after a sci a patient may experience all of the following except: a. spasticity b. resting tremor c. autonomic dysreflexia d. orthostatic hypotension
Answers
The right response is resting tremor (option b). A patient may have spasticity, autonomic dysreflexia, and orthostatic hypotension following a spinal cord injury (SCI). SCI is not often linked to resting tremor.
SCI can interfere with the body's ability to communicate with the brain, leading to a variety of physical symptoms. Spasticity, which manifests as stiffness, muscle spasms, and increased muscle tone, is a frequent consequence. Patients with SCI at or above the T6 level may develop autonomic dysreflexia, a potentially fatal illness that is characterised by an abrupt rise in blood pressure. When someone stands up, their blood pressure drops, causing lightheadedness and dizziness. This condition is known as orthostatic hypotension.
While essential tremor, Parkinson's disease, and other neurological illnesses are frequently linked to resting tremor, SCI is not typically one of them.
learn more about autonomic dysreflexia here:
https://brainly.com/question/30331093
#SPJ11
The right response is resting tremor (option b). A patient may have spasticity, autonomic dysreflexia, and orthostatic hypotension following a spinal cord injury (SCI). SCI is not often linked to resting tremor.
SCI can interfere with the body's ability to communicate with the brain, leading to a variety of physical symptoms. Spasticity, which manifests as stiffness, muscle spasms, and increased muscle tone, is a frequent consequence. Patients with SCI at or above the T6 level may develop autonomic dysreflexia, a potentially fatal illness that is characterised by an abrupt rise in blood pressure. When someone stands up, their blood pressure drops, causing lightheadedness and dizziness. This condition is known as orthostatic hypotension.
While essential tremor, Parkinson's disease, and other neurological illnesses are frequently linked to resting tremor, SCI is not typically one of them.
learn more about autonomic dysreflexia here:
brainly.com/question/30331093
#SPJ4
Related Questions
(a) An insulating sphere with radiusa has a uniform charge density rho. The sphere isnot centered at the origin but at. Show that the electric field inside thesphere is given by.
(b) An insulating sphere of radius R has a spherical holeof radius a located within its volume and centered adistance b from the center of the sphere. The solid partof the sphere has a uniform volume charge density rho. Findthe magnitude and direction of the electric fieldinside the hole, and show thatis uniform over the entire hole.[Hint: Use the principle of superposition and the resultof part (a).]
Answers
a. The electric field is E = (kρa^3/r^2) r
b. The magnitude of the electric field inside the hole of the sphere is (kρa^3/b^2 - kρ(4/3)πa^3/(b^2 - a^2)) j
a)
The electric field inside an insulating sphere with radius a and uniform charge density rho is,
E = (kq/r^2) r
Where
q = volume charge density * volume of the sphere
= rho*(4/3)πa^3
q = (4/3)πa^3ρ
The electric field is:,
E = (kq/r^2) r
= (kρa^3/r^2) r
b)
E = E_solid_sphere - E_hollow_sphere
The electric field due to the charge density inside the hole of the sphere is zero because the sphere is insulating. Therefore, the electric field inside the hole due to the charge density is zero and is uniform over the entire hole.The electric field due to the solid sphere can be found using the result from part (a),E_solid_sphere = (kρa^3/b^2) j
The electric field inside the hole due to the solid sphere is,E_hollow_sphere = -(kρ(4/3)πa^3/(b^2 - a^2)) j
Therefore, the magnitude and direction of the electric field inside the hole of the sphere areE = E_solid_sphere - E_hollow_sphere
= (kρa^3/b^2 - kρ(4/3)πa^3/(b^2 - a^2)) j
Learn more about the electric field:
brainly.com/question/28453368
#SPJ11
the escape velocity of the earth is about 11 km/s. the sun has an escape velocity of 600 km/s. a neutron star can have an escape velocity of 150,000 km/s. what is the escape velocity at the event horizon of a black hole? group of answer choices 150,000 km/s 600,000 km/s (2x the speed of light) 300,000 km/s (the speed of light) 200,000 km/s 450,000 km/s (1.5x the speed of light)
Answers
The escape velocity at the event horizon of a black hole is 300,000 km/s, which is the speed of light.
The escape velocity is the minimum velocity required for an object to escape the gravitational pull of a celestial body. It is directly proportional to the mass of the celestial body and inversely proportional to the distance from the center of the body. The escape velocity at the event horizon of a black hole is calculated using the formula v = √(2GM/r), where G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the black hole, and r is the radius of the event horizon.
The event horizon is the point of no return, beyond which nothing, not even light, can escape. Given the mass of a black hole, the event horizon can be calculated, and then the escape velocity can be determined. For a black hole, the escape velocity at the event horizon is approximately 300,000 km/s, which is the speed of light.
To know more about the escape velocity visit:
https://brainly.com/question/3454178
#SPJ11
A man stands in front of a vertical plane mirror which is fixed on a
wall as shown in the diagram below. The image formed by the
mirror is also shown.
The man looks at the image of his feet.
a. Complete the ray diagram to show how the man is able to see the
image of his feet in the mirror.
b. What is the purpose of the normal line in the diagram?
c. State which angle does x represent.
d. What's the type and direction of the image formed by the mirror?
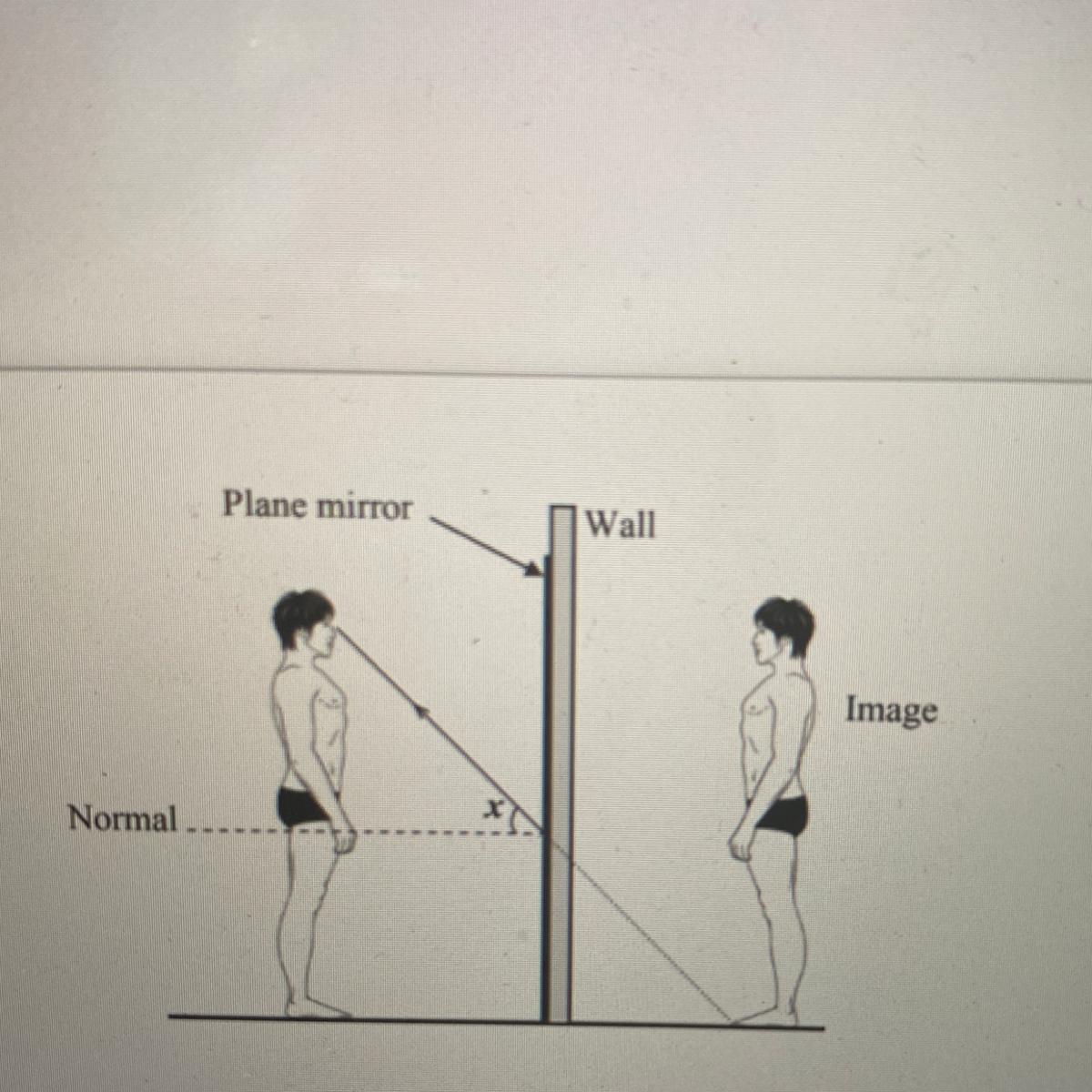
Answers
Answer:
a) ray horizontal and ray leaves his feet
b) The normal line respect to which the angles are measured,
c) The angle x is the reflected angle
d) virtual image, right image
Explanation:
a) To complete the rays, you must draw a horizontal ray at the height of the man's head, this ray touches the mirror perpendicularly, therefore it bounces in the same direction.
The other ray leaves his feet and touches the mirror at one point, it is reflected with the same angle, by the law of reflection and reaches the eyes of man, the brain creates an extension of this ray and at the point of the floor creates the image point.
b) The normal line is a line perpendicular to the surface with respect to which the angles are measured,
c) The angle x is the reflected angle, which is equal to the incident angle according to the law of reflection
d) The image is formed by the prolongation of the rays of light, therefore it is a virtual image and as it has the same direction of the man it is a right image
what is a homogeneous mixture in which particles never separate?
Answers
Answer:
is sugar and water becouse sugar can solote the water
A moving body must undergo a change of
Answers
Answer:
objects that is at rest will remain at rest and an objects in motion will remain in motion with the same velocity unless changed by an unbalanced force.
Explanation:
A moving body must undergo a change of position.
What is inertia?The concept of inertia states that an object will maintain its current motion unless a force changes its speed or direction. The phrase should be understood as a shortened form of Newton's first law of motion's description of "the principle of inertia."
The inertia of motion is the resistance offered by the body to continue to be in the uniform motion unless an external force acts on it.
Movement is a change in a body part's position in relation to the entire body. It is one of the key characteristics shared by all living things. Examples of movement include eating, breathing, and eye blinking. Therefore, we may conclude that at least one portion of our body moves in some way every second.
Hence, a moving body must undergo a change of position.
Learn more about inertia here:
https://brainly.com/question/15164317
#SPJ6
Can someone help me with this please

Answers
An Austin volleyball player bumps a 5 kg ball into the air. It reaches a height of 2.8 meters. How fast was the ball going as it got bumped into the air?
O 137.2 m/s
O 7.4 m/s
O 19.6 m/s
O 14 m/s
Answers
Answer:
v = 7.4 m/s
Explanation:
Given that,
Mass if a volleyball, m = 5 kg
The ball reaches a height of 2.8 m
We need to find how fast the ball is going as it bumped into the air. Ket the velocity is v. Using the conservation of energy to find it as follows :
\(mgh=\dfrac{1}{2}mv^2\\\\v=\sqrt{2gh} \\\\v=\sqrt{2\times 9.8\times 2.8} \\\\=7.4\ m/s\)
So, the required speed is 7.4 m/s. Hence, the correct option is (b).
A car travels for 10s at a steady speed of 20 m/s along a straight road. The traffic lights ahead change to red, and the car slows down with a constant deceleration, so that it halts after a further 8s.
Answers
Answer:
The right solution is "2.5 m/s²". A further explanation is given below.
Explanation:
The given values are:
Initial velocity,
= 20 m/s
Final velocity,
= 0 m/s
Time,
= 8 s
As we know,
⇒ \(Acceleration=\frac{Final \ velocity-Initial \ velocity}{2}\)
On substituting the values, we get
⇒ \(=\frac{0-20}{8}\)
⇒ \(=\frac{-20}{8}\)
⇒ \(=-2.5 \ m/s^2\)
Georgie was pulling her brother (of mass 27 kg) in a 12.1 kg sled with a constant force of 40 N for one block (92 m). How much work did Georgie do?
Answers
Georgie did 3,648 Joules of work by pulling her brother and the sled for one block.
The work done by Georgie can be calculated using the formula: Work = Force × Distance. In this case, the force applied by Georgie is 40 N, and the distance covered is 92 m. Therefore, the work done is equal to 40 N × 92 m = 3,648 J.
Work is a measure of the energy transferred when a force acts on an object and causes it to move. In this scenario, Georgie applied a constant force of 40 N to pull her brother and the sled. The work done is directly proportional to the force applied and the distance covered. By multiplying the force and distance values, we find that Georgie performed 3,648 Joules of work.
To learn more about Joules, click on:
brainly.com/question/13196970
#SPJ11
Georgie did 3,648 Joules of work by pulling her brother and the sled for one block.
The work done by Georgie can be calculated using the formula: Work = Force × Distance. In this case, the force applied by Georgie is 40 N, and the distance covered is 92 m. Therefore, the work done is equal to 40 N × 92 m = 3,648 J.
Work is a measure of the energy transferred when a force acts on an object and causes it to move. In this scenario, Georgie applied a constant force of 40 N to pull her brother and the sled. The work done is directly proportional to the force applied and the distance covered. By multiplying the force and distance values, we find that Georgie performed 3,648 Joules of work.
To learn more about Joules, click on:
brainly.com/question/13196970
#SPJ11
Which of the following products will have elastic demand (alcohol, gasoline, travel souvenirs, cigarettes)
Answers
The product among alcohol, gasoline, travel souvenirs, cigarettes that will have elastic demand is cigarettes.
What is elastic demand?Elastic demand refers to a situation in which a change in the price of a good or service results in a more significant change in the amount demanded. When the percentage change in quantity demanded is greater than the percentage change in price, the demand for the product is said to be elastic.
When the quantity demanded of a product decreases significantly when the price rises, the demand for the product is said to be elastic. Similarly, when a slight change in price causes a significant change in quantity demanded, the demand is said to be elastic. Conversely, if a product's price increases by a small percentage, and the demand for the product decreases by a smaller percentage, the demand for the product is said to be inelastic.
Cigarettes, of all the products listed above, are likely to have an elastic demand.
This is because smokers who are addicted to cigarettes are more likely to quit smoking or reduce their consumption in response to an increase in the price of cigarettes compared to the other goods.
Thus, a slight increase in the price of cigarettes is likely to cause a significant decrease in the number of cigarettes consumed.
learn more about elastic demand here
https://brainly.com/question/1048608
SPJ11
If Newton's third law was true, then why does a table move when I push it? If the table exerted the same amount of force to me, why does it move?
Answers
Cond Concept question showing the difference between charge and charge density 22.19 Consider the point P located distance d above the lef end of a rod of length d. Assume the rod carries charge distributed uniformly over the length of the rod. For this sinuation, assume the rod produces electric field vector E
0
at the point P. a) How does the field change if rod length is doubled using the same amount of charset? Assume the point P is still located distance d above the left end of the rod. b) How does the ficld change if rod length is doubled using the same amount of charge densin? Asume the point P is still located distance d above the left end of the rod.
Answers
In first scenario, the electric field vector's magnitude would be halved. In second scenario, the electric field vector's magnitude at point P would be doubled.
Charge and charge density are two concepts of electricity, and the following are the differences between them:
Charge: Charge is a property of matter that causes it to experience electrical and magnetic phenomena. It is the fundamental quantity that is responsible for electric phenomena. The SI unit of charge is Coulomb (C), and its symbol is ‘Q’. The charge of an object can be positive or negative or neutral. The charge on an object is measured using an electrostatic balance or an electroscope.
Charge Density: Charge density refers to the amount of charge per unit volume or unit area of a substance. Charge density is the amount of charge per unit length on a given rod. Its SI unit is Coulomb per meter cubed (C/m³). The charge density on an object can be either uniform or non-uniform, i.e., it may be constant over the surface area or may vary throughout it. An electric field vector E is produced by a rod carrying a charge distributed uniformly over the length of the rod. Let the magnitude of the charge be Q. Now, let us consider the following scenarios:
a) How does the field change if rod length is doubled using the same amount of charge?
Assume the point P is still located distance d above the left end of the rod. In this situation, if the rod's length is doubled, the charge will remain the same. Since the charge is distributed uniformly, the charge per unit length would be half of the initial value.
Therefore, the electric field vector's magnitude would be halved.
b) How does the field change if rod length is doubled using the same amount of charge density? Assume the point P is still located distance d above the left end of the rod.In this situation, if the rod's length is doubled, the charge density will remain constant. So, the total charge on the rod will be doubled, and the charge per unit length will remain constant.
As a result, the electric field vector's magnitude at point P would be doubled.
Learn more about electric field visit:
brainly.com/question/11482745
#SPJ11
Condensation raises the temperature of the vapor (True or False).
Answers
Answer:
true
Explanation:
A cubic box of side a, oriented as shown, contains an unknown charge. The vertically directed electric ?eld has a uniform magnitude E at the top surface and 2 E at the bottom surface. How much charge Q is inside the box?
Answers
The charge Q inside the box, after applying Gauss's law is ε₀ \(E a^2\).
Since the electric field is uniform and vertically directed, the electric field lines will be parallel to each other, as shown in the figure.
Let's apply Gauss's law to a cube with a length of side x, where x < a. The cube is shown in blue in the figure. The electric flux through the top and bottom faces of the cube are \(E x^2\) and \(2E x^2\), respectively, since the electric field is uniform on each face.
By Gauss's law, the electric flux through any closed surface is equal to the charge enclosed by the surface divided by the permittivity of free space (ε₀). The cube encloses a charge Q, so the electric flux through the cube is Q/ε₀. Therefore, we have:
\(E x^2 + 2E x^2 = Q/ε₀\)
Simplifying, we get:
Q = ε₀\(E a^2\)
Therefore, the charge Q inside the box is ε₀ \(E a^2.\)
To know more about Gauss's law, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/14767569#
#SPJ11
when plotted on the blank plots, which answer choice would show the motion of an object that has uniformly accelerated from 2 m/s to 8 m/s in 3 s?
Answers
The answer choice that would show the motion of the object described is a straight line with a positive slope starting from (0, 2) and ending at (3, 8).
To determine the correct answer choice, we need to consider the characteristics of uniformly accelerated motion and how it would be represented on a velocity-time graph. Uniformly accelerated motion means that the object's velocity increases by a constant amount over equal time intervals. In this case, the object starts with an initial velocity of 2 m/s and accelerates uniformly to a final velocity of 8 m/s in 3 seconds.
On a velocity-time graph, velocity is represented on the y-axis (vertical axis) and time is represented on the x-axis (horizontal axis). The slope of the graph represents the acceleration, while the area under the graph represents the displacement of the object.
To illustrate the motion described, we need a graph that starts at 2 m/s, ends at 8 m/s, and shows a uniform increase in velocity over a period of 3 seconds. The correct answer choice would be a straight line with a positive slope starting from (0, 2) and ending at (3, 8).
To learn more about, motion, click here, https://brainly.com/question/33317467
#SPJ11
A man has a mass of 85 kg. What is his weight?
Answers
he weights 187.393 pounds
Answer:833N
Explanation: A. P. E. X.
An FM radio station broadcasts radio waves with a frequency of 96,000,000 Hz. What is the speed of these radio waves if they have a wavelength of 3.1 m?
Answers
Speed = 96,000,000 x 3.1
Speed = 297600000
Which is a result of using a machine?
Answers
Answer:
Yes labor is required therefor jobs like cashier, and other low skill labor jobs I'll not be required
Explanation:
An object with a mass of 10 kg is rolled down a frictionless ramp from a height of 3 meters. If a factory worker at the bottom of the ramp slows the object until it comes to a stop, how much work must the factory worker have done
Answers
Answer:
The amount of work the factory worker must to stop the rolling ramp is 294 joules
Explanation:
The object rolling down the frictionless ramp has the following parameters;
The mass of the object = 10 kg
The height from which the object is rolled = 3 meters
The work done by the factory worker to stop the rolling ramp = The initial potential energy, P.E., of the ramp
Where;
The potential energy P.E. = m × g × h
m = The mass of the ramp = 10 kg
g = The acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s²
h = The height from which the object rolls down = 3 m
Therefore, we have;
P.E. = 10 kg × 9.8 m/s² × 3 m = 294 Joules
The work done by the factory worker to stop the rolling ramp = P.E. = 294 joules
Can some help me please im confused ♀️ !!! I,ll give you BRAINLIES

Answers
Answer:
2 seconds
Explanation:
QUESTION 1A 102.3 kg archer is standing on level ice (neglect friction) fires a 99 g arrow to the right at 104.2 m/s. What is the recoil speed ofthe archer? (report your answer to at least the thousandth's place)
Answers
Conservation of momentum
Pix = Pfx
m1= Archer's mass = 102.3 kg
v1 = Archer's velocity =
m2 = arrow's mass = 99g = 0.099 kg
v2f= arrow's velocity = 104.2 m/s
0= m1 v1 + m2 v2
V1= -( m2/m1) v2
V1 = - (0.099 kg /102.3 kg) *104.2 m/s
V1= - 0.1008 m/s
At a construction site a wrench strikes the ground with a speed of 24.0 m/s. a) from what height was it dropped? b) for how long was it falling?
Answers
Explanation:
vf = vo + at
24 = 0 + 9.81 t
t = 2. 45 s
d = do + vo t + 1/2 a t^2
0 = do + 0 *t + 1/2 (-9.81 )(2.45)^2
do = 29.4 m
A boat in the trough of a wave takes 3 seconds to reach the highest point of the wave. The velocity of the wave is 5 m/s. What is its wavelength?
Answers
Answer:
wavelength is equal to speed over frequency
A boat in the trough of a wave takes 3 seconds to reach the highest peak of the wave, then its wavelength will be equal to 30 m.
What is Frequency?The frequency of an event is its repetition per time unit. In a contrast to spatial frequency, it is also often referred to as temporal frequency, and in a contrast to angular frequency, it's often referred to as conventional frequency.
The standard unit is hertz (Hz), which is equal to one per second. The reciprocal of frequency is period, which itself is defined as the amount of time for one cycle of a repeating occurrence.
From the given data in the question,
Total time, t = 3s + 3s
t = 6 seconds.
Frequency, f = 1/6s
f = 0.1666 Hz
Now, let's find out the wavelength,
λ = υ/f
= 5/0.1666
λ = 30 m.
Therefore, the wavelength will be equal to 30 m.
To know more about Frequency:
https://brainly.com/question/5102661
#SPJ2
Activities that can help reduce the stress level in a family include A. exercising B. reading C. going for a walk D. all of the above Please select the best answer from the choices provided. A B. ОС
Answers
Answer:
D. all the above
Explanation:
Took the quiz.
Answer: D) all the above
Explanation: :)
If an object is initially traveling at a velocity of 6 ms-1, then decelerates for 2 seconds, at which point its velocity is 2 ms-1, what is the acceleration of the object?
Answers
Answer:
\(\boxed {\boxed {\sf a= -2 \ m/s^2 }}\)
Explanation:
We are asked to find the acceleration of an object. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time.
It is the change in velocity over time.
\(a= \frac{v_f-v_i}{t}\)
The object is originally traveling at 6 meters per second, then it decelerates to 2 meters per second in 2 seconds.
\(v_f\)= 2 m/s \(v_i\)= 6 m/s t= 2 sSubstitute the values into the formula.
\(a= \frac{2 \ m/s- 6 \ m/s }{2 \ s}\)
Solve the numerator.
\(a= \frac{-4 \ m/s }{2 \ s }\)
Divide.
\(a= -2 m/s/s\)
\(a= -2 \ m/s^2\)
The acceleration of the object is -2 meters per second squared.
If an object is initially traveling at a velocity of 6 ms-1, then decelerates for 2 seconds, The acceleration of the object is -2 m/s². The negative sign indicates that the object is decelerating.
Given:
Initial velocity (u) = 6 m/s
Final velocity (v) = 2 m/s
Time taken (t) = 2 seconds
To find the acceleration of the object, the formula for acceleration:
acceleration (a) = (final velocity - initial velocity) / time
a = (2 - 6 ) / 2
a = (-4) / 2
a = -2 m/s²
The acceleration of the object is -2 m/s². The negative sign indicates that the object is decelerating (slowing down) during this time.
To know more about the acceleration:
https://brainly.com/question/11936480
#SPJ3
A student places two books on a table. One book weighs less than the other book
Which book has less potential energy (PE)? *
(10 Points)
Answers
A 0.15 kg baseball and a 7.25 kg bowling ball are both rolling along at 3 m/s. which object is easier to stop and why?
A) the bowling ball because it has less inertia
B) the baseball because it has more inertia
C) the bowling ball because heavy objects are naturally prone to stop their own
D) the baseball because it has less inertia
Answers
Can someone answer this?

Answers
!!AYO I NEED HELP, YOU WILL GET 100 POINTS :)
In everyday language, the term acceleration is used to describe something that is speeding up, while deceleration is used to describe something that is slowing down. In physics, the word deceleration is not used at all. Instead, physicists talk about positive and negative acceleration. To understand this better, think about an object that is slowing down continuously until it stops, and then it starts to speed up and go backwards. The object is involved in one continuous process, so it does not make sense to use two different and opposite terms (acceleration and deceleration) to describe the same process. Acceleration is simply a vector quantity that involves a magnitude and a direction. Post a few short scenarios involving motion, in which you describe what is happening in everyday terms, including deceleration. Examine the postings of your classmates. Try to describe their scenarios using the scientific concepts of positive and negative acceleration. Examine the attempts of your classmates to describe motion scenarios using negative acceleration. Do you think they correctly describe the motion in the scenarios? Suggest any improvements that are necessary to make the descriptions correct
Answers
An example of acceleration is someone that's riding a carousel and a skydiver that's in free fall and deceleration is when one presses the brake while driving.
What is acceleration?It should be noted that acceleration simply means the rate at which velocity changes with time.
In this case, an example of acceleration is someone that's riding a carousel and a skydiver that's in free fall and deceleration is when one presses the brake while driving. Acceleration can also be the fall of an apple from the tree.
Learn more about acceleration on:
https://brainly.com/question/950219
A spring of k=500 N/m that is initially compressed 2m is used to launch a 100N load of bricks up a 2 m tall
hill. Find the speed of the bricks at the top of the hill.
e. What would the speed at the top of the hill be with 2m of initial compression if 15% of the energy is
dissipated through friction?
Answers
Speed of the bricks at the top of hill is calculated as 6.26 m/s. e) speed of the bricks at top of hill with 2 m of initial compression and 15% energy dissipation is calculated as 13.04 m/s.
What is energy?The capacity or power to do work, like the capacity to move any object by the application of force is called energy.
Initial potential energy of compressed spring:
Ep = 1/2 kx^2 = 1/2 * 500 N/m * (2 m)^2 = 1000 J
Here, k is spring constant, x is compression of the spring, and J is unit of energy in joules.
Final potential energy of the bricks:
Ep = m g h = 100 N * 9.81 m/s^2 * 2 m
= 1962 J
As, Ep = Ep
1/2 kx^2 = m g h
v = sqrt(2gh) = sqrt(2 * 9.81 m/s^2 * 2 m) = 6.26 m/s
Therefore, speed of the bricks at the top of the hill is 6.26 m/s.
e. If 15% of energy is dissipated through friction, final kinetic energy of the bricks at the top of hill will be 85% of initial potential energy of compressed spring.
0.85 * 1000 J = 1/2 mv^2
v = sqrt(170 / 1)
= 13.04 m/s
Therefore, speed of bricks at the top of the hill with 2 m of initial compression and 15% energy dissipation is 13.04 m/s.
To know more about energy, refer
https://brainly.com/question/13881533
#SPJ1