Consider a normal shock wave moving with a velocity of 680 m/s into still air at standard atmospheric conditions (p
1 =1 atm and T
1 =288 K). a. Using the equations of Sec. 7.2, calculate T 2 ,p 2 , and u p behind the shock wave. b. The normal shock table, Table A.2, can be used to solve moving shock wave problems simply by noting that the tables pertain to flow velocities (hence, Mach numbers) relative to the wave. Use Table A.2 to obtain T 2 ,p 2 , and u p for this problem
Answers
To calculate T2, p2, and up behind the shock wave, we can use the equations and the normal shock table provided. substitute into the equations to calculate T2, p2, and up.
To obtain the values for T2, p2, and up for this problem using Table A.2, you would need to refer to the table yourself. Table A.2 typically provides the properties behind a normal shock wave for different Mach numbers, including the pressure ratio (p2/p1), temperature ratio (T2/T1), and velocity ratio (up/a).You can look up the specific Mach number M1 (determined using the given velocity ahead of the shock and the speed of sound) in the table to find the corresponding values for T2/T1, p2/p1, and up/a.
To know more about Mach visit :
https://brainly.com/question/29538118
#SPJ11
Related Questions
2. A metal cube with an edge length x is expanding uniformly as a consequence
of being heated. Find the:
(a) Change in volume of the cube as x increases from 2.00 to 2.01 centimeters.
(b) Average rate of change of volume of the cube with respect to an edge length as x
increases from 2.00 to 2.01 centimeters.
(c) Instantaneous rate of change of volume of the cube with respect to an edge length
at the instant when x = 2 centimeters.
3. Use the definition of the derivative to find the equation of the line that passes through
the point (1, 5) and is parallel to the tangent line to f (x) = 1
x at x = 3.
Answers
A. the change in volume of the cube is approximately 0.120601 cm^3. B. the average rate of change of volume of the cube with respect to an edge length is approximately 12.0601 cm^3/cm. C. the equation of the line that passes through the point (1, 5) and is parallel to the tangent line to f(x) = 1/x at x = 3 is y = (-1/9)x + 14/9.
(a) To find the change in volume of the cube as x increases from 2.00 to 2.01 centimeters, we need to calculate the difference in volume between these two values.
The volume of a cube is given by V = x^3, where x is the edge length.
For x = 2.00 cm, the volume V1 = (2.00 cm)^3 = 8.00 cm^3.
For x = 2.01 cm, the volume V2 = (2.01 cm)^3 = 8.120601 cm^3.
The change in volume is ΔV = V2 - V1 = 8.120601 cm^3 - 8.00 cm^3 ≈ 0.120601 cm^3.
Therefore, the change in volume of the cube is approximately 0.120601 cm^3.
(b) The average rate of change of volume of the cube with respect to an edge length as x increases from 2.00 to 2.01 centimeters can be calculated by dividing the change in volume by the change in edge length.
ΔV = 0.120601 cm^3 (from part a)
Δx = 2.01 cm - 2.00 cm = 0.01 cm
The average rate of change of volume is ΔV/Δx = 0.120601 cm^3 / 0.01 cm ≈ 12.0601 cm^3/cm.
Therefore, the average rate of change of volume of the cube with respect to an edge length is approximately 12.0601 cm^3/cm.
(c) The instantaneous rate of change of volume of the cube with respect to an edge length at the instant when x = 2 centimeters can be found by taking the derivative of the volume function V = x^3 with respect to x and evaluating it at x = 2.
dV/dx = 3x^2
At x = 2 cm, the instantaneous rate of change of volume is dV/dx evaluated at x = 2:
dV/dx = 3(2 cm)^2 = 12 cm^2.
Therefore, the instantaneous rate of change of volume of the cube with respect to an edge length at x = 2 centimeters is 12 cm^2.
To find the equation of the line that passes through the point (1, 5) and is parallel to the tangent line to f(x) = 1/x at x = 3, we need to determine the slope of the tangent line.
The derivative of f(x) = 1/x is given by f'(x) = -1/x^2.
At x = 3, the slope of the tangent line is f'(3) = -1/(3^2) = -1/9.
Since the line we want to find is parallel to the tangent line, it will have the same slope. So the slope of the line is -1/9.
Using the point-slope form of a linear equation, we can write the equation of the line as:
y - y1 = m(x - x1),
where (x1, y1) is the given point (1, 5) and m is the slope.
Substituting the values, we have:
y - 5 = (-1/9)(x - 1).
Expanding and rearranging the equation, we get:
y = (-1/9)x + 14/9.
Therefore, the equation of the line that passes through the point (1, 5) and is parallel to the tangent line to f(x) = 1/x at x = 3 is y = (-1/9)x + 14/9.
To learn more about volume
https://brainly.com/question/14197390
#SPJ11
A rope is run over a massless pulley. The left-hand side of the rope is attached to a 3 kg mass, which rests on the ground. The right side of the rope is attached to a 5 kg mass, which is some unknown height above the ground. The system is released from rest. What is the magnitude of the instantaneous acceleration of the system when it is released from rest?
Answers
Given:
Mass attached to the left-hand side = 3 kg
Mass attached to the right-hand side = 5 kg
Let's find the magnitude of the instantaneous acceleration of the system when it is released from rest.
Apply the formula:
\(\begin{gathered} a=\frac{net\text{ pulling force}}{total\text{ mass}} \\ \\ a=\frac{(m_2\times g)-(m_1\times g)}{m_1+m_2} \end{gathered}\)Where:
m1 = 3 kg
m2 = 5 kg
g = 9.8 m/s^2
Thus, we have:
\(\begin{gathered} a=\frac{(5\times9.8)-(3\times9.8)}{3+5} \\ \\ a=\frac{49-29.4}{8} \\ \\ a=\frac{19.6}{8} \\ \\ a=2.45m/s^2 \end{gathered}\)The magnitude of the instantaneous acceleration is 2.45 m/s².
ANSWER:
2.45 m/s²
A thin lens with a focal length of 5.90 cm is used as a simple magnifier. What angular magnification is obtainable with the lens if the object is at the focal point?
Answers
The angular magnification (M) obtained with a thin lens used as a simple magnifier when the object is at the focal point is -1.
The angular magnification is given by the formula:
M = -f / (f - d)
Where:
M is the angular magnification,
f is the focal length of the lens,
d is the distance between the object and the lens.
In this case, since the object is at the focal point, the distance between the object and the lens (d) is equal to the focal length of the lens (f). Substituting the values, we have:
M = -f / (f - f)
M = -f / 0
M = -1
Therefore, when the object is at the focal point, the angular magnification obtained with the lens is -1.
To know more about angular magnification, click here:
https://brainly.com/question/32673431
#SPJ11
What is promising evidence of a habitat that might support life
on the planet Mars?
Detailed Answer please, will give thumb up rating definitely
Answers
A promising evidence of a habitat that might support life on the planet Mars is water.
There is evidence supporting the existence of liquid water on Mars from numerous sources. The finding of repeated black streaks on Martian slopes and the presence of hydrated minerals suggest the potential of seasonal or location-specific briny water flows. A necessary component of life as known is liquid water.
Additionally, Mars possesses underground ecosystems that could provide defence against radiation and severe surface conditions. Researchers have found evidence of ancient underground hydrothermal systems as well as beneath ice. These settings might offer consistent conditions for the development of microbial life. Methane gas has been found in the Martian atmosphere, along with variations over time, and this has led to questions regarding its origin. Both geological and biological processes can result in the production of methane.
Read more about Mars on:
https://brainly.com/question/28224926
#SPJ4
A resistor dissipates 1.80 W when the rms voltage of the emf is 9.50 V . Part A At what rms voltage will the resistor dissipate 11.5 W
Answers
The rms voltage required for a resistor to dissipate 11.5 W is 21.8 V.
The power (P) dissipated by a resistor is given by P = V²/R, where V is the voltage across the resistor and R is the resistance. We are given that the resistor dissipates 1.80 W when the rms voltage is 9.50 V, so we can write:
1.80 watt(W) = (9.50 V)²/R
Solving for R, we get:
R = (9.50 V)²/1.80 W = 49.97 Ω
To find the rms voltage required for the resistor to dissipate 11.5 W, we can use the same equation:
11.5 W = V²/49.97 Ω
Solving for V, we get:
V = √(11.5 W * 49.97 Ω) = 21.8 V
learn more about rms voltage here:
https://brainly.com/question/13507291
#SPJ11
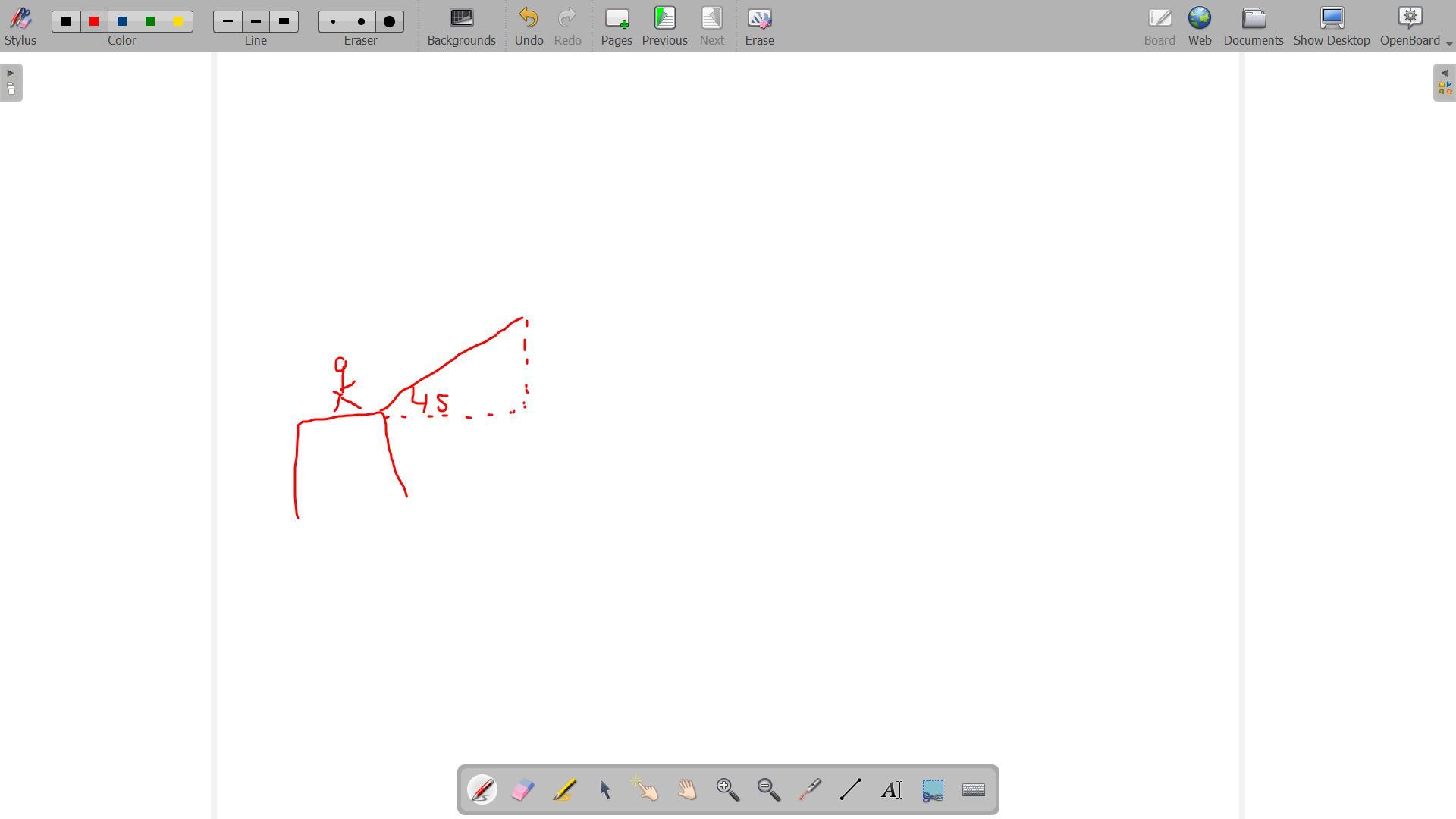
A DIVER JUMPS UP OFF A PIER AT AN ANGLE OF 45 DEGREES WITH AN INITIAL VELOCITY OF 4.5 M/S. HOW LONG DOES IT TAKE TO HIT THE WATER? AND HOW FAR FROM THE PIER WILL THE DIVER HIT THE WATER? (ASSUME THE LEVEL OF WATER IS THE SAME AS THE PIER)
Answers
Answer:
0.65 seconds
2.07m
Explanation:
Here we need to look at the vertical and the horizontal components of the initial velocity.
In terms of his hitting the water.
Define the upwards direction as positive
We know his initial upwards velocity (u) is 4.5sin(45)
His displacement (s) when he hits the water is zero
Acceleration due to gravity is -9.8
We want to find t
So using s=ut+1/2a\(t^{2}\)
0=4.5sin(45)t+1/2(-9.8)\(t^{2}\)
Take out a common t
0=t(4.5sin45-4.9t)
t=0 or t= 0.65
The first answer is not valid so the answer is 0.65.
Now we can look at the horizontal component
It takes him 0.65 seconds to hit the water, he travels at a constant horizontal velocity of 4.5cos45
Therefore using s=vt
s=4.5cos45 x 0.65= 2.07m away
A 5nC charge is located at (0,7)cm and another 2nC charge is located at (−3,0)cm. What would be the magnitude of the net electric field at the origin (0,0)cm ?
Answers
The magnitude of the net electric field at the origin (0,0) cm is approximately \(83.19 × 10^6 N/C\).
To calculate the magnitude of the net electric field at the origin, we need to calculate the electric fields generated by each charge and then sum them up.
The electric field at a point due to a point charge is given by Coulomb's Law:
E = k * (q / \(r^2\))
where E is the electric field, k is the electrostatic constant (\(9 × 10^9 Nm^2/C^2\)), q is the charge, and r is the distance from the charge to the point.
Let's calculate the electric fields generated by each charge at the origin:
For the 5nC charge:
q1 = 5nC
r1 = 7 cm = 0.07 m
E1 = k * (q1 / \(r1^2\))
For the 2nC charge:
q2 = 2nC
r2 = 3 cm = 0.03 m
E2 = k * (q2 / \(r2^2\))
Now, we can calculate the net electric field by summing up the electric fields:
E_net = E1 + E2
Substituting the values and performing the calculations:
\(E1 = (9 × 10^9 Nm^2/C^2) * (5 × 10^(-9) C) / (0.07 m)^2\)
E1 ≈ 9188571.43 N/C
\(E2 = (9 × 10^9 Nm^2/C^2) * (2 × 10^(-9) C) / (0.03 m)^2\)
E2 ≈ 74000000 N/C
E_net = E1 + E2
E_net ≈ 83188571.43 N/C
To know more about electric field refer to-
https://brainly.com/question/11482745
#SPJ11
active oxygen and free radicals are believed to be exacerbating factors in causing cell injury and aging in living tissue (see citation below). researchers are therefore interested in understanding the protective role of natural antioxidants. in the study of one such antioxidant (hsian-tsao leaf gum), the antioxidation activity of the substance has been found to depend on concentration in the following way: in this equation, the dependent variable is a quantitative measure of antioxidant activity at concentration . the constant represents a limiting or equilibrium value of this activity, and a positive rate constant. let and reformulate the given initial value problem in terms of this new dependent variable, .
Answers
In this particular question, the task is to reformulate the given initial value problem in terms of a new dependent variable, using the constants and variables provided. The initial value problem is related to the study of an antioxidant, Hsian-tsao leaf gum, and its antioxidation activity, which depends on concentration in a certain way.
The dependent variable is a quantitative measure of antioxidant activity at concentration, while the constant represents a limiting or equilibrium value of this activity, and a positive rate constant. The goal is to use this information to reformulate the problem in terms of a new dependent variable.
The specific details of this reformulation will depend on the constants and variables provided, but it is important to focus on the key concepts and to provide a clear and concise answer that directly addresses the question at hand.
Learn more about antioxidation:
https://brainly.com/question/13151490
#SPJ11
You have a working electrical parallel circuit with three light bulbs, then 1 bulb burns
out.
Describe how electric current flows through the parallel circuit after 1 of the 3 bulbs
burns out?
Answers
Answer:
but the answer should be no as if 3 bulbs are connected together if one burns out the whole circuit will stop .hope you understood
please mark me as brainlist
Why are streams and rivers important for ecosystems?
Answers
Hope this helps please mark as brainliest!
A body moves at distance of 10meter a long horizontal by force of 9Niwton then what is work is done
Answers
The work done by the force of 9 Newtons over a distance of 10 meters is 90 Joules.
To calculate the work done by the force, we need to use the formula:
Work = Force x Distance x cos(theta)
where theta is the angle between the force vector and the displacement vector.
In this case, the body is moving horizontally, so the angle between the force vector and the displacement vector is 0 degrees. Therefore, cos(theta) = cos(0) = 1.
We are given that the force acting on the body is 9 Newtons, and the distance moved by the body is 10 meters.
Substituting these values into the formula, we get:
Work = 9 N x 10 m x cos(0)
Work = 90 Joules
To know more about displacement vectors, here
brainly.com/question/30466999
#SPJ1
An 18.0 N force pulls a cart against a 15.0 N frictional force. The speed
of the cart increases 1.0 m/s every 5.0 s. What is the cart's mass?
Someone please help me on this I only have a few minutes
Answers
Answer:
m = 15 kg
Explanation:
Applied force to the cart, F' = 18 N
Force of friction, f = 15 N
Net force acting on the cart,
F = F' - f
F = 18 - 15
F = 3 N
The change in velocity of the cart is 1 m/s every 5 s.
We need to find the mass of the cart.
The formula of net force is given by :
F = ma, where a is the acceleration of the cart
\(F=\dfrac{m\Delta v}{t}\\\\m=\dfrac{Ft}{\Delta v}\\\\m=\dfrac{3\times 5}{1}\\\\m=15\ kg\)
So, the cart's mass is 15 kg.
What is the average velocity of a hiking group that traveled 20 miles north for five hours
Answers
Explaining:
20 divided by 5 = 4
How can you determine the class of lever of simple machine?
Answers
Answer:
A first-class lever has the fulcrum between the load and the effort. A second-class lever has the load between the effort and the fulcrum. A third-class lever has the effort between the load and the fulcrum. A see-saw is an example of a first-class lever.
Explanation:
Which plant has the highest density? A. NeptuneB. JupiterC. EarthD. Mercury
Answers
To find:
Which of the planets has the highest density.
Explanation:
Neptune is known as the ice planet. It has a higher density than gas giants but a lower density than rocky planets. The density of the Neptune is 1638 kg/m³.
Jupiter is known as a gas giant. Gas giants has the lowest densities. The density of Jupiter is 1326 kg/m³.
The Earth and the Mercury are rocky planets. The densities of rocky planets are more than that of the gas giants and ice giants. The density of the Earth is 5514 kg/m³ and the density of the Mercury is 5429 kg/m³.
Final answer:
On comparing the densities of the planets, the Earth has the highest density.
Thus the correct answer is option C.
which of these galaxies would you most likely find at the center of a large cluster of galaxies?
Answers
Answer:
a large elliptical galaxy
Explanation:
I need the explanation too, if possible.

Answers
When we arrange the objects in increasing strength of gravitational attraction, the following results:
Electron-butterflyElectron-dogButterfly-rockRock-dogHow do I arrange the objects in increasing order?To arrange the objects in increasing strength of gravitational attraction, we shall determine the gravitational force between each pair oif the objects. Details below:
For electron-dog:
Mass of electron (M₁) = 9.11×10⁻³¹ KgMass of dog (M₂) = 20 KgDistance apart (r) = 1 mGravitational constant (G) = 6.67×10¯¹¹ Nm²/Kg²Gravitational force (F) =?F = GM₁M₂ / r²
F = (6.67×10¯¹¹ × 9.11×10⁻³¹ × 20) / 1²
F = 1.22×10⁻³⁹ N
For butterfly-rock:
Mass of butterfly (M₁) = 5.0×10⁻⁴ KgMass of rock (M₂) = 8 KgDistance apart (r) = 1 mGravitational constant (G) = 6.67×10¯¹¹ Nm²/Kg²Gravitational force (F) =?F = GM₁M₂ / r²
F = (6.67×10¯¹¹ × 5.0×10⁻⁴ × 8) / 1²
F = 2.67×10⁻¹³ N
For electron-butterfly:
Mass of electron (M₁) = 9.11×10⁻³¹ KgMass of butterfly (M₂) = 5.0×10⁻⁴ KgDistance apart (r) = 1 mGravitational constant (G) = 6.67×10¯¹¹ Nm²/Kg²Gravitational force (F) =?F = GM₁M₂ / r²
F = (6.67×10¯¹¹ × 9.11×10⁻³¹ × 5.0×10⁻⁴) / 1²
F = 3.04×10⁻⁴⁴ N
For rock-dog:
Mass of rock (M₁) = 8 KgMass of dog (M₂) = 20 KgDistance apart (r) = 1 mGravitational constant (G) = 6.67×10¯¹¹ Nm²/Kg²Gravitational force (F) =?F = GM₁M₂ / r²
F = (6.67×10¯¹¹ × 8 × 20) / 1²
F = 1.07×10⁻⁸ N
From the above calculations, we have the gravitational attraction as:
Electron-dog = 1.22×10⁻³⁹ NButterfly-rock = 2.67×10⁻¹³ NElectron-butterfly = 3.04×10⁻⁴⁴ NRock-dog = 1.07×10⁻⁸ NThus, arranging in increasing order, we have:
Electron-butterflyElectron-dogButterfly-rockRock-dogLearn more about gravitational force:
https://brainly.com/question/24299568
#SPJ1
What must change in order for electromagnetic induction to occur in a wire coil?.
Answers
Answer:
The magnetic field through the coil must change.
Explanation:
Convert gr 1 (grain) to mg
Answers
To convert gr 1 (grain) to mg, you would multiply the number of grains by 64.8. Therefore, 1 grain is equal to 64.8 mg.
To convert a measurement from one unit to another, we need to use a conversion factor that relates the two units. In this case, we want to convert from grains (gr) to milligrams (mg).
The conversion factor between grains and milligrams is 1 gr = 64.8 mg. This means that for every 1 grain, there are 64.8 milligrams. We can use this conversion factor to convert any given number of grains to milligrams.
For example, if we have 5 grains and want to know how many milligrams that is, we would multiply 5 grains by 64.8 mg/gr. This gives us:
5 gr * 64.8 mg/gr = 324 mg
So, 5 grains is equal to 324 milligrams.
Similarly, if we want to convert 1 grain to milligrams, we just need to multiply 1 grain by the conversion factor of 64.8 mg/gr. This gives us:
1 gr * 64.8 mg/gr = 64.8 mg
So, 1 grain is equal to 64.8 milligrams.
Therefore, to convert any number of grains to milligrams, we simply multiply the number of grains by 64.8.
Visit here to learn more about conversion factor brainly.com/question/30166433
#SPJ11
What is the name of the part of the wave that is labeled -
answer: amplitude
the ones who have to watch the video
Answers
Answer:
amplitude
Explanation:
sound travel and it amplifies
3.
If you are part of a center or network, you can use program-level data to
A. change the way you record and maintain information.
B. identify professional development needs.
C. improve the management systems to support child learning.
D. change the way you speak with families
Answers
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Answer: A
Explanation:
Evaporation requires the particles to _____ energy.
Answer:
create
release
absorb
destroy
Answers
Answer:
Release
Explanation:
The water is heated until
you are riding on a bicycle at constant speed. relative to your viewpoint, use the right-hand-rule to find the direction of the angular momentum vector of the front wheel. a. to the left. b. to the right. c. downward. d. upward.
Answers
The direction of the angular momentum vector will be upward (d), as that
is the direction in which your fingers will curl using the right-hand rule,
since the front wheel of a bicycle rotates clockwise when viewed from
the rider's perspective. Therefore option d) upward is correct.
To use the right-hand-rule to find the direction of the angular
momentum vector of the front wheel of a bicycle when
riding at a constant speed, we need to follow these steps:
Extend your right hand with your thumb pointing in the direction of the
velocity of the front wheel (forward).
Curl your fingers towards the direction of rotation of the wheel
(clockwise).
The direction in which your fingers curl gives the direction of the angular
momentum vector.
Since the front wheel of a bicycle rotates clockwise when viewed from
the rider's viewpoint, the direction of the angular momentum vector will
be upward (d), as that is the direction in which your fingers will curl using
the right-hand- rule.
for such more question on direction
https://brainly.com/question/26711803
#SPJ11
Which statement is true according to Newton's second law of motion?
Answers
Answer:
When a net force acts on a body it produces acceleration in body the magnitude of tries acceleration is directly proportional to the net force acting and inversely proportional to the mass of the body
Mathematical form
F=ma
Explanation:
I hope it will help you
Jose has two bar magnets. He pushes the ends of the two magnets together and then lets it go. The magnets move quickly apart. Which of the following statements best explains why this happens
A.The north poles of the two magnets are facing each other.
B.One magnet is a north pole & one magnet is a south pole.
C.The ends of the magnets repel each other but the centers attract. D.One magnet is storing energy & one magnet is releasing energy.
Answers
Answer:
A. like poles repel or push apart
A box has a momentum of 38.0 kg*m/s to the right. A 88.3 N force pushes it to the right for 0.338 s. What is the final momentum of the box? (unit = kg*m/s)
Answers
Answer:
63.8454kgm/s
Explanation:
According to Newton's second law;
Force = mass ×acceleration
Fore = m(v-u)/t
Force = mv-mu/t
MV is the final momentum
mu is the initial momentum = 38kgm/s
Force = 88.3N
Time = 0.338s
Substitute and get mv
88.3 = mv-38/0.338
88.3×0.338 = mv-38
29.8454 = mv-38
MV = 29.8454+34
mv = 63.8454kgm/s
Hence the final momentum is 63.8454kgm/s
Answer:
67.8
Explanation:
im an acellus student, and this is the answer that i got when doing the problem.
im talking about this qeastion

Answers
Answer:
a. Winter.
Explanation:
Answer:
Winter
Explanation:
Find the force that is necessary! Multiple choice. 8 points. Will give brainliest.

Answers
Answer:
F/6.
Explanation:
Let 'M' represent the mass of the block.
Let 'F' represent the force on earth.
Let 'a' represent the acceleration on earth.
Let 'Fm' represent the force on the moon.
Let 'am' represent the acceleration on the moon.
Recall:
Force (F) = mass (M) x acceleration (a)
F = M•a
Making M the subject
M = F/a
But,
Acceleration on the moon (am) = 1/6 acceleration (a) of earth.
am = 1/6a
Fm = M•am
M = Fm/am
M = Fm/(1/6a)
Since the mass of an object is constant,
Therefore,
Mass on earth = mass on moon
Mass on earth (M) = F/a
Mass on moon (M = Fm/(1/6a)
F/a = Fm/(1/6a)
Cross multiply
Fm × a = F × 1/6a
Divide both side by a
Fm = (F × 1/6a) /a
Fm = F/6
Therefore, the force necessary to give the moon bound block the same acceleration is F/6.
An 800 kg car exerts 4000N of applied force on a level road while
being opposed by 700 N of friction. Determine the acceleration of the car.

Answers
Answer:
a = 4.125 [m/s^2]
Explanation:
In order to calculate the value of acceleration, we must use Newton's second law, which tells us that the sum of forces must be equal to the product of mass by acceleration.
ΣF = m*a
where:
ΣF = sum of forces [N]
m = mass [kg]
a = acceleration [m/s^2]
Performing a summation of forces on the x-axis, we have:
4000 - 700 = m*a
4000 - 700 = 800*a
a = 4.125 [m/s^2]
A sphere of mass m1 is attached to an ideal spring, then pulled downward from its equilibrium position and released from rest. A sphere of mass m2 is hung from a massless string of length L, pulled to the right from its equilibrium position, and released from rest. If both spheres have the same period of oscillation, then what is the spring constant of the spring attached to m1
Answers
Answer:
k = \(\frac{g \ m_1}{L}\)
Explanation:
In this exercise the two cases presented are a simple harmonic motion, with angular velocity
spring - mass w² = k / m₁
simple pendulum (string- mass m₂) w² = g / L
angular velocity and period are related
w = 2π/ T
since they indicate that the two periods are equal, the angular velocities are also equal, therefore we can equal the two equations
\(\frac{k}{m1} = \frac{g}{L}\)
k = \(\frac{g \ m_1}{L}\)