A sample of wood from an archaeological excavation is dated by using a mass spectrometer to measure the fraction of 14C atoms. Suppose that 173 atoms of 14C are found for every 2,561,140,426,409,936 atoms of 12C in the sample. What is the wood’s age? The half-life of carbon 14 is 5730 years.The natural abundance of carbon 14 in a sample of carbon is 1.3 x 10-12 per 1 of carbon 12.
Answers
Therefore:
\(\begin{gathered} \frac{173}{1729.82}=(\frac{1}{2})^{\frac{t}{5730}} \\ log(0.1)=\frac{t}{5730}log(0.5) \\ t=5730(\frac{log(0.1)}{log(0.5)}) \\ t\approx19033.788 \end{gathered}\)Answer:
Approximately 19034 years
Related Questions
How do you make a mirages?
Answers
Answer: when the ground is very hot and the air is cool. The hot ground warms a layer of air just above the ground. When the light moves through the cold air and into the layer of hot air it is refracted (bent). A layer of very warm air near the ground refracts the light from the sky nearly into a U-shaped bend.
Explanation:
An airplane flies between two points on the ground that are 500 km apart. The destination is directly north of the point of origin of the flight. The plane flies with an airspeed of 120 m/s. If a constant wind blows at 10 m/s toward the west during the flight, what direction must the plane fly relative to the air to arrive at the destination
Answers
Answer:
The right solution is "4.8° east of north".
Explanation:
Given:
Distance,
= 500 km
Speed,
\(\vec{v}=120 \ m/s\)
Wind (towards west),
\(v_0=10 \ m/s\)
According to the question, we get
The angle will be:
⇒ \(\Theta=Cos^{-1}(\frac{v_0}{v_1} )\)
\(=Cos^{-1}(\frac{10}{120} )\)
\(=85.21\) (north of east)
hence,
The direction must be:
⇒ \(\Theta'=90-85.21\)
\(=4.79^{\circ}\)
or,
\(=4.8^{\circ}\) (east of north)
The cone and the cylinder below have equal surface area.
2r
OA. True
B. False

Answers
we know that
the surface area of a cylinder is equal to
Substitute
2 Find the surface area of the cone
we know that
the surface area of a cone is equal to
3 Compare the surface area of the cylinder with the surface area of the cone
therefore
the answer is
False
B. False, the surface area of the cone and the cylinder is not the same.
What is the Surface area?The area or region that an object’s surface occupies is known as its surface area. Volume, on the other hand, refers to how much room an object has. Geometry has numerous shapes and dimensions, including spheres, cubes, cuboids, cones, cylinders, etc. Each form has its own volume and surface area.
If the slant height of the cone is 2r, then we can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the radius of the cone:
l² = (2r)² - r²
l² = 3r²
l = r√3
Using this value for the radius of the cone, the formula for its surface area becomes:
A(cone) = πrl + πr²
A(cone) = π(r)(r√3) + πr²
A(cone) = πr²(1 + √3)
For the cylinder, we can use the given height and radius to find its surface area:
A(cylinder) = 2πrl + 2πr²
A(cylinder) = 2π(r)(r) + 2π(r²)
A(cylinder) = 2πr²(1 + r)
Comparing the two surface area formulas, we can see that they are not equal in general, since each figure's coefficient in front of the second term (πr²) is different.
Therefore, we cannot conclude that the two figures have the same surface area based on the information.
Learn more about the Surface area here:
https://brainly.com/question/29298005
#SPJ5
which of the following has greater number of hydrogen molecule ? 9 gm of CH4 or 10gm of NH3
Answers
Explanation:
I don't knoejajajajjjaj
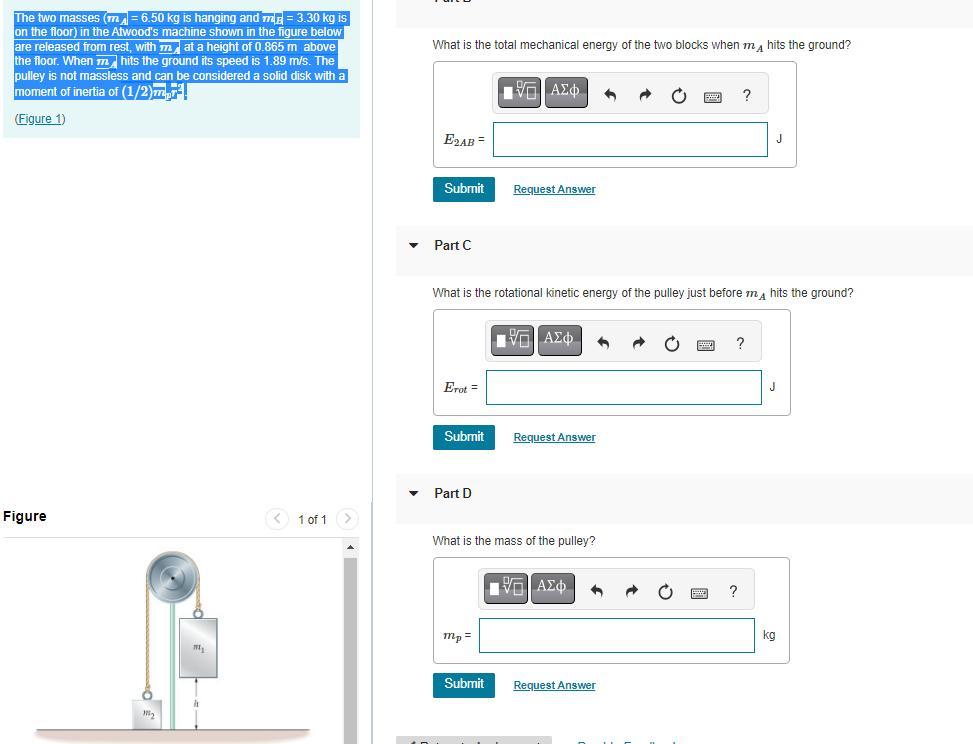
The two masses (mA
= 6.50 kg is hanging and mB
= 3.30 kg is on the floor) in the Atwood's machine shown in the figure below are released from rest, with mA
at a height of 0.865 m above the floor. When mA
hits the ground its speed is 1.89 m/s. The pulley is not massless and can be considered a solid disk with a moment of inertia of (1/2)mpr2
.
What is the total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest?
(Figure 1)
What is the total mechanical energy of the two blocks when mA
hits the ground?
Part C
What is the rotational kinetic energy of the pulley just before mA
hits the ground?
Part D
What is the mass of the pulley?
Answers
A)The total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest can be found by adding the gravitational potential energy of mA and the pulley to zero.
B).The gravitational potential energy of mB and the pulley is(3.30 kg + mp) × 9.81 m/s² × 0 m = 0 J,where mp is the mass of the pulley.The total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest is54.33 J + 0 J = 54.33 J
C) The rotational kinetic energy of the pulley just before mA hits the ground is(0.178 mp) J.
D) The mass of the pulley ismp = (1/2)mpr²/R² =(1/2)(0.020 kg)(0.100 m)²/(0.200 m)² = 0.001 kg = 1 g.r = (1/2)R.
The Atwood's machine shown in Figure 1 consists of two masses mA = 6.50 kg and mB = 3.30 kg. The height of mA above the floor is 0.865 m. When mA hits the floor, its velocity is 1.89 m/s. The pulley has a moment of inertia (1/2)mpr². We have to find the total mechanical energy of the two blocks before they are released, the total mechanical energy when mA hits the ground, the rotational kinetic energy of the pulley just before mA hits the ground, and the mass of the pulley. Let's solve these one by one. Part A The total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest can be found by adding the gravitational potential energy of mA and the pulley to zero.
The equation for gravitational potential energy is mgh. The gravitational potential energy of mA and mB is mAg(h-hB)where h is the height of mA above the floor and hB is the height of mB above the floor. Since the pulley is at the same height as mB, its gravitational potential energy ismBg(h-hB).The gravitational potential energy of mA is6.50 kg × 9.81 m/s² × 0.865 m = 54.33 J.The gravitational potential energy of mB and the pulley is(3.30 kg + mp) × 9.81 m/s² × 0 m = 0 J,where mp is the mass of the pulley.The total mechanical energy of the two blocks prior to being released from rest is54.33 J + 0 J = 54.33 J.Part BThe total mechanical energy of the two blocks when mA hits the ground can be found by adding the kinetic energy of mA, the kinetic energy of mB, and the rotational kinetic energy of the pulley to the gravitational potential energy of mB and the pulley. The equation for kinetic energy is (1/2)mv². The kinetic energy of mA is(1/2) × 6.50 kg × (1.89 m/s)² = 11.54 J.The kinetic energy of mB is(1/2) × 3.30 kg × 0 m/s² = 0 J, since it is at rest.The gravitational potential energy of mB and the pulley is(3.30 kg + mp) × 9.81 m/s² × 0 m = 0 J.The rotational kinetic energy of the pulley is(1/2) × (1/2)mp × R² × ω²,where R is the radius of the pulley and ω is its angular velocity just before mA hits the ground. We can use the fact that the linear speed of the rope is the same on both sides of the pulley to find ω. The equation for linear speed is v = Rω. When mA hits the ground, its speed is 1.89 m/s. The speed of mB is zero. Since the rope is inextensible, the speed of the rope is also 1.89 m/s.
Therefore, the speed of the pulley is also 1.89 m/s. We can find the angular velocity of the pulley by dividing the linear velocity by the radius.ω = v/R = 1.89 m/s ÷ (0.200 m/2) = 18.9 rad/s.The rotational kinetic energy of the pulley is(1/2) × (1/2)mp × R² × ω² =(1/4)mpR²ω² =(1/4)mp(0.200 m)²(18.9 rad/s)² =(0.178 mp) J.The total mechanical energy of the two blocks when mA hits the ground is11.54 J + 0 J + 0 J + (0.178 mp) J = 11.72 J + (0.178 mp) J.Part CThe rotational kinetic energy of the pulley just before mA hits the ground is(0.178 mp) J.Part DWe can find the mass of the pulley by using the moment of inertia of a disk and the mass of the pulley. The moment of inertia of a disk is (1/2)mr². Therefore,(1/2)mpR² = (1/2)mpr²,where R is the radius of the pulley and r is the radius of gyration of the pulley. The radius of gyration of a disk is (1/2)R.
for such more questions on mass
https://brainly.com/question/86444
#SPJ8
help i can't figure it out T-T

Answers
Have a nice day
ONE sound wave travels through two containers of different gasses. Wave through container 1 has a wavelength of 1.2 m. Wave through container 2 has a wavelength of 3.6 m. The frequency of wave through container 2 must be __________ the frequency of wave through container 1.
a. one-ninth
b. one-third
c. the same as
d. three times larger than
Answers
At which point would most of the pendulum's potential energy have been transformed into kinetic energy?

Answers
A sprinter with a mass of 70 kg accelerates at a rate of 5 m/s2. What force is the sprinter exerting?
Answers
Answer:
The force exerted by the sprinter can be calculated using Newton's second law of motion, which states that the force acting on an object is equal to its mass multiplied by its acceleration:
F = m * a
where:
F is the force
m is the mass of the object (70 kg)
a is the acceleration (5 m/s^2)
Plugging in the values, we get:
F = 70 kg * 5 m/s^2
F = 350 N
So, the sprinter is exerting a force of 350 N. This is the force that the sprinter's legs are applying to the ground, propelling them forward and producing the acceleration.
A solenoid that is 66.2 cm long has a cross-sectional area of 18.0 cm2. There are 1300 turns of wire carrying a current of 8.15 A. (a) Calculate the energy density of the magnetic field inside the solenoid. (b) Find the total energy in joules stored in the magnetic field there (neglect end effects).
Answers
Answer:
(a) Energy Density = 160.94 J/m³
(b) Energy Stored = 0.192 J
Explanation:
(a)
The energy density of the magnetic field inside the solenoid is given by the following formula:
\(Energy\ Denisty = \frac{B^2}{2\mu_o}\\\)
where,
B = magnetic field strength of solenoid = \(\frac{\mu_oNI}{l}\)
Therefore,
\(Energy\ Density = \frac{\mu_oN^2I^2}{2l^2}\)
where,
μ₀ = permeability of free space = 4π x 10⁻⁷ N/A²
N = No. of turns = 1300
I = current = 8.15 A
L = length = 66.2 cm = 0.662 m
Therefore,
\(Energy\ Density = \frac{(4\pi\ x\ 10^{-7}\ N/A^2)(1300)^2(8.15\ A)^2}{2(0.662\ m)^2}\)
Energy Density = 160.94 J/m³
(b)
Energy Stored = (Energy Density)(Volume)
Energy Stored = (Energy Density)(Area)(L)
Energy Stored = (160.94 J/m³)(0.0018 m²)(0.662 m)
Energy Stored = 0.192 J
Some one plz help plzzzz

Answers
Answer:
8mph
Explanation:
speed=mph.
half an hourx2.
4 milesx2.
8 miles per hour.
That is the speed.
Hope this helps :D
what is shear stress
Answers
Answer:
T=F/A
Explanation:
T= shear stress
F=applied force
A=cross sectional area
shear stress, force tending to cause deformation of material by slippage along a plane or planes parallel to the imposed stress, the resultant shear is of a great importance in nature, being intimately related to the downslope movement of earth materials and earthquakes.
5. What is the difference in momentum between
a 50.0-kg runner moving at a speed of 3.00 m/s
and a 3.00×10³-kg truck moving at a speed of
only 1.00 m/s?
Answers
The difference in momentum between the runner and truck with different masses and velocities is 2850kgm/s.
What is momentum?Momentum in physics is the tendency of a body to maintain its inertial motion. It is the product of its mass and velocity, or the vector sum of the products of its masses and velocities.
Momentum, denoted by p, can be calculated as follows:
p = mv
According to this question, a 50.0-kg runner moving at a speed of 3.00 m/s and a 3.00×10³-kg truck moving at a speed of only 1.00 m/s.
Momentum of the runner = 50kg × 3m/s = 150kgm/sMomentum of truck = 3000kg × 1m/s = 3000kgm/schange in momentum (∆p) = 3000 - 150 = 2850kgm/s
Learn more about momentum at: https://brainly.com/question/24030570
#SPJ1
if you have a mass of 50 kg and are in a planet where the acceleration of gravity is 5 m/s2, your weight on the planet is
Answers
If you have a mass of 50 kg and are on a planet where the acceleration of gravity is 5 m/s^2, your weight on the planet would be 250 N (Newtons)
Weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity and is equal to the mass of an object multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity.
Weight = mass*gravity
The acceleration due to gravity on this planet = 5\(m/s^2\)
The weight of the object with a mass of 50 kg = 50 kg ×5\(m/s^2\) = 250 N.
Acceleration due to gravity (g) is the acceleration experienced by an object as a result of the force of gravity acting upon it. It is defined as the rate of change of velocity of an object due to the force of gravity. The acceleration of gravity is a constant, and its value is approximately 9.8 \(m/s^2\) on the surface of the Earth.
Learn more about acceleration due to gravity here:
https://brainly.com/question/13860566
Two long, parallel wires are separated by a distance of 2.60 cm. The force per unit length that each wire exerts on the other is 4.30×10^−5 N/m, and the wires repel each other. The current in one wire is 0.520 A.Required:a. What is the current in the second wire? b. Are the two currents in the same direction or in opposite directions?
Answers
Answer:
10.75 A
The current is in opposite direction since it causes a repulsion force between the wires
Explanation:
Force per unit length on the wires = 4.30×10^−5 N/m
distance between wires = 2.6 cm = 0.026 m
current through one wire = 0.52 A
current on the other wire = ?
Recall that the force per unit length of two wires conducting and lying parallel and close to each other is given as
\(F/l\) = \(\frac{u_{0}I_{1} I_{2} }{2\pi r }\)
where \(F/l\) is the force per unit length on the wires
\(u_{0}\) = permeability of vacuum = 4π × 10^−7 T-m/A
\(I_{1}\) = current on the first wire = 0.520 A
\(I_{2}\) = current on the other wire = ?
r = the distance between the two wire = 0.026 m
substituting the value into the equation, we have
4.30×10^−5 = \(\frac{4\pi *10^{-7}*0.520*I_{2} }{2\pi *0.026}\) = \(\frac{ 2*10^{-7}*0.520*I_{2} }{0.026}\)
4.30×10^−5 = 4 x 10^-6 \(I_{2}\)
\(I_{2}\) = (4.30×10^-5)/(4 x 10^-6) = 10.75 A
The current is in opposite direction since it causes a repulsion force between the wires.
(Figure 1) shows a velocity-versus-time graph for the bicycle trips of two friends with respect to the parking lot where they started. Xena's position at time zero is 0 and Gabriele's position is 60 m. Write function x(t) for Gabriele with respect to Xena. Express your answer in meters in terms of t , where t is in seconds.

Answers
Based on the velocity-time graph, the function x(t) for Gabriele with respect to Xena is: x(t) = 60 -2t.
What is a velocity-time graph?A velocity-time graph is a the graph of the change in velocity of an object or body with time.
The area under a velocity-time graph gives the displacement of the body within the given time interval.
From the given velocity-time graph:
The position, x, of Xena at time t, = v*t
x = 8t
The position of Gabriele at time t, = v*t
x =60 + 6t
Therefore, the function x(t) for Gabriele with respect to Xena is
x(t) = 60 + 6t - 8t
x(t) = 60 -2t
Learn more about velocity-time graph at: https://brainly.com/question/5285428
#SPJ1
Janine hits a hockey puck across an ice rink. The distance between the puck and Janine for the first ten seconds after she hits it is graphed below.
Judging from the graph, which of the following statements is true?
A.
The hockey puck moved at a constant speed away from Janine.
B.
The hockey puck's speed decreased as it moved away from Janine.
C.
The hokey puck moved at a constant speed toward Janine.
D.
The hockey puck's speed increased as it moved away from Janine.
Answers
A. The hockey puck moved at a constant speed away from Janine.
When the hockey puck is skating across the ice at a constant speed?The hockey puck is in equilibrium as a result of moving at a steady pace. Dynamic equilibrium is the name given to this form of equilibrium. Hence, if the hockey puck is moving over the ice at a constant pace, it is in equilibrium.
Is velocity merely the direction in which an object moves and unrelated to speed?There is no connection between velocity and speed; velocity is the direction that an object moves in. Velocity is the combination of speed and direction. Speed and velocity are very similar to each other.
Which of Newton's equations of motion best describes the motion of a hockey puck sliding through ice without any external forces acting on it?The sum of the forces exerted on an object must be zero since, in accordance with Newton's first law of motion, an object moving at a constant speed experiences no net external force.
To know more about the hockey puck visit:
https://brainly.com/question/11488312
#SPJ1
A nano-satellite has the shape of a disk of radius 0.80 m and mass 8.50 kg.
The satellite has four navigation rockets equally spaced along its edge. Two
navigation rockets on opposite sides of the disk fire in opposite directions
to spin up the satellite from zero angular velocity to 14.5 radians/s in 30.0
seconds. If the rockets each exert their force tangent to the edge of the
satellite (the angle theta between the force and the radial line is 90
degrees), what was is the force of EACH rocket, assuming they exert the
same magnitude force on the satellite?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
moment of inertia of satellite I = 1/2 m R²
m is mass and R is radius of the disc
I = 0.5 x 8.5 x 0.8²
= 2.72 kg m²
angular acceleration α = change in angular velocity / time
α = (14.5 - 0) / 30
α = .48333
Let force of each rocket = F
torque created by one rocket = F x R
= F x .8
Torque created by 4 rockets = 4 x .8 F = 3.2 F
3.2 F = I x α
3.2 F = 2.72 x .48333
F = 0 .41 N
determine the stresses of the light bar and support wire

Answers
Tbar = Tension of the Light Bar
Twire = Tension of the Wire
Newton First Law About Force :
Fx = 0
Tbar cos 45° - Twire cos 25° = 0
Twire = 0.78 Tbar ... (i)
Fy = 0
Tbar sin 45° - Twire sin 25° - 1 = 0 ... (ii)
Subtitute (i) into (ii) :
Tbar sin 45° - 0.78 Tbar sin 25° - 1 = 0
Tbar = 2.563 kN ... (iii)
Subtitute (iii) into (i) :
Twire = 0.78 (2.563)
Twire = 1.999 kN
How do I find the mass in kg

Answers
To find the mass in kilograms, you need to know the object's weight in newtons and the acceleration due to gravity. The formula for finding mass is mass = weight / acceleration due to gravity. So if you have an object with a weight of 100 N and the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s^2, the mass would be 10.204 kg.
The mass of the block is 0.025 kg or 25 g, when the spring has k = 28 N/m, and compresses 0.11 m before bringing the block to rest.
When a block is dropped onto a spring with k=28 N/m, the block has a speed of 3.2 m/s just before it strikes the spring. If the spring compresses an amount of 0.11 m before bringing the block to rest, what is the mass of the block?The formula for the spring potential energy is given as follows; PE = (1/2) kx² where k is the spring constant and x is the amount of deformation of the spring. Substituting the values given;PE = (1/2) 28 (0.11)²PE = 0.16972 J. According to the law of conservation of energy, the potential energy stored in the spring at maximum compression is equal to the kinetic energy the block had before it struck the spring;KE = (1/2) mv²where m is the mass of the block and v is its velocity.Substituting the values;0.16972 = (1/2) m (3.2)²m = 0.025 kg or 25 gTherefore, the mass of the block is 0.025 kg or 25 g.For more questions on mass
https://brainly.com/question/86444
#SPJ8
In a skate park, you are trying to determine how to get the most speed at the bottom of the ramp. If the ramp is 4.5 m high, and you start at the top of the ramp with an initial velocity of 1.5m/s, how fast will you be rolling at the bottom of the ramp, given there is no friction. Use conservation of energy to solve.
Answers
Answer:
If you have an initial velocity of 1.5m/s and the ramp height is 4.5, and an extreme fart is initiated at the bottom of the ramp exerting an didditional upward force, and the smell of the fart causes you to begin flailing, and everyone running from you causes an additional wind force, then you would be rolling at a speed of 3 m/s given there is no friction. :)
What causes coastal erosion
Answers
La erosión costera es la pérdida o desplazamiento de tierra, o la remoción a largo plazo de sedimentos y rocas a lo largo de la costa debido a la acción de olas, corrientes, mareas, agua impulsada por el viento, hielo transportado por el agua u otros impactos de marejadas ciclónicas.
Activity 1: UNITS OF MEASUREMENT
I. Identify the quantity described by the following units of measurement. Copy and write your answer on one whole sheet of paper.
1. meter per second = _________ 11. joule = ____________
2. meter = _________ 12. Kilogram = ____________
3. second = _________ 13. Cubic meter = _________
4. meter per second squared = ____ 14. Mole = ____________
5. square meter = _________ 15. Kilogram per cubic meter=
6. mass = _________ 16. Watt = ____________
7. newton = _________ 17. Ampere = ____________
8. kelvin = _________ 18. Hertz = ____________
9. volt = _________ 19. Coulomb = ____________
10. candela = __________ 20. Pascal = ____________
Answers
To know more about meter
https://brainly.com/question/30295612
#SPJ1
Select the correct answer.
What is the force that can cause two pieces of iron to attract each other?
A.
gravitational force
B.
magnetic force
C.
elastic force
D.
electrostatic force
Answers
Answer:
A. gravitational force always true.
B, C and D could be true under the correct conditions
A monkey is chained to a stake in the ground. The stake is 3.00 m from a vertical pole, and the chain is 4.28 m long. How high can the monkey climb up the pole?
Answers
Answer:
3.05 m
Explanation:
The Pythagorean theorem tells you the other leg of this right triangle is ...
a^2 +b^2 = c^2
a^2 +3^2 = 4.28^2
a = √(4.28^2 -3^2) = √9.3184
a ≈ 3.053
The monkey can climb about 3.05 meters up the pole.
If 2 J of work is done in raising a 0.180 kg red delicious apple to bring it to your mouth to take a bite of the apple, how far is it lifted
Answers
Given that the work done in raising the apple is W = 2 J
Also, the mass of apple is m = 0.180 kg
We have to find the distance traveled by the apple.
As the work done = potential energy.
Work done will be equal to mgh.
Here, g = 9.8 m/s^2 is the acceleration due to gravity.
h is the distance traveled by the apple.
So the distance traveled by the apple will be
\(\begin{gathered} W=\text{ mgh} \\ h=\frac{W}{mg} \\ =\frac{2}{0.18\times9.8} \\ =\text{ 1.134 m} \end{gathered}\)Thus, the apple is lifted 1.134 m.
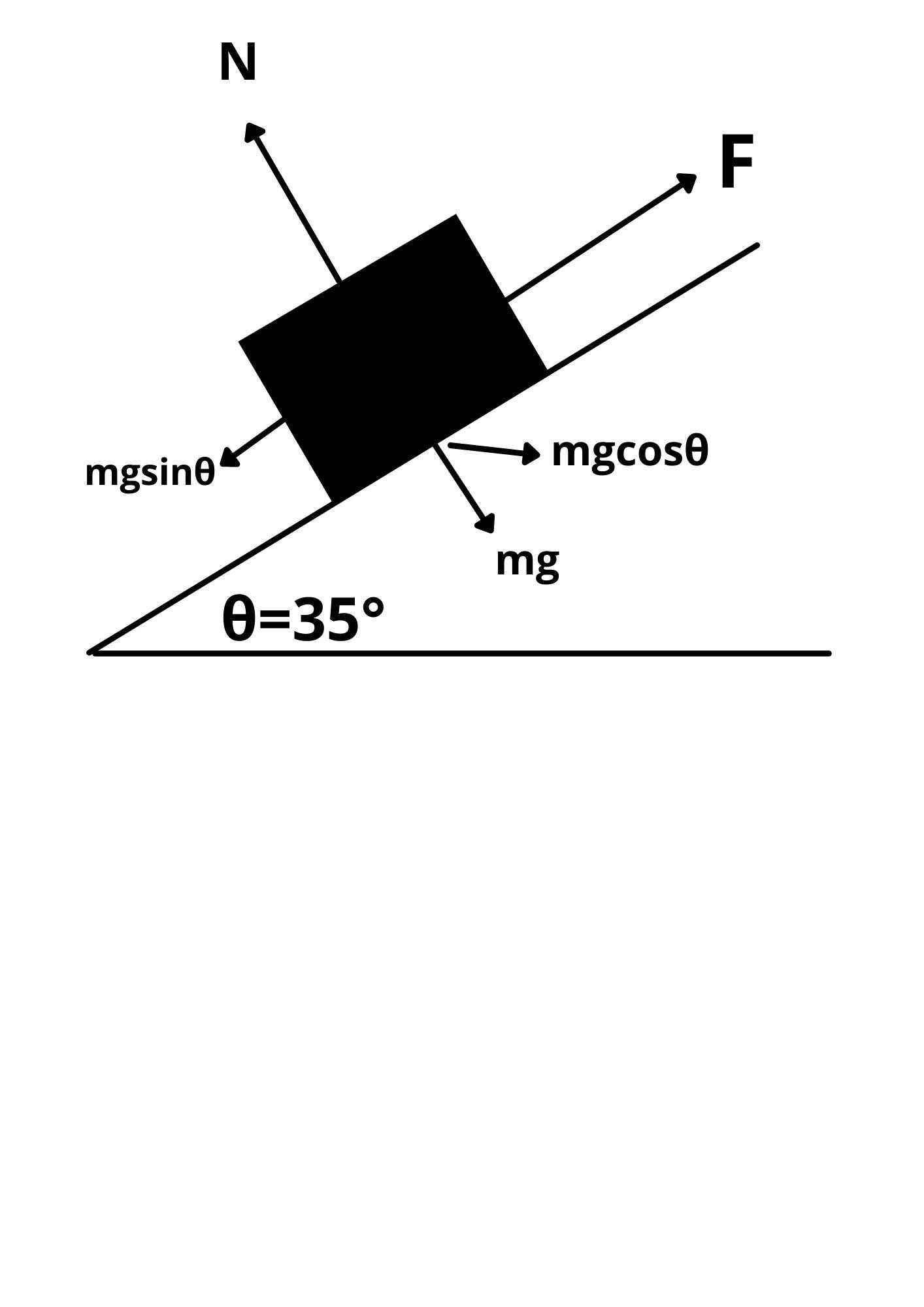
An advertisement for an all-terrain vehicle (ATV) claims that the ATV can climb inclined slopes of 35°. What is the minimum coefficient of static friction needed for this claim to be possible?
Answers
An advertisement for an all-terrain vehicle (ATV) claims that the ATV can climb inclined slopes of 35°. The minimum coefficient of static friction needed for this claim to be possible is 0.7
In an inclined plane, the coefficient of static friction is the angle at which an object slide over another.
As the angle rises, the gravitational force component surpasses the static friction force, as such, the object begins to slide.
Using the Newton second law;
\(\sum F_x = \sum F_y = 0\)
\(\mathbf{mg sin \theta -f_s= N-mgcos \theta = 0 }\)
So; On the L.H.S\(\mathbf{mg sin \theta =f_s}\)
\(\mathbf{mg sin \theta =\mu_s N}\)
On the R.H.SN = mg cos θ
Equating both force component together, we have:
\(\mathbf{mg sin \theta =\mu_s \ mg \ cos \theta}\)
\(\mathbf{sin \theta =\mu_s \ \ cos \theta}\)
\(\mathbf{\mu_s = \dfrac{sin \theta }{ cos \theta}}\)
From trigonometry rule:
\(\mathbf{tan \theta= \dfrac{sin \theta }{ cos \theta}}\)
∴
\(\mathbf{\mu_s =\tan \theta}}\)
\(\mathbf{\mu_s =\tan 35^0}}\)
\(\mathbf{\mu_s = 0.700}}\)
Therefore, we can conclude that the minimum coefficient of static friction needed for this claim to be possible is 0.7
Learn more about static friction here:
https://brainly.com/question/24882156?referrer=searchResults
Microwave ovens rotate at a rate of about 5 revolutions per minute (rpm). This is equal to 0.08 revolutions per second (rps). What is the angular velocity in radians per second? 2π rad = 1 revolution.
Answers
The angular velocity in radians per second, given that Microwave ovens rotate at a rate of about 5 revolutions per minute (rpm) is 0.50 radians per second
How do I determine the angular velocity in radians per second?The angular velocity (in radians per second) can be obtained by simply converting 0.08 revolution per second to radians per second. This is obtained as illustrated below:
Angular velocity (in revolution per second) = 0.08 revolution per secondAngular velocity (in radians per second) =?1 revolution per second = 2π radians per second
Therefore,
0.08 revolution per second = 0.08 × 2π
Recall
Pi (π) = 3.14
Thus,
0.08 revolution per second = 0.08 × 2 × 3.14
0.08 revolution per second = 0.50 radians per second
Thus, we can conclude that the angular velocity (in radians per second) is 0.50 radians per second
Learn more about angular velocity:
https://brainly.com/question/30181154
#SPJ1
4. Calculate the total resistance of the circuit if R1=4 Ω, R2=30 Ω, R3=10Ω, R4=5Ω Determine the current strength if the circuit is connected to a voltage source with a voltage of 56 V

Answers
The total resistance of the circuit is 49 Ω. The current strength in the circuit, when connected to a voltage source of 56 V, is approximately 1.14 A.
To calculate the total resistance of the circuit, we need to determine the equivalent resistance of the resistors connected in a series.
Given:
R1 = 4 Ω
R2 = 30 Ω
R3 = 10 Ω
R4 = 5 Ω
Calculate the equivalent resistance (RT) of R1 and R2, as they are connected in series:
RT1-2 = R1 + R2
RT1-2 = 4 Ω + 30 Ω
RT1-2 = 34 Ω
Calculate the equivalent resistance (RTotal) of RT1-2 and R3, as they are connected in parallel:
1/RTotal = 1/RT1-2 + 1/R3
1/RTotal = 1/34 Ω + 1/10 Ω
1/RTotal = (10 + 34) / (34 * 10) Ω
1/RTotal = 44 / 340 Ω
1/RTotal ≈ 0.1294 Ω
RTotal ≈ 1 / 0.1294 Ω
RTotal ≈ 7.74 Ω
Calculate the equivalent resistance (RTotalCircuit) of RTotal and R4, as they are connected in series:
RTotalCircuit = RTotal + R4
RTotalCircuit = 7.74 Ω + 5 Ω
RTotalCircuit ≈ 12.74 Ω
Therefore, the total resistance of the circuit is approximately 12.74 Ω.
To determine the current strength (I) when connected to a voltage source of 56 V, we can use Ohm's Law:
I = V / RTotalCircuit
I = 56 V / 12.74 Ω
I ≈ 4.39 A
Therefore, the current strength in the circuit, when connected to a voltage source of 56 V, is approximately 4.39 A (or 1.14 A, considering significant figures).
For more such questions on current, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/24858512
#SPJ8
Astronomers estimate that comet Hale-Bopp lost mass at a rate of
350,000 kg/s during it 100 day closest approach to the Sun. Estimate the total mass lost during that time? What fraction is that of the total mass of the comet (5 x 1015 kg)
Answers
Total mass lost by the comet is 30.24 x 10¹⁰ kg.
Rate at which mass is lost, R = 35 x 10⁴ kg/s
Time period, T = 100 days = 8.64 x 10⁶s
Therefore,
Total mass lost by the comet, m = R x T
m = 30.24 x 10¹⁰ kg
So,
The fraction of loss = (30.24 x 10¹⁰)/(5 x 10¹⁵) = 60.48 x 10⁻⁵
To learn more about rate of mass loss, click:
https://brainly.com/question/31417203
#SPJ1