve?The length of such a wave is expressed by its wavelength. The wavelength is the distance between one wave's crest and the following wave's crest. The wavelength can also be determined by measuring from "groove" (bottom) of one pulse to the "trough" of the following wave.
Briefing:Given:
Number of oscillation per seconds = 1.5
Wavelength; λ = 3m
Speed of the wave; ν = ?
The number of instances of a repeating phenomena per unit of time is what we meant by frequency.
Given that the pulse oscillates 1.5 times per second, its frequency is 1.5 Hz.
Speed = ν*f
ν = 3m * 1.5Hz
ν = 3m * 1.5s⁻¹
ν = 4.5ms⁻¹
ν =4.5 m/s
To know more about Wavelength visit:
https://brainly.com/question/13533093
#SPJ4
One design feature to ensure that the thermometer measured the desired range of temperature
Answers
Answer:
tube (sufficiently) long / not too short.
the darcy-weisbach formula states that the rate of energy loss in a pipe is
Answers
The Darcy-Weisbach formula is used to calculate the rate of energy loss in a pipe due to frictional losses. This formula is commonly used in the field of fluid mechanics and is based on the principle that the pressure drop across a pipe due to frictional losses is proportional to the square of the flow rate.
The formula can be expressed as follows:
ΔP = (f * L * ρ * V^2) / (2 * D)
Where ΔP is the pressure drop across the pipe, f is the Darcy friction factor, L is the length of the pipe, ρ is the density of the fluid, V is the average velocity of the fluid, and D is the diameter of the pipe.
The Darcy friction factor is a dimensionless quantity that depends on the Reynolds number, which is a measure of the fluid flow regime. For laminar flow, the friction factor is constant and equal to 64/Re. For turbulent flow, the friction factor is more complicated and depends on the roughness of the pipe wall, as well as the Reynolds number.
Overall, the Darcy-Weisbach formula is an important tool for engineers and scientists who need to design and analyze piping systems. By using this formula, they can estimate the pressure drop across a pipe and ensure that the system is operating efficiently.
Learn more about energy here
https://brainly.com/question/30337295
#SPJ11
A Copper rod whese lenght at 30°C is 10cm is heated find its new length. Take linear expansivity of copper as 0000017k
Answers
If a copper rod whose coefficient of linear expansion is 0.000017 is heated at 30⁰C and its length is 10cm, Then the new length of the copper rod is 10.0051cm.
What is linear expansion?If a body is subjected to expansion by virtue of temperature then its length gets increased by some extent that new length is given by,
Ln=L₀(1+\(\alpha\)Δt)
where Ln = New length after expansion.
L₀= Original length of the body.
\(\alpha\)= Coefficient of linear expansion.
Δt= Change in temperature.
Here in the question, given
L₀=10cm
t= 30°C
\(\alpha\)= 0.000017
new length
Ln= 10(1+0.000017×30)
Ln=10.0051cm
Hence the new length of the copper rod after the expansion is 10.0051cm.
To learn more about linear expansion click:
https://brainly.com/question/14780533
#SPJ9
If there is a 0.10 kg sample of the unknown metal alloy originally at 150℃, that is placed in 1.0 kg water at 20℃, and the final temperature rises to 23.5 ℃, what is the specific heat capacity?
Specific Heat of Water: 4180 J/kg ℃
Answers
Answer:
We now introduce two concepts useful in describing heat flow and temperature change. The heat capacity ( C ) of a body of matter is the quantity of heat ( q ) it absorbs or releases when it experiences a temperature change ( ΔT ) of 1 degree Celsius (or equivalently, 1 kelvin)
C=qΔT(12.3.1)
Heat capacity is determined by both the type and amount of substance that absorbs or releases heat. It is therefore an extensive property—its value is proportional to the amount of the substance.
For example, consider the heat capacities of two cast iron frying pans. The heat capacity of the large pan is five times greater than that of the small pan because, although both are made of the same material, the mass of the large pan is five times greater than the mass of the small pan. More mass means more atoms are present in the larger pan, so it takes more energy to make all of those atoms vibrate faster. The heat capacity of the small cast iron frying pan is found by observing that it takes 18,140 J of energy to raise the temperature of the pan by 50.0 °C
Explanation:
A fly undergoes a displacement of -5. 80 m while accelerating at -1. 33 m/s for 4. 22 s what was the initial velocity of the fly.
Answers
The fly has an average velocity of
v[ave] = ∆x/∆t = (-5.80 m) / (4.22 s) ≈ -1.37 m/s
If its acceleration is constant, then its average velocity is also equal to the average of its initial and final velocities,
v[ave] = (v[initial] + v[final]) / 2
which tells us that
v[initial] ≈ -1.37 m/s - 1/2 v[final]
The fly's final velocity after some time t is given by
v[final] = v[initial] + (-1.33 m/s²) t
so that after 4.22 s, we have
v[final] ≈ v[initial] - 5.61 m/s
Substitute this into the equation for v[initial] :
v[initial] ≈ -1.37 m/s - 1/2 (v[initial] - 5.61 m/s)
Solve for v[initial] :
3/2 v[initial] ≈ -1.37 m/s + 1/2 (5.61 m/s)
⇒ v[initial] ≈ 0.955 m/s
if buoyant force push things upwards, why don't hot air balloons and planes get pushed into outer space
Answers
Answer:
I think that's because the force of gravity is greater than the buoyant force, and for the hot air balloons, they can increase/decrease the temperature of the air in the balloon in order for it to rise/fall for more control. For planes, they use aerodynamics as well as the help of a couple of engines to thrust the plane forward. I hope this helps.